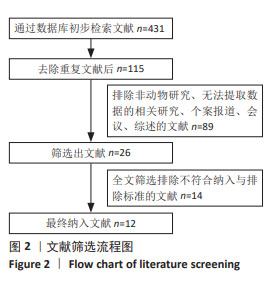
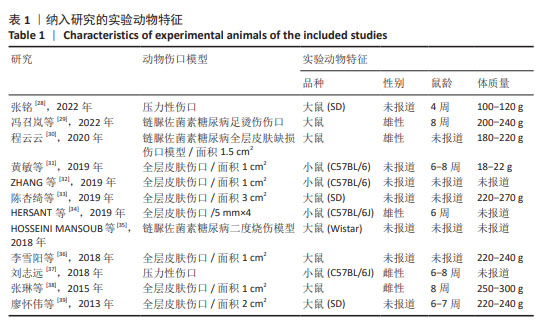
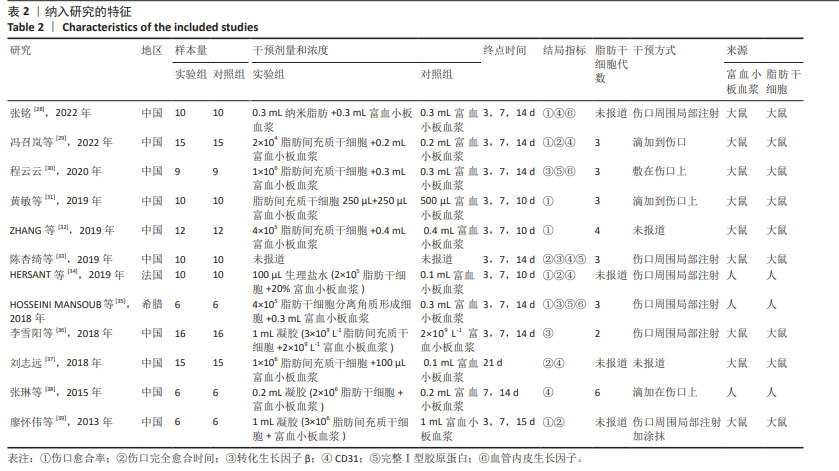
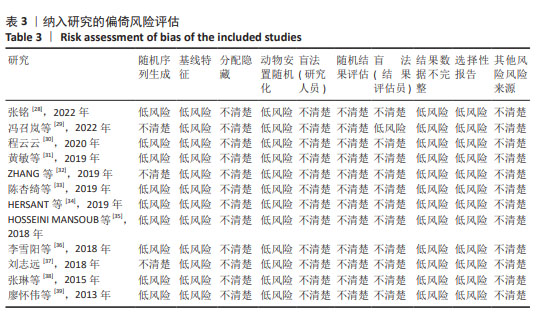
[1] GRAVES N, PHILLIPS CJ, HARDING K. A narrative review of the epidemiology and economics of chronic wounds. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187(2):141-148.
[2] AL ABOUD AM, MANNA B. Wound Pressure Injury Management. 2020 Jun 28. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2023.
[3] TEJADA S, BATLE JM, FERRER MD, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen in the Process of Wound Healing. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(15):1682-1693.
[4] ZHAO R, LIANG H, CLARKE E, et al. Inflammation in Chronic Wounds. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2085.
[5] SUN H, PULAKAT L, ANDERSON DW. Challenges and New Therapeutic Approaches in the Management of Chronic Wounds. Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(12):1264-1275.
[6] DUSCHER D, BARRERA J, WONG VW, et al. Stem Cells in Wound Healing: The Future of Regenerative Medicine? A Mini-Review. Gerontology. 2016;62(2):216-225.
[7] BRAZIL JC, QUIROS M, NUSRAT A, et al. Innate immune cell-epithelial crosstalk during wound repair. J Clin Invest. 2019; 129(8):2983-2993.
[8] SHOJAEI F, RAHMATI S, BANITALEBI DM. A review on different methods to increase the efficiency of mesenchymal stem cell-based wound therapy. Wound Repair Regen. 2019; 27(6):661-671.
[9] MARANDA EL, RODRIGUEZ-MENOCAL L, BADIAVAS EV. Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Dermal Repair in Burns and Diabetic Wounds. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(1):61-70.
