中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 2507-2512.doi: 10.12307/2025.390
• 皮肤粘膜组织构建 skin and mucosal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
邮票异体皮植皮在特重度烧伤Meek皮片移植失败后的应用
田晨阳1,陶 克2,计 鹏1,王耘川1,胡大海1,高晓文1,郑 朝1
- 1空军军医大学第一附属医院烧伤与皮肤外科,陕西省西安市 710000;2温州医科大学附属第一医院创面修复中心与再生医学中心创面修复科,浙江省温州市 325000
Application of stamp-shaped skin allograft in extremely severe burns following failure of Meek skin grafting
Tian Chenyang1, Tao Ke2, Ji Peng1, Wang Yunchuan1, Hu Dahai1, Gao Xiaowen1, Zheng Zhao1
- 1Department of Burns and Skin Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Air Force Military Medical University, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Wound Repair, Wound Repair Center and Regenerative Medicine Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
烧伤:是由于火焰、高温液体及气体、金属化学物、寒冷或辐射等原因导致皮肤完整性的破坏及皮肤黏膜屏障的丧失,具有一系列的并发症,如实质性疼痛、体液丢失增加、局部及全身感染和深部组织干性坏死。对于严重烧伤,较大的创面可迅速导致脱水和休克。
异体皮:主要来源为尸体皮肤。异体生物材料的产品特点包括具有皮肤屏障功能,阻止水分、电解质、蛋白质和热量的丢失和细菌侵入;黏附性与自体皮相同,有促进上皮化的作用,但有时呈现占位现象;异体皮具有抗原性,移植后2周左右被排斥。
邮票异体皮移植:将异体皮修剪为边长不规则邮票皮片,保持间距至少5 mm左右,贴于延迟愈合创面处,已有明显种子皮处不贴异体皮,之后采用凡士林纱布覆盖创面,覆盖无菌纱布,加压包扎,隔日换药。
背景:部分特重度烧伤患者采用Meek皮片移植的术后效果并不能令人满意,出现了延迟愈合或皮片移植失败的问题。对于皮源不足的Meek皮片移植失败患者的治疗研究较少,此次研究探索了一种治疗的新方法。
目的:观察邮票异体皮植皮技术在特重度烧伤Meek皮片移植失败后的疗效。
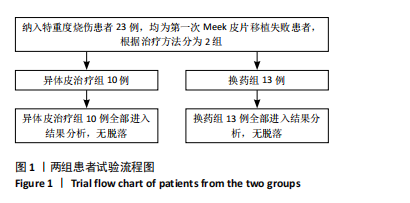
方法:纳入空军军医大学第一附属医院烧伤科2013年8月至2023年8月收治Meek皮片移植术后愈合不良的23例特重度烧伤患者,根据治疗方式不同分为2组,其中异体皮治疗组10例,换药组13例。对比两组患者二次Meek植皮术前血红蛋白、血小板计数、白蛋白计数、白细胞计数、中性粒细胞,降钙素原及微生物培养阳性率;二次Meek植皮术前、术后皮片成活率;手术次数及脓毒血症发生率;以及术后3,6个月创面瘢痕情况。
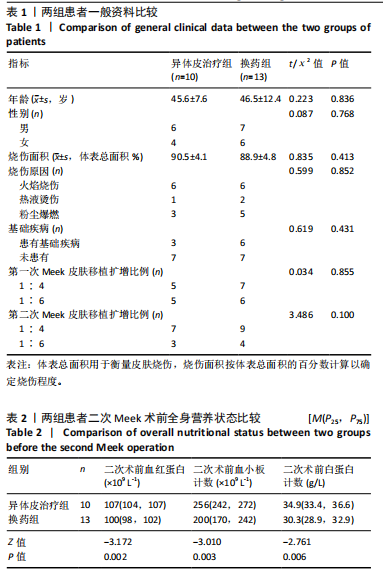
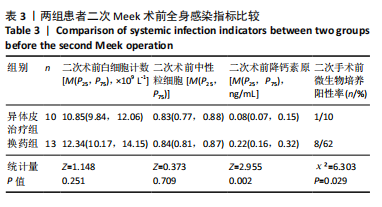
结果与结论:①异体皮治疗组的二次Meek植皮术前血红蛋白、血小板计数、白蛋白计数均明显高于换药组(Z=-3.172,P=0.002;Z=
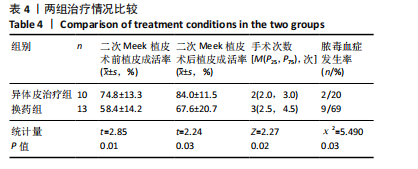
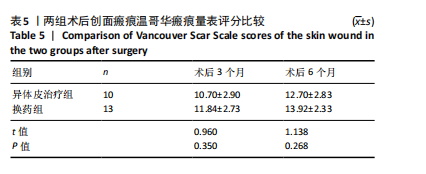
-3.010,P=0.003;Z=-2.761,P=0.006);②两组二次Meek植皮术前白细胞计数、中性粒细胞相比差异无显著性意义(Z=1.148,P=0.251;Z=0.373,P=0.709);但异体皮治疗组二次术前降钙素原计数明显低于换药组(Z=2.955,P=0.002);③换药组烧伤患者二次术前微生物培养阳性率高于异体皮治疗组(χ²=6.303,P=0.029);④异体皮治疗组的二次Meek植皮术前植皮成活率(74.8±13.3)%明显高于换药组(58.4±14.2)%(t=2.85,P=0.01),术后植皮成活率(84.0±11.5)%明显高于换药组(67.6±20.7)%(t=2.24,P=0.03);⑤异体皮治疗组后期手术次数少于换药组(Z=2.27,P=0.02);⑥换药组烧伤患者脓毒血症发生率明显高于异体皮治疗组(χ2=5.490,P=0.03);⑦两组手术后3,6个月瘢痕温哥华瘢痕量表评分相比差异无显著性意义(t=0.960,1.138,P > 0.05);⑧提示邮票状异体皮在治疗Meek微型移植术后皮片愈合不良创面时具有较好的疗效,患者后期皮片利用率明显增高,减少了创面感染的概率,解决了皮源不足的问题。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2787-0498(田晨阳)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: