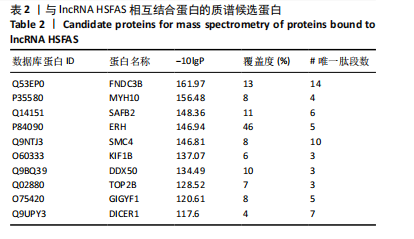
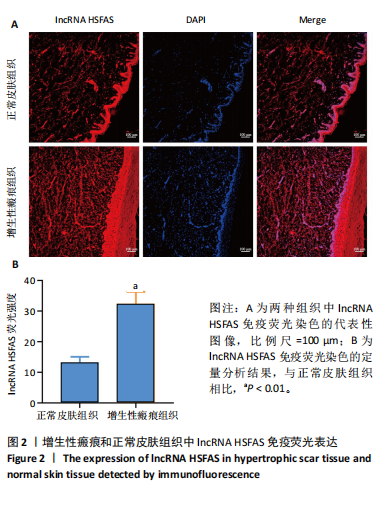
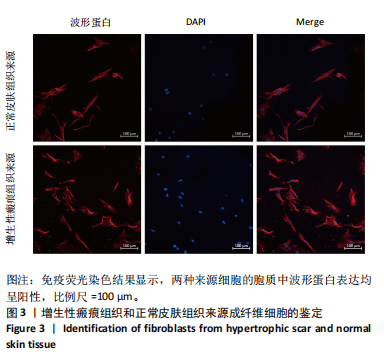
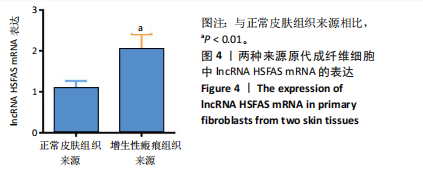
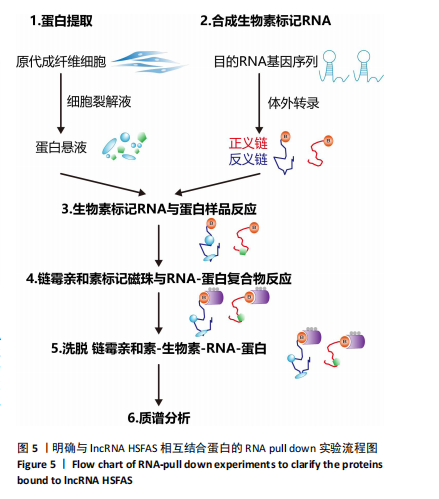
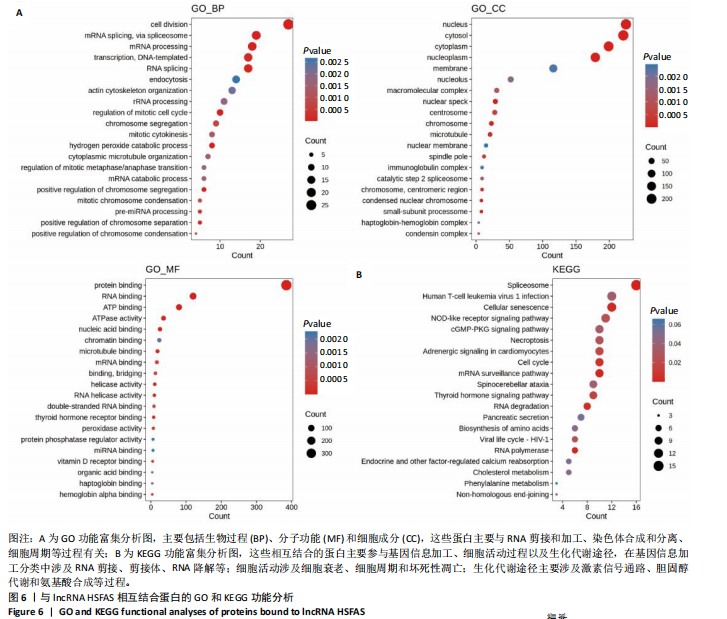
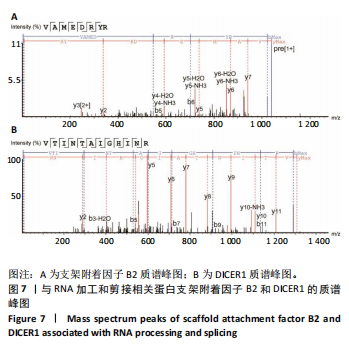
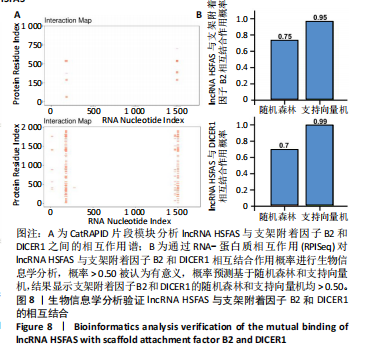
[1] FINNERTY CC, JESCHKE MG, BRANSKI LK, et al. Hypertrophic scarring: the greatest unmet challenge after burn injury. Lancet. 2016; 388(10052):1427-1436.