[10] KIM WS, PARK BS, SUNG JH. The wound-healing and antioxidant effects of adipose-derived stem cells. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009;9(7):879-887.
[11] ROUSSELLE P, MONTMASSON M, GARNIER C. Extracellular matrix contribution to skin wound re-epithelialization. Matrix Biol. 2019;75-76:12-26.
[12] MA T, FU B, YANG X, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote cell proliferation, migration, and inhibit cell apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cutaneous wound healing. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):10847-10854.
[13] ZHANG Y, BAI X, SHEN K, et al. Exosomes Derived from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Diabetic Chronic Wound Healing through SIRT3/SOD2. Cells. 2022; 11(16):2568.
[14] HASSAN WU, GREISER U, WANG W. Role of adipose-derived stem cells in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2014;22(3): 313-325.
[15] HU N, CAI Z, JIANG X, et al. Hypoxia-pretreated ADSC-derived exosome-embedded hydrogels promote angiogenesis and accelerate diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2023;157:175-186.
[16] OUYANG L, QIU D, FU X, et al. Overexpressing HPGDS in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduces inflammatory state and improves wound healing in type 2 diabetic mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):395.
[17] NOLAN GS, SMITH OJ, JELL G, et al. Fat grafting and platelet-rich plasma in wound healing: a review of histology from animal studies. Adipocyte. 2021;10(1):80-90.
[18] JAMES IB, COLEMAN SR, RUBIN JP. Fat, Stem Cells, and Platelet-Rich Plasma. Clin Plast Surg. 2016;43(3):473-488.
[19] KUFFLER DP. Platelet-Rich Plasma Promotes Axon Regeneration, Wound Healing, and Pain Reduction: Fact or Fiction. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52(2):990-1014.
[20] REN ZQ, DU B, DONG HJ, et al. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Repairs Burn Wound and Reduces Burn Pain in Rats. J Burn Care Res. 2022;43(1):263-268.
[21] KOBAYASHI E, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, SCULEAN A, et al. Effects of platelet rich plasma (PRP) on human gingival fibroblast, osteoblast and periodontal ligament cell behaviour. BMC Oral Health. 2017;17(1):91.
[22] LUBKOWSKA A, DOLEGOWSKA B, BANFI G. Growth factor content in PRP and their applicability in medicine. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2012;26(2 Suppl 1): 3S-22S.
[23] NAKAMURA S, ISHIHARA M, TAKIKAWA M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) promotes survival of fat-grafts in rats. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;65(1):101-106.
[24] BLUMENSCHEIN AR, FREITAS-JUNIOR R, MOREIRA MA, et al. Is the combination of fat grafts and platelet rich plasma effective in rats? Acta Cir Bras. 2016;31(10): 668-674.
[25] SMITH OJ, LEIGH R, KANAPATHY M, et al. Fat grafting and platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: A feasibility-randomised controlled trial. Int Wound J. 2020;17(6):1578-1594.
[26] RANGASWAMY M. Regenerative Wound Healing by Open Grafting of Autologous Fat and PRP-Gel - A New Concept and Potential Alternative to Flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9(1):e3349.
[27] HOOIJMANS CR, ROVERS MM, DE VRIES RB, et al. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:43.
