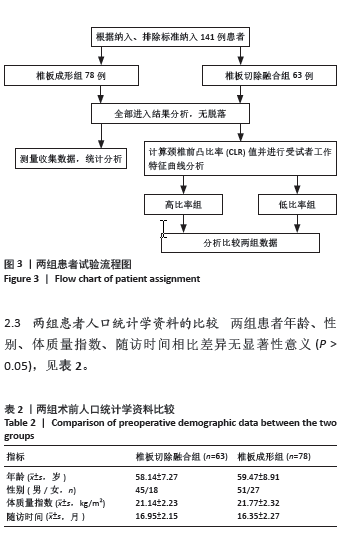
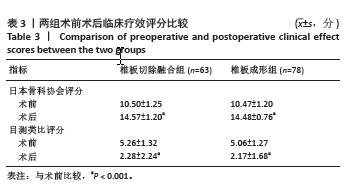
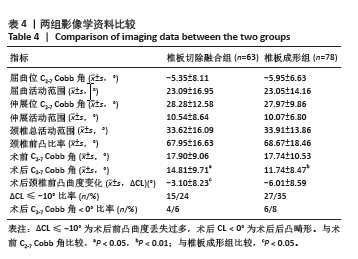
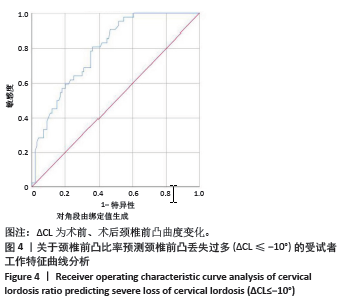
[1] LAW MD, BERNHARDT M, WHITE AA. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a review of surgical indications and decision making. Yale J Biol Med. 1993; 66(3):165-177.
[2] LIU F, YANG SD, HUO LS, et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical compressive myelopathy: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltim). 2016;95(23):e3588.
[3] ADOGWA O, HUANG K, HAZZARD M, et al. Outcomes after cervical laminectomy with instrumented fusion versus expansile laminoplasty: a propensity matched study of 3185 patients. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22(3):549-553.
[4] KUMAR VG, REA GL, MERVIS LJ, et al. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: functional and radiographic long-term outcome after laminectomy and posterior fusion. Neurosurgery. 1999;44(4):771-778.
[5] SODEYAMA T, GOTO S, MOCHIZUKI M, et al. Effect of decompression enlargement laminoplasty for posterior shifting of the spinal cord. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(15):1527-1532.
[6] KONG C, LI XY, SUN XY, et al. The ratio of C2-C7 Cobb angle to T1 slope is an effective parameter for the selection of posterior surgical approach for patients with multisegmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Orthop Sci. 2020;25(6):953-959.
[7] FUJISHIRO T, HAYAMA S, OBO T, et al. Gap between flexion and extension ranges of motion: a novel indicator to predict the loss of cervical lordosis after laminoplasty in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2021;35(1):8-17.
[8] ONO K, MURATA S, MATSUSHITA M, et al. Cervical Lordosis Ratio as a Novel Predictor for the Loss of Cervical Lordosis After Laminoplasty. Neurospine. 2021;18(2):311-318.
[9] WHITE AA 3RD, JOHNSON RM, PANJABI MM, et al. Biomechanical analysis of clinical stability in the cervical spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975;(109): 85-96.
[10] 李程,郭开今,李强,等. Arch钛板与侧块螺钉固定治疗颈椎后纵韧带骨化症疗效比较[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2017,23(10):873-878.
[11] XU R, HAMAN SP, EBRAHEIM NA, et al. The anatomic relation of lateral mass screws to the spinal nerves. A comparison of the Magerl, Anderson, and An techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(19):2057-2061.
[12] 伍少玲,马超,伍时玲,等. 颈椎功能障碍指数量表的效度与信度研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2008,23(7):625-628.
[13] 王宇,李翔宇,刘承鑫,等. 多节段颈椎前路术后颈椎前凸角丢失的危险因素分析[J]. 首都医科大学学报,2022,43(1):149-155.
[14] HIRABAYASHI K, MIYAKAWA J, SATOMI K, et al. Operative results and postoperative progression of ossification among patients with ossification of cervical posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1981; 6(4):354-364.
[15] BABA H, UCHIDA K, MAEZAWA Y, et al. Lordotic alignment and posterior migration of the spinal cord following en bloc open-door laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy: a magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurol. 1996; 243(9):626-632.
[16] LEE CH, JAHNG TA, HYUN SJ, et al. Expansive Laminoplasty Versus Laminectomy Alone Versus Laminectomy and Fusion for Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: Is There a Difference in the Clinical Outcome and Sagittal Alignment?. Clin Spine Surg. 2016; 29(1):E9-E15.
[17] STEPHENS BF, RHEE JM, NEUSTEIN TM, et al. Laminoplasty Does not Lead to Worsening Axial Neck Pain in the Properly Selected Patient With Cervical Myelopathy: A Comparison With Laminectomy and Fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(24):1844-1850.
[18] PARACINO R, FASINELLA MR, MANCINI F, et al. Review of laminoplasty versus laminectomy in the surgical management of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Surg Neurol Int. 2021;12:44..
[19] 郑博隆,郝定均,杨小彬,等.单开门椎板成形术和椎板切除并侧块螺钉内固定术治疗颈椎后纵韧带骨化症的疗效比较[J].脊柱外科杂志, 2018,16(1):14-21.
[20] LEE SH, SUK KS, KANG KC, et al. Outcomes and Related Factors of C5 Palsy Following Cervical Laminectomy With Instrumented Fusion Compared With Laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(10):E574-E579.
[21] EPSTEIN NE. Commentary on article: Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy: A meta-analysis of clinical and radiological outcomes by Chang-Hyun Lee et al. Surg Neurol Int. 2015;6(Suppl 14):S379-S382.
[22] LIN S, ZHOU F, SUN Y, et al. The severity of operative invasion to the posterior muscular-ligament complex influences cervical sagittal balance after open-door laminoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(1):127-135.
[23] FUNABA M, IMAJO Y, SUZUKI H, et al. The Deterioration of Cervical Kyphosis During Neck Flexion after Laminoplasty Affects the Surgical Outcome of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Global Spine J. 2023;13(8): 2497-2507.
[24] 严宏伟. 后路经肌间隙保留伸肌群的颈椎椎板成形术治疗脊髓型颈椎病[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2022,43(2):287-288.
[25] ISEDA K, TAKAHASHI K, NAKAJIMA M. Indication of C2-C7 Cervical Laminoplasty with Muscle and Ligament Preservation in Patients with Kyphosis. World Neurosurg. 2023;175:e44-e54.
[26] IIZUKA H, NAKAJIMA T, IIZUKA Y, et al. Cervical malalignment after laminoplasty: relationship to deep extensor musculature of the cervical spine and neurological outcome. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;7(6):610-614.
[27] KIM TH, LEE SY, KIM YC, et al. T1 slope as a predictor of kyphotic alignment change after laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(16):E992-E997.
[28] ZHANG JT, LI JQ, NIU RJ, et al. Predictors of cervical lordosis loss after laminoplasty in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(4):1205-1210.
[29] LI XY, KONG C, SUN XY, et al. Influence of the Ratio of C2-C7 Cobb Angle to T1 Slope on Cervical Alignment After Laminoplasty. World Neurosurg. 2019;124:e659-e666.
[30] CHENG X, CHEN Z, SUN X, et al. Favorable cervical extension capacity preventing loss of cervical lordosis after laminoplasty due to spontaneous restoration of initial lordosis. Spine J. 2024;24(1):94-100.
|