1 对象和方法 Subjects and methods
1.1 设计 分组对照观察、细胞学实验,盲法评估,两组间比较采用独立t检验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2022年12月至2023年8月在新疆医科大学协同实验楼及科技楼完成。
1.3 对象
1.3.1 组织来源 收集 2022-2023 年新疆医科大学第一附属医院整形外科手术切除治疗符合入选标准的增生性瘢痕组织共6例,男性3例,女性3例,年龄(36±7)岁,病变部位分为上臂(1例)、面部(2例)、腹部(3例);正常皮肤组织患者6例,男性3例,女性3例,年龄(38±6)岁,上眼睑(3例)、下眼睑(3例)。该项研究已经新疆医科大学第一临床医学院伦理委员会批准,伦理批号:20170214-71。
增生性瘢痕患者纳入标准:①年龄18-60岁;②处于增生期增生性瘢痕皮肤;③有创伤、感染、手术或烫伤等病史;④未经过激光、注射等治疗。
增生性瘢痕患者排除标准:①瘢痕疙瘩;②依从性差者。
正常皮肤组织供者纳入标准:①术区无创伤、烫伤、烧伤病史;②无先天性免疫缺陷病或皮肤病。
正常皮肤组织供者排除标准:①皮肤有感染、溃疡;②术区有手术/外伤史。
1.3.2 实验主要试剂、仪器 FBS 胎牛血清(Gibico,澳洲)、PBS (Hyclone,美国);青霉素、链霉素溶液(Gibico,美国);CCK-8 试剂 (bioss,美国); Annexin V-FITC 细胞凋亡检测试剂盒(BD,美国);脂质体 Lipo8000 转染试剂 (碧云天,上海);miR-192-5p模拟物、miR-192-5p抑制物(锐博,广州);Trizol试剂(Invitrogene,美国);表皮调节素抗体、抗Ⅰ型胶原抗体、抗Ⅲ型胶原抗体、抗GAPDH 抗体 (ABclonal,中国);表皮调节素野生型 (WT)、表皮调节素突变型 (MT)和表皮调节素质粒引物、miR-192-5p前向引物、 U6前向引物(生工,中国);荧光素酶报告基因检测试剂盒 (promega,美国);miRNA 提取分离试剂盒 DP501,KR211,FP411 (天根,中国);SYBRGreen荧光定量试剂盒-RR820A、PCR反转录试剂盒-RR047A(Takara,日本);实时荧光定量PCR仪、凝胶成像分析系统 (Bio-Rad,美国);酶标仪 (Thermo,美国)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 细胞培养 切取增生性瘢痕组织,放置于PBS中转移至超净台,用含3%双抗的PBS漂洗3次,用眼科剪修剪至约1 cm×1 cm的组织块,培养皿内贴壁4 h后,加入含体积分数15%胎牛血清的完全培养基8 mL。待7-10 d后镜下观察细胞从组织块中爬出,将组织块移植于新培养皿,于旧培养皿中加入0.25%胰蛋白酶(含EDTA)1.5 mL均匀置于温箱消化1.5 min,镜下见细胞形态改变后,加入4 mL培养基终止消化,离心5 min后,弃上清液,混合培养基重悬细胞,将传代后培养皿置于恒温培养箱继续培养,注意细胞密度,使其均匀分布,每4 d加液或换液1次。待镜下观察细胞爬出融合至 85%-90%时,即可将组织块移入新的培养皿内继续固定和培养,0.25%胰酶消化爬出的原代细胞后继续传代培养。正常皮肤组织成纤维细胞同理分离培养,见表1。

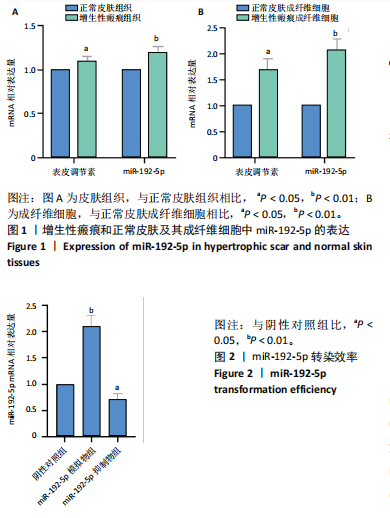
1.4.2 组织和细胞中miR-192-5p、表皮调节素mRNA的表达情况 取增生性瘢痕组织、正常皮肤组织及两组相应的成纤维细胞,采用Trizol试剂提取细胞总RNA来检测miR-192-5p和表皮调节素的mRNA表达,取2 μg总RNA经反转录生成cDNA。用以模板、引物和Taq PCR Master Mix试剂构成反应体系行qRT-PCR。反应程序为:95 ℃ 30 s;95 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 35 s,40个循环,记录Ct值。分别以U6和GAPDH为内参照,采用2-ΔΔCt法评估miR-192-5p和表皮调节素 mRNA的相对表达水平。引物序列见表2。

