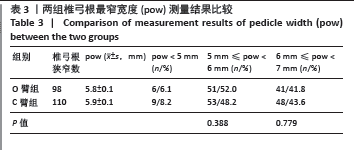
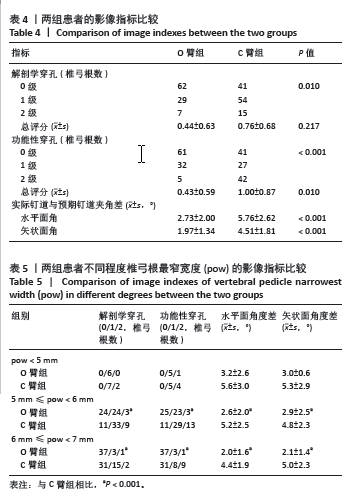
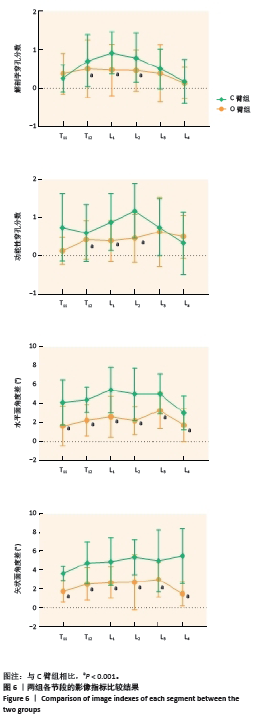
[1] 徐峰,康辉,魏坦军,等. 椎弓根螺钉不同固定方法治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学分析 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(9):1313-1317.
[2] PHAN K, RAO PJ, MOBBS RJ. Percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation for treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: Systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;135:85-92.
[3] CORIC D, ROSSI VJ, PELOZA J, et al. Percutaneous, Navigated Minimally Invasive Posterior Cervical Pedicle Screw Fixation. Int J Spine Surg. 2020;14(3):14-21.
[4] GAZZERI R. Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation Technique in the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine-Tips and Tricks. Surg Technol Int. 2016; 28(2):303-310.
[5] LU J, CHEN Y, HU M, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of using percutaneous pedicle screw internal fixation for thoracolumbar fractures. Ann Palliat Med. 2022;11(1):250-259.
[6] ESSES SI, SACHS BL, DREYZIN V. Complications Associated with the Technique of Pedicle Screw Fixation A Selected Survey of ABS Members. Spine. 1993;18(15):2231-2239.
[7] MOBBS RJ, SIVABALAN P, LI J. Technique, challenges and indications for percutaneous pedicle screw fixation. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(6): 741-749.
[8] 戚力升, 谢明忠, 李森. 胸腰段脊柱椎弓根形态及相关因素分析[J]. 中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2017,9(3):175-181.
[9] FENG W, WANG W, CHEN S, et al. O-arm navigation versus C-arm guidance for pedicle screw placement in spine surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2020;44(5):919-296.
[10] DELCONT MR, OU-YANG DC, BURGER EL, et al. Alternative Uses of O-Arm and Stealth Navigation Technology Over 10 Years: The University of Colorado Experience. Orthopedics. 2023;46(2):e89-e97.
[11] 康辉, 徐峰, 席金涛, 等. 经皮伤椎置入万向椎弓根螺钉治疗胸腰椎骨折 [J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(20):1831-1835.
[12] XU P, LIN J, XIAO H, et al. Feasibility of C2 Pedicle Screw Fixation with the “in-out-in” Technique for Patients with Basilar Invagination. Spine. 2023. doi:10.1097/BRS.000000000000004757.
[13] 凌宸, 刘臻, 毛赛虎, 等. O型臂联合CT三维导航系统辅助颈椎椎弓根螺钉置入的准确性研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022,32(3): 207-213.
[14] ORIEF T, ALFAWAREH M, HALAWANI M, et al. Accuracy of percutaneous pedicle screw insertion in spinal fixation of traumatic thoracic and lumbar spine fractures. Surg Neurol Int. 2018;9:78.
[15] BOON TOW BP, YUE WM, SRIVASTAVA A, et al. Does Navigation Improve Accuracy of Placement of Pedicle Screws in Single-level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: A Comparison Between Free-hand and Three-dimensional O-Arm Navigation Techniques. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(8):E472-E477.
[16] VIJAYAN R, DE SILVA T, HAN R, et al. Automatic pedicle screw planning using atlas-based registration of anatomy and reference trajectories. Phys Med Biol, 2019;64(16):165020.
[17] 邹守平, 卢道云, 叶力. 微创经皮伤椎置钉治疗胸腰椎骨折:6个月随访脊柱生物力学变化 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(24): 3865-3869.
[18] ZHENG Z, ZHANG L, ZHU Y, et al. Percutaneous cortical bone trajectory screw fixation versus traditional open pedicle screw fixation for type A thoracolumbar fractures without neurological deficit. J Robot Surg. 2023; 17(1): 233-241.