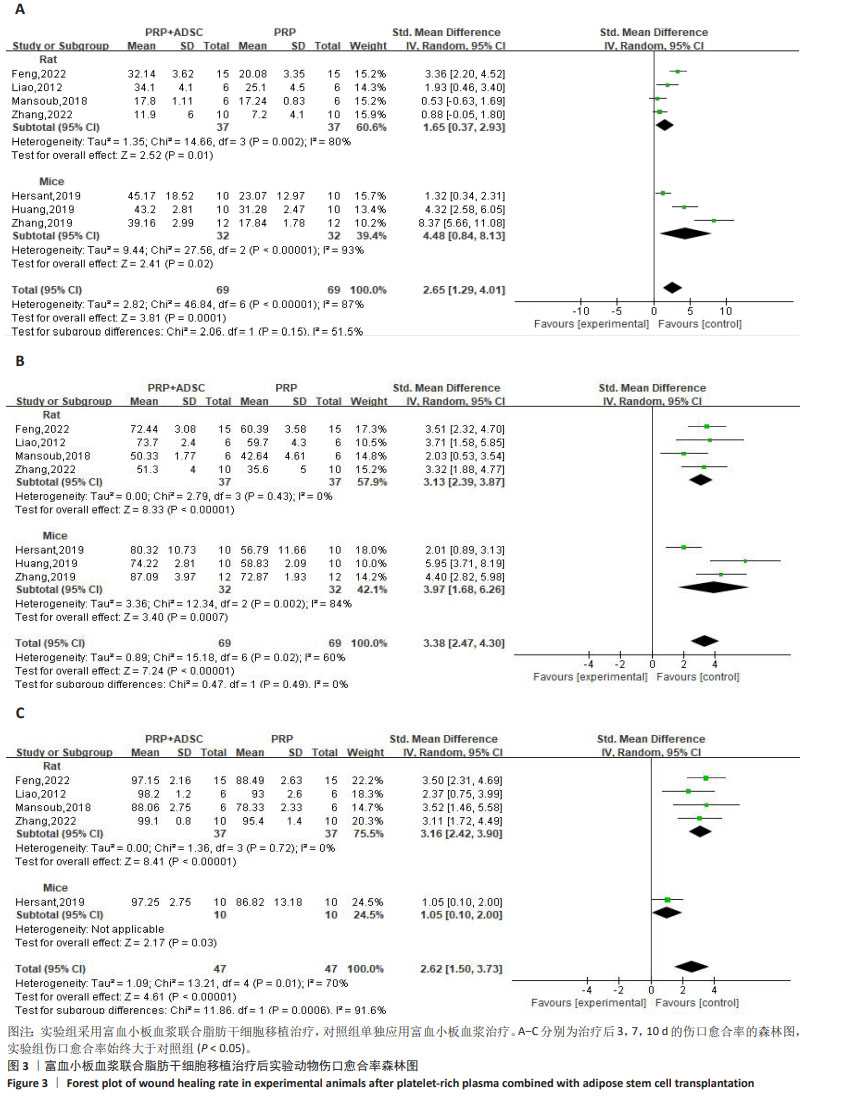
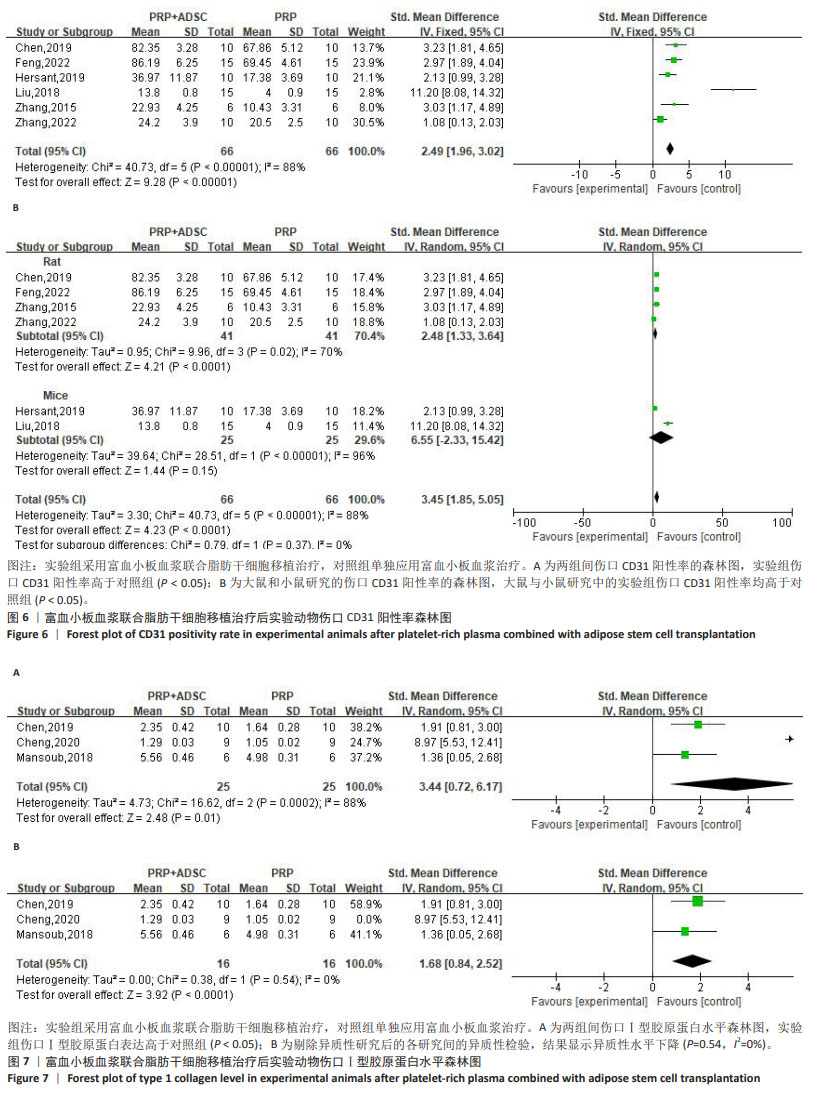
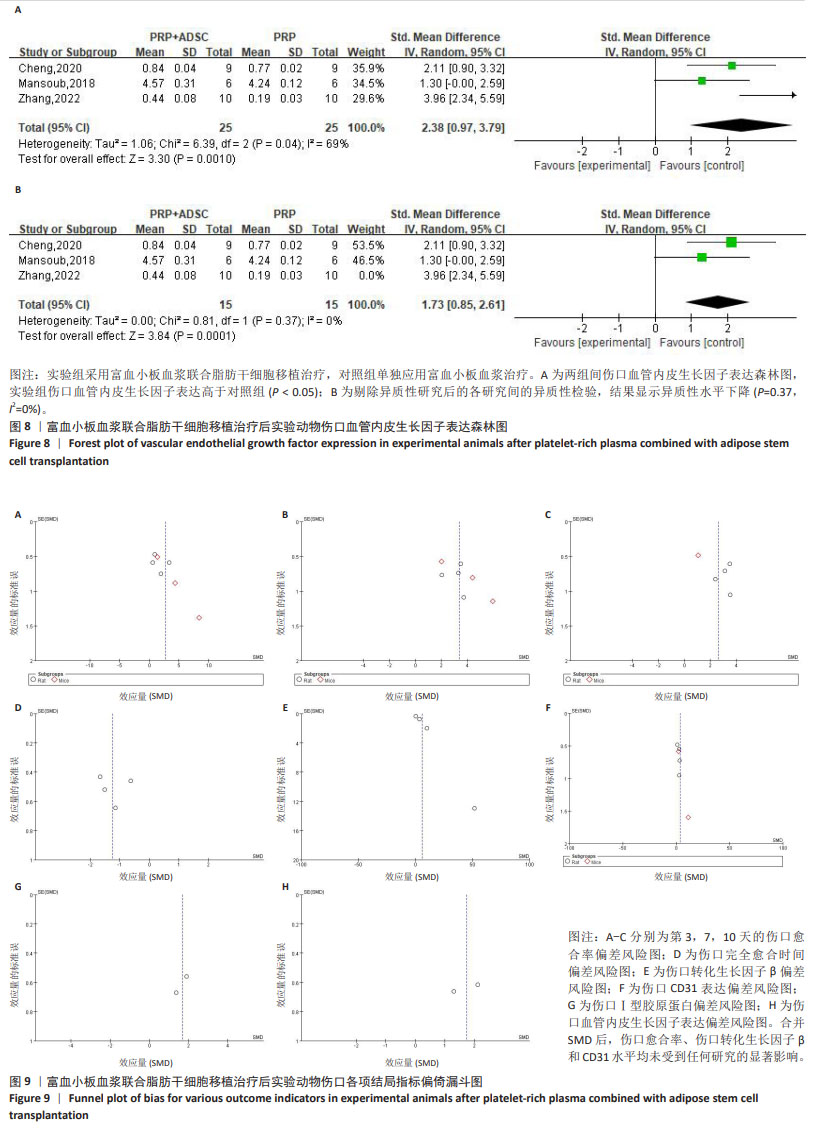
[28] 张铭.纳米脂肪联合富血小板血浆修复压力性损伤创面的基础研究[D].潍坊:潍坊医学院,2022.
[29] 冯召岚,盛健健,董爱武,等.自体富血小板凝胶联合脂肪干细胞促进糖尿病足大鼠创面修复的机制研究[J].中国医学创新,2022,19(23):24-30.
