中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 1512-1522.doi: 10.12307/2025.022
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的分子机制
李佳林1,2,3,4,5,张耀东1,2,3,4,5,娄艳茹1,2,3,4,5,于 洋1,2,3,4,5,杨 蕊1,2,3,4,5
- 1北京大学第三医院,妇产科,生殖医学中心,女性生育力促进全国重点实验室,北京市 100191;2国家妇产疾病临床医学研究中心(北京大学第三医院),北京市 100191;3辅助生殖教育部重点实验室(北京大学),北京市 100191;4生殖内分泌与辅助生殖技术北京市重点实验室,北京市 100191;5国家临床重点专科建设项目(2023)专项资金,北京市 100191
-
收稿日期:2023-11-07接受日期:2024-01-27出版日期:2025-03-08发布日期:2024-06-28 -
通讯作者:杨蕊,博士,副主任医师,副教授,北京大学第三医院,妇产科,生殖医学中心,女性生育力促进全国重点实验室;国家妇产疾病临床医学研究中心(北京大学第三医院);辅助生殖教育部重点实验室(北京大学);生殖内分泌与辅助生殖技术北京市重点实验室;国家临床重点专科建设项目(2023)专项资金,北京市 100191 -
作者简介:李佳林,女,2001年生,河南省洛阳市人,汉族,北京大学第三医院在读硕士,主要从事间充质干细胞改善卵巢功能研究。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划课题(2021YFC2700605),项目负责人:杨蕊;国家自然科学基金项目(82171632),项目负责人:杨蕊;北京大学临床医学+X青年专项(PKU2023LCXQ045),项目负责人:杨蕊
Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome
Li Jialin1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Zhang Yaodong1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Lou Yanru1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Yu Yang1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Yang Rui1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- 1State Key Laboratory of Female Fertility Promotion, Center for Reproductive Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China; 2National Clinical Research Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology (Peking University Third Hospital), Beijing 100191, China; 3Key Laboratory of Assisted Reproduction (Peking University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China; 4Beijing Key Laboratory of Reproductive Endocrinology and Assisted Reproductive Technology, Beijing 100191, China; 5National Clinical Key Specialty Construction Program, P. R. China (2023), Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2023-11-07Accepted:2024-01-27Online:2025-03-08Published:2024-06-28 -
Contact:Yang Rui, MD, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, State Key Laboratory of Female Fertility Promotion, Center for Reproductive Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China; National Clinical Research Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology (Peking University Third Hospital), Beijing 100191, China; Key Laboratory of Assisted Reproduction (Peking University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China; Beijing Key Laboratory of Reproductive Endocrinology and Assisted Reproductive Technology, Beijing 100191, China; National Clinical Key Specialty Construction Program, P. R. China (2023), Beijing 100191, China -