[2] RAY S, JU X, SUN H, et al. The IL-6 trans-signaling-STAT3 pathway mediates ECM and cellular proliferation in fibroblasts from hypertrophic scar. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133(5):1212-1220.
[3] BHARADIA SK, BURNETT L, GABRIEL V. Hypertrophic Scar. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2023;34(4):783-798.
[4] BOMBARO KM, ENGRAV LH, CARROUGHER GJ, et al. What is the prevalence of hypertrophic scarring following burns? Burns. 2003; 29(4):299-302.
[5] ALTEMIR A, BOIXEDA P. Laser Treatment of Burn Scars. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022;113(10):938-944.
[6] LIN S, QUAN G, HOU A, et al. Strategy for hypertrophic scar therapy: Improved delivery of triamcinolone acetonide using mechanically robust tip-concentrated dissolving microneedle array. J Control Release. 2019;306:69-82.
[7] EDWARDS J. Hypertrophic scar management. Br J Nurs. 2022;31(20): S24-S31.
[8] FRECH FS, HERNANDEZ L, URBONAS R, et al. Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids: Advances in Treatment and Review of Established Therapies. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24(2):225-245.
[9] ZHANG J, YU L, XU Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA upregulated in hypothermia treated cardiomyocytes protects against myocardial infarction through improving mitochondrial function. Int J Cardiol. 2018;266:213-217.
[10] LI X, WU Z, FU X, et al. lncRNAs: insights into their function and mechanics in underlying disorders. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2014; 762:1-21.
[11] XU H, GUO X, TIAN Y, et al. Knockdown of lncRNA-NEAT1 expression inhibits hypoxia-induced scar fibroblast proliferation through regulation of the miR-488-3p/COL3A1 axis. Exp Ther Med. 2022;24(1):442.
[12] MA F, SHEN J, ZHANG H, et al. A novel lncRNA FPASL regulates fibroblast proliferation via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in hypertrophic scar. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022;55(2): 274-284.
[13] 姜怡邓,马芳,沈江涌,等.一种用于增生性瘢痕诊断的lncRNA标志物及其应用[P].宁夏回族自治区:CN116622838A,2023-08-22.
[14] BARONE N, SAFRAN T, VORSTENBOSCH J, et al. Current Advances in Hypertrophic Scar and Keloid Management. Semin Plast Surg. 2021; 35(3):145-152.
[15] FERNÁNDEZ-GUARINO M, BACCI S, PÉREZ GONZÁLEZ LA, et al. The Role of Physical Therapies in Wound Healing and Assisted Scarring. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(8):7487.
[16] KNOWLES A, GLASS DA 2ND. Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41(3):509-517.
[17] ANZARUT A, OLSON J, SINGH P, et al. The effectiveness of pressure garment therapy for the prevention of abnormal scarring after burn injury: a meta-analysis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62(1):77-84.
[18] LEVENTHAL D, FURR M, REITER D. Treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2006;8(6):362-368.
[19] JALALI M, BAYAT A. Current use of steroids in management of abnormal raised skin scars. Surgeon. 2007;5(3):175-180.