1.4.3 qRT-PCR检测增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞中miR-192-5p的转染效率 使用lipo8000转染miR-192-5p mimic和miR-192-5p inhibitor至增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞48 h后,先用DP501试剂盒提取细胞中的总RNA,再使用KR211cDNA第一链合成试剂盒,通过反转录反应获得cDNA,用以模板、引物和Taq PCR Master Mix试剂构成反应体系行qRT-PCR。反应程序同1.4.2,记录Ct值。以U6为内参,采用2-ΔΔCt法评估miR-192-5p mimic和 miRNA-192-5p inhibitor的mRNA相对表达水平。
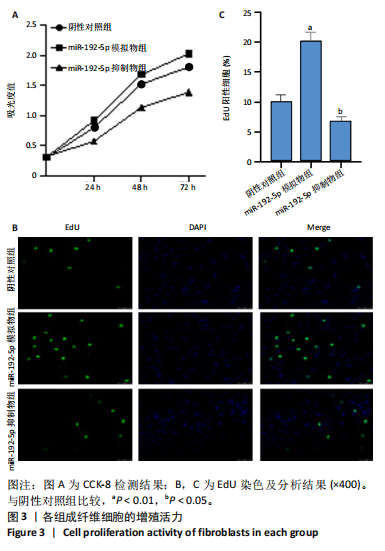
1.4.4 CCK-8和EDU法检测瘢痕成纤维细胞的增殖活力 准备4块96孔板,按0,24,48,72 h 将4板分为4组,每板按横向分为3组,纵向分为阴性对照组、miR-192-5p 模拟物组和 miR-192-5p 抑制物组,每组3个复孔。将增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞按5×106 L-1的细胞浓度接种于96孔板中,每孔接种100 μL,后用脂质体Lipo8000按说明书分别转染miR-192-5p 模拟物和miR-192-5p抑制物于相应分组。按96板分组,将10 μL CCK-8溶液与90 μL DMEM混合加入每个孔,置于细胞培养箱中避光孵育1 h,酶标仪测量吸光度值(450 nm 波长),计算细胞活力。
将细胞按照前述分组转染后按5×104接种在20 mm共聚焦小皿,后1∶500 稀释EdU (10 mmol/L)与细胞培养液混合,等体积加入0.5 mL EdU工作液于皿中,温箱孵育细胞 2 h。EdU标记细胞后用40 g/L的多聚甲醛固定细胞15 min,用含3% BSA的PBS洗涤3次;每孔再用含0.3% Triton X-100的PBS室温孵育15 min,用含3% BSA的PBS洗涤细胞一两次。配制 Click Additive Solution并配置Click反应液,将0.5 mL Click 反应液加入每孔,室温避光孵育30 min;用含3% BSA的PBS洗涤3次,DAPI 染色液处理细胞5-10 min,PBS洗涤2次;最后,使用激光共聚焦显微镜观察细胞。
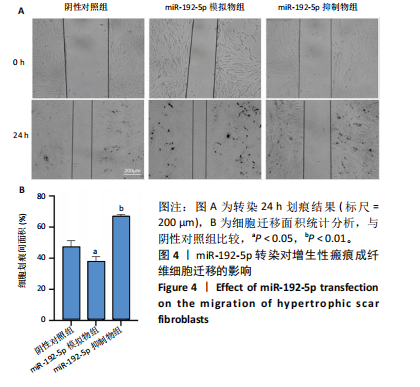
1.4.5 划痕实验检测成纤维细胞迁移能力 首先,于超净台内用标记笔在6孔板背后每隔0.5 cm划横线,将瘢痕成纤细胞按1×105接种在6孔板中。隔天观察,当细胞密度达到90%时,取10 μL枪头在6孔板底细胞面垂直划一条与标记线垂直的线。将漂浮脱落下来的未贴壁细胞用PBS洗涤3 次,每次3 min,再每孔加入2 mL完全培养基。按1.4.4分组转染细胞,摇晃均匀后于显微镜下拍摄图像(0 h),并记录拍摄位置与时间。将转染后6孔板放置37 ℃
培养箱中培养 24 h后,拍摄相同位置的照片,并记录位置与时间。通过比较各时间点的划痕宽度,计算愈合速度和细胞迁移速度。使用Image J 软件计算划痕面积,并计算相对划痕宽度。相对划痕宽度= (相应时间点划痕宽度/0 h划痕宽度)×100%。实验重复3次。
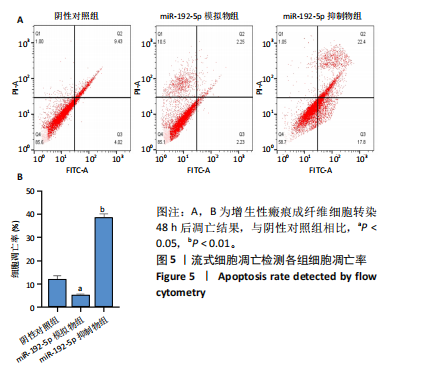
1.4.6 流式细胞术检测成纤维细胞凋亡 6孔板接种增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞,接种细胞浓度为1×106 L-1,加入2.5 mL完全培养液。当细胞密度均匀并达到90%融合时,按1.4.4分组转染细胞。随后,胰酶消化,离心收集细胞,按试剂盒说明书加入相应试剂。流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡比例,计算细胞凋亡率。