[19] JESWANI S, DRAZIN D, HSIEH JC, et al. Instrumenting the small thoracic pedicle: the role of intraoperative computed tomography image-guided surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2014; 36(3): E6.
[20] SOLITRO GF, WHITLOCK K, AMIROUCHE F, et al. Currently Adopted Criteria for Pedicle Screw Diameter Selection. Int J Spine Surg. 2019; 13(2):132-145.
[21] 刘旭, 张进. CT及三维重建在胸腰椎骨折患者椎弓根宽度测量研究中的应用[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2019,25(7):607-610.
[22] POOLMAN AM, WESSELS Q, SCHOOR AV, et al. Thoracolumbar transitional vertebrae: Quantitative differentiation and associated numeric variation in the vertebral column using skeletal remains. J Anat. 2023;243(2):311-318.
[23] PRIYA A, NARAYAN RK, GHOSH SK, et al. Analysing lumbar pedicle morphometry observed via traditional and recent modalities. J Orthop. 2023;43:17-24.
[24] PETRONE B, ALBANO J, STOCKTON R, et al. Demographic Analysis of Pedicle Diameter, and Estimated Pedicle Screw Length of the Lumbar Spine in a Diverse Population. Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(2):259-265.
[25] MORITA K, OHASHI H, KAWAMURA D, et al. Thoracic and lumbar spine pedicle morphology in Japanese patients. Surg Radiol Anat. 2021;43(6): 833-842.
[26] ZHAO Q, ZHANG H, HAO D, et al. Complications of percutaneous pedicle screw fixation in treating thoracolumbar and lumbar fracture. Medicine. 2018;97(29):e11560.
[27] 曾红生, 陈子华, 陈建威, 等. 经伤椎椎弓根螺钉置入内固定修复胸腰椎骨折:远期效果及生物力学分析 [J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(4):571-576.
[28] PERDOMO-PANTOJA A, ISHIDA W, ZYGOURAKIS C, et al. Accuracy of Current Techniques for Placement of Pedicle Screws in the Spine: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 51,161 Screws. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:664-678.
[29] WANG H, ZHENG B, GU H, et al. O-Arm- and Guide-Device-Assisted Personalized Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. J Pers Med. 2023;13(4):595.
[30] LU YJ, MIAO YM, ZHU TF, et al. Comparison of the Wiltse Approach and Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation Under O-arm Navigation for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(5): 1618-1627.
[31] LU J, CHEN W, LIU H, et al. Does Pedicle Screw Fixation Assisted by O-Arm Navigation Perform Better Than Fluoroscopy-guided Technique in Thoracolumbar Fractures in Percutaneous Surgery?: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(6):247-253.
[32] ASAMOTO S, KOJIMA K, WINKING M, et al. Optimized Screw Trajectory for Lumbar Cortical Bone Trajectory Pedicle Screws Based on Clinical Outcome: Evidence Favoring the Buttress Effect Theory. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2018;79(6):464-470.
[33] LEE KY, KIM MW, SEOK SY, et al. The Relationship between Superior Disc-Endplate Complex Injury and Correction Loss in Young Adult Patients with Thoracolumbar Stable Burst Fracture. Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9(4):465-471.
[34] MANBACHI A, COBBOLD RS, GINSBERG HJ. Guided pedicle screw insertion: techniques and training. Spine J. 2014;14(1): 165-179.
[35] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, IMABAYASHI H. Impact of Screw Diameter and Length on Pedicle Screw Fixation Strength in Osteoporotic Vertebrae: A Finite Element Analysis. Asian Spine J. 2021;15(5): 566-574.
[36] 陆声榆, 沙轲, 陆彩玲, 等. O臂导航在骶髂螺钉置钉中的应用[J]. 广西医科大学学报,2021,38(12):2352-2356.
[37] ZHAO J, JIANG H, ZHUGE Y, et al. Risk Factors for the Drift Phenomenon in O-arm Navigation-Assisted Pedicle Screw Placement during Spinal Deformity Surgery. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(1):118-123.
[38] MATHEW JE, MOK K, GOULET B. Pedicle violation and Navigational errors in pedicle screw insertion using the intraoperative O-arm: A preliminary report. Int J Spine Surg. 2013;7:e88-e94.
[39] CROCI DM, NGUYEN S, STREITMATTER SW, et al. O-Arm Accuracy and Radiation Exposure in Adult Deformity Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2023;171:e440-e446.
[40] YOKOTA K, KAWANO O, SAKAI H, et al. Intraoperative Radiation Exposure from O-arm-based 3D Navigation in Spine Surgery. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2023;7(6):496-503.
[41] CRAWFORD BD, NCHAKO CM, REBEHN KA, et al. Transpedicular Screw Placement Accuracy Using the O-Arm Versus Freehand Technique at a Single Institution. Global Spine J. 2022;12(3):447-451. |