[20] NAEINI FF, NAJAFIAN J, AHMADPOUR K. Bleomycin tattooing as a promising therapeutic modality in large keloids and hypertrophic scars. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32(8):1023-1029; discussion 1029-1030.
[21] LECLÈRE FM, MORDON SR. Twenty-five years of active laser prevention of scars: what have we learned? J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2010;12(5): 227-234.
[22] O’BRIEN L, JONES DJ. Silicone gel sheeting for preventing and treating hypertrophic and keloid scars. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(9):CD003826.
[23] SHIH R, WALTZMAN J, EVANS GR. Plastic Surgery Educational Foundation Technology Assessment Committee. Review of over-the-counter topical scar treatment products. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007; 119(3):1091-1095.
[24] HASHEMI M, MOOSAVI MS, ABED HM, et al. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) H19 in human cancer: From proliferation and metastasis to therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2022;184:106418.
[25] RICHART L, PICOD-CHEDOTEL ML, WASSEF M, et al. XIST loss impairs mammary stem cell differentiation and increases tumorigenicity through Mediator hyperactivation. Cell. 2022;185(12):2164-2183.e25.
[26] JING Y, JIANG X, LEI L, et al. Mutant NPM1-regulated lncRNA HOTAIRM1 promotes leukemia cell autophagy and proliferation by targeting EGR1 and ULK3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40(1):312.
[27] YANG F, LV S. LncRNA EPB41L4A-AS1 Regulates Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Metastasis in Breast Cancer. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2022; 52(1):3-11.
[28] DUAN BX, GENG XR, WU YQ. lncRNA RNCR2 facilitates cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in melanoma through HK2-mediated Warburg effect via targeting miR-495-3p. Neoplasma. 2021; 68(4):692-701.
[29] SHEN M, DUAN C, XIE C, et al. Identification of key interferon-stimulated genes for indicating the condition of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2022;13:962393.
[30] SU L, HAN J. Non-coding RNAs in hypertrophic scars and keloids: Current research and clinical relevance: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;256(Pt 1):128334.
[31] FAN P, WANG Y, LI J, et al. lncRNA PAPPA-AS1 Induces the Development of Hypertrophic Scar by Upregulating TLR4 through Interacting with TAF15. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:3170261.
[32] MA F, LIU H, XIA T, et al. HSFAS mediates fibroblast proliferation, migration, trans-differentiation and apoptosis in hypertrophic scars via interacting with ADAMTS8. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024;56(3):440-451.
[33] ZHEN H, YAO Y, YANG H. SAFB2 Inhibits the Progression of Breast Cancer by Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway via NFAT5. Mol Biotechnol. 2023;65(9):1465-1475.
[34] HUTTER K, LOHMÜLLER M, JUKIC A, et al. SAFB2 Enables the Processing of Suboptimal Stem-Loop Structures in Clustered Primary miRNA Transcripts. Mol Cell. 2020;78(5):876-889.e6.
[35] CHERNEY RE, EBERHARD QE, GIRI G, et al. SAFB associates with nascent RNAs and can promote gene expression in mouse embryonic stem cells. RNA. 2023;29(10):1535-1556.
[36] KÜPER C, BECK FX, NEUHOFER W. NFAT5-mediated expression of S100A4 contributes to proliferation and migration of renal carcinoma cells. Front Physiol. 2014;5:293.
[37] AMARA S, ALOTAIBI D, TIRIVEEDHI V. NFAT5/STAT3 interaction mediates synergism of high salt with IL-17 towards induction of VEGF-A expression in breast cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2016;12(2):933-943.
[38] REYES-CASTRO RA, CHEN SY, SEEMANN J, et al. Phosphorylated nuclear DICER1 promotes open chromatin state and lineage plasticity of AT2 tumor cells in lung adenocarcinomas. Sci Adv. 2023;9(30):eadf6210.
[39] CAMINO LP, DUTTA A, BARROSO S, et al. DICER ribonuclease removes harmful R-loops. Mol Cell. 2023;83(20):3707-3719.e5.
[40] LAN W, CHEN S, TONG L. MicroRNA-215 Regulates Fibroblast Function: Insights from a Human Fibrotic Disease. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(12): 1973-1984. |