[30] 程云云.ADSCs-PRP对糖尿病大鼠创面愈合的影响及机制研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2020.
[31] 黄敏,颜洪.脂肪间充质干细胞条件培养液联合富血小板纤维蛋白修复小鼠皮肤损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(1):18-23.
[32] ZHANG L, ZHANG B, LIAO B, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in combination with adipose-derived stem cells promotes skin wound healing through activating Rho GTPase-mediated signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(7):4100-4112.
[33] 陈杏绮,罗志军,殷安柱,等.同种异体脂肪干细胞联合自体富血小板血浆凝胶修复大鼠皮肤软组织创面的临床效果[J].中国药物经济学,2019,14(10):84-87+93.
[34] HERSANT B, SID-AHMED M, BRAUD L, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves the Wound Healing Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Paracrine and Metabolism Alterations. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:1234263.
[35] HOSSEINI MANSOUB N, GÜRDAL M, KARADADAŞ E, et al. The role of PRP and adipose tissue-derived keratinocytes on burn wound healing in diabetic rats. Bioimpacts. 2018;8(1):5-12.
[36] 李雪阳,杨超,沈才齐,等.TGFβ1参与的脂肪干细胞-富血小板血浆凝胶促进大鼠创面修复的机制研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2018,17(22):2385-2389.
[37] 刘志远.富血小板血浆负载人脂肪来源干细胞促进小鼠压疮愈合的实验研究[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2018.
[38] 张琳,富泽龙,冯锐.人脂肪干细胞复合富血小板血浆治疗裸鼠放射性皮肤损伤的实验研究[J].医学研究杂志,2015, 44(7):57-61.
[39] 廖怀伟,韩超,刘丽忠,等.富血小板血浆凝胶对脂肪干细胞修复皮肤软组织缺损创面的影响[J].重庆医学,2013,42(32): 3859-3862.
[40] 蒋宇江,黄志群,唐强.烧伤残余创面发病机制及治疗研究进展[J].中国烧伤创疡杂志,2023,35(6):439-442+455.
[41] ZHANG L, HU C, XU W, et al. Advances in wound repair and regeneration: Systematic comparison of cell free fat extract and platelet rich plasma. Front Chem. 2022;10: 1089277.
[42] VINISH M, CUI W, STAFFORD E, et al. Dendritic cells modulate burn wound healing by enhancing early proliferation. Wound Repair Regen. 2016;24(1):6-13.
[43] LIU W, WANG DR, CAO YL. TGF-beta: a fibrotic factor in wound scarring and a potential target for anti-scarring gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2004;4(1): 123-136.
[44] DOUGLAS HE. TGF-ß in wound healing: a review. J Wound Care. 2010;19(9): 403-406.
[45] WEBER CE, LI NY, WAI PY, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, TGF-β, and osteopontin in wound healing and tissue remodeling after injury. J Burn Care Res. 2012;33(3):311-318.
[46] BRANTON MH, KOPP JB. TGF-beta and fibrosis. Microbes Infect. 1999;1(15): 1349-1365.
[47] DELISSER HM, NEWMAN PJ, ALBELDA SM. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (CD31). Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1993;184:37-45.
[48] LIU L, ZHENG CX, ZHAO N, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Aggregation-Released Extracellular Vesicles Induce CD31(+) EMCN(+) Vessels in Skin Regeneration and Improve Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(20):e2300019.
[49] KOLOKOLCHIKOVA EG, ZHIRKOVA EA, GOLOVATENKO-ABRAMOV PK, et al. Morphofunctional evaluation of the effect of collagen-1-based dressing on skin regeneration after burn trauma in mice of two genetic strains. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2010;149(1):154-160.
[50] GAN L, FAGERHOLM P, PALMBLAD J. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor VEGFR-2 in the regulation of corneal neovascularization and wound healing. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2004; 82(5):557-563.
[51] GOSWAMI AG, BASU S, HUDA F, et al. An appraisal of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): the dynamic molecule of wound healing and its current clinical applications. Growth Factors. 2022;40(3-4): 73-88.
[52] LI L, LIU H, XU C, et al. VEGF promotes endothelial progenitor cell differentiation and vascular repair through connexin 43. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):237. |