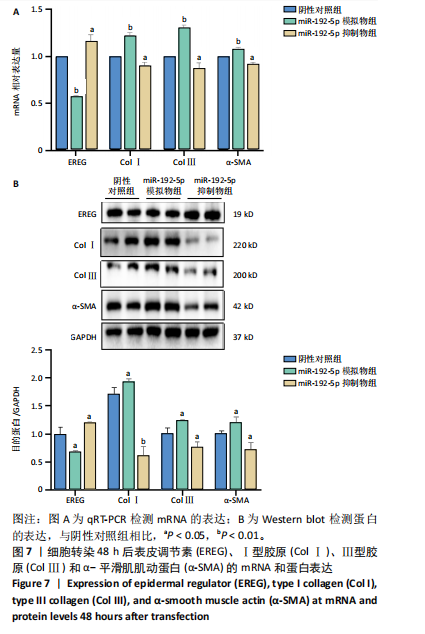
1.4.7 Western blot 法检测相关蛋白表达 收集各组细胞沉淀,加入适量的裂解液(PMSF∶RIPA=1∶100)在冰上吹打裂解100下,置于冰上10 min,此步骤重复3次。于4 ℃12 000 r/min离心20 min,离心后取上清液,通过BCA蛋白质定量法(定2 μg/μL)测定蛋白含量后,每组取蛋白4 μL进行SDS-PAGE电泳,之后将分离的蛋白湿转至PVDF膜,5×脱脂奶粉在上下震荡式摇床中对PVDF膜进行封闭,加入一抗(表皮调节素、Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白抗体,稀释比例1∶1 000)4 ℃孵育过夜,二抗常温孵育1 h,通过显色成像并用Image-J软件分析灰度值做量化分析。
1.4.8 qRT-PCR法检测相关基因表达 将增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞按1×108 L-1细胞接种于10 cm2培养皿中,显微镜下观察细胞生长融合至80%,按1.4.4分组转染48 h后,将培养皿内加入RIPA裂解液进行裂解,检测方法、扩增条件同1.4.2,引物序列见表2。
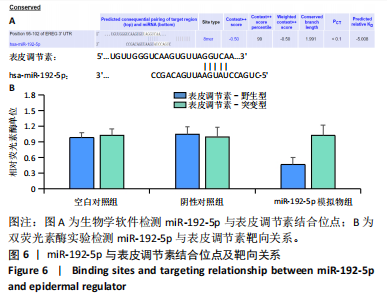
1.4.9 生物信息学预测miR-192-5p下游结合位点 应用靶基因预测数据库 miRDB(https://mirdb.org/mirdb/index.html)和Targetscan(www.targetscan.org/ vert_80/) 预测miR-192-5p潜在结合位点,表皮调节素可能与其互为靶标。
1.4.10 双荧光素酶实验检测miR-192-5p与表皮调节素的靶向关系 通过构建野生型(WT)和突变型(MT)双荧光素酶报告载体,研究miR-192-5p与表皮调节素的相互作用。首先,根据生物信息学网站预测的miR-192-5p与表皮调节素的结合位点,设计并合成含有靶基因表皮调节素的双荧光素酶报告载体(包含预测的 miR-192-5p结合位点),这些载体分为野生型(WT)和突变型(MT)。将增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞接种于24孔板中,并培养至适当的细胞密度。分别将含有表皮调节素的野生型质粒(WT)和突变型质粒(MT)转染至培养的增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞中。细胞通过lipofectamine 8000与miR-192-5p模拟物和miR-192-5p阴性对照物和表皮调节素3’UTR(WT或MUT)报告质粒共转染。转染48 h后,收集细胞,并使用荧光素酶报告基因检测试剂盒分别检测荧光素酶和肾荧光素酶的活性。Renilla荧光素酶为内参用于校正转染效率,而荧光素酶用于检测目标基因表达。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①增生性瘢痕组织和正常皮肤组织及细胞中miRNA-192-5p及表皮调节素的表达;②增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞miRNA-192-5p转染效率;③miR-192-5p转染后增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖活力、迁移及凋亡情况;④miRNA-192-5p对表皮调节素的靶向作用;⑤miR-192-5p转染后对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞中相关蛋白和mRNA的表达。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 27.0统计软件分析及Graphpad prism 8.0软件绘图。两组间比较采用独立t检验,所有数据以x±s表示,P < 0.05 表示差异有显著性意义。该文章统计学方法由新疆医科大学统计学专家审核。