About author:Li Jialin, Master candidate, State Key Laboratory of Female Fertility Promotion, Center for Reproductive Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China; National Clinical Research Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology (Peking University Third Hospital), Beijing 100191, China; Key Laboratory of Assisted Reproduction (Peking University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100191, China; Beijing Key Laboratory of Reproductive Endocrinology and Assisted Reproductive Technology, Beijing 100191, China; National Clinical Key Specialty Construction Program, P. R. China (2023), Beijing 100191, China -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program, No. 2021YFC2700605 (to YR); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82171632 (to YR); Clinical Medicine Plus X Young Scholars Project of Peking University, No. PKU2023LCXQ045 (to YR)
摘要:
文题释义:
间充质干细胞分泌组:是指间充质干细胞来源的生物活性物质,包括可溶性成分和细胞外囊泡。可溶性成分有可溶血性蛋白质、核酸和脂质等。与移植间充质干细胞相比,应用间充质干细胞分泌组具有相似的治疗效果。胞外囊泡:是指不可再生的、膜包裹和大多数细胞均可释放到细胞外的一种颗粒。细胞外囊泡最初被认为是“垃圾车”,运输无用的物质到细胞外,现在细胞外囊泡被认为是细胞间通信的有效载体,被受体细胞摄取,可以调节受体细胞的生物学功能。
背景:大量研究证实间充质干细胞分泌组的治疗有效性与间充质干细胞相当,但对于其发挥作用的机制尚不清楚。
目的:总结近年来关于间充质干细胞分泌组的研究进展,探究其发挥治疗作用的分子机制,分析目前面临的问题并展望未来发展方向。
方法:以“exosomes,mesenchymal stem cells secrete,extracellular vesicles,mesenchymal stem cells,mechanism”为英文检索词检索PubMed数据库相关文献,排除与文章研究目的无关及重复性文章,同时结合文献追踪的方法,最终纳入符合要求的109篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①间充质干细胞分泌组通过递送遗传物质、免疫调节因子和生长因子等到靶细胞,通过激活靶细胞抗凋亡和促生存途径,调节血管生成,调节纤维化以及调节免疫微环境,促进组织修复和再生。②间充质干细胞分泌组在疾病治疗方面的潜力也得到证实,大量研究结果表明,间充质干细胞分泌组可以作为炎症疾病和退行性疾病的新型无细胞替代治疗方法。③近年来,经过工程化改造间充质干细胞分泌组发挥的治疗作用更加高效,但是由于间充质干细胞分泌组的异质性以及成分的复杂性,其发挥治疗作用的具体机制尚不清楚。④目前,仍需要进一步研究来明确间充质干细胞分泌组发挥治疗作用的关键靶点,并且未来应结合工程化和基因工程技术等,研发出具有创新性的特异型、增强型间充质干细胞分泌组。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3682-1495 (李佳林)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
李佳林, 张耀东, 娄艳茹, 于 洋, 杨 蕊. 间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522.
Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522.
用[10-11],因为胰岛素样生长因子基因沉默和血管内皮生长因子敲低限制了间充质干细胞对肾小管修复的作用。
间充质干细胞的免疫调节特性也支持间充质干细胞的旁分泌假说。间充质干细胞能够分泌一系列调节免疫反应的生物活性因子,进而调节多种T淋巴细胞活性,并能够改变树突状细胞、幼稚和效应T细胞以及自然杀伤细胞的细胞因子产生,从而产生抗炎表型[12-13]。
关于细胞外囊泡,最初被认为是“垃圾车”,最近被证明是细胞间通讯的重要介质。在2009年,实验证明注射间充质干细胞后急性肾损伤的恢复可能是由间充质干细胞释放的微粒介导的,并表明间充质干细胞来源的微粒可以激活肾小管上皮细胞的增殖程序;同时结果表明这些效应是RNA依赖性的,因为对微泡进行RNA酶预处理可以消除这种有效性[14]。在2010年,胞外囊泡被证明在细胞间转移微小RNA(microRNA,miRNA),并且转移的miRNA在受体细胞中显示RNA干扰效应[15]。在2008年,另一项关于心脏的研究表明在缺血/再灌注损伤的猪和小鼠模型中,使用间充质干细胞的条件培养基,梗死面积显著减小[16]。在2011年,同一研究小组证实,心脏保护作用是由间充质干细胞释放的外泌体介导的[17]。
旁分泌的一个关键组成部分是胞外囊泡,胞外囊泡可以通过3种机制调节靶细胞功能。首先胞外囊泡表达多种类型表面蛋白,可以通过直接刺激靶细胞来充当信号复合物;胞外囊泡与靶细胞膜融合后,还可以在细胞间转移受体或活性脂质;更重要的是,胞外囊泡被靶细胞内化后可以递送蛋白质以及核酸分子以调节靶细胞功能[18]。微泡和外泌体都表现出修复和再生特性,但外泌体是无细胞疗法中特征最清楚及使用最广泛的胞外囊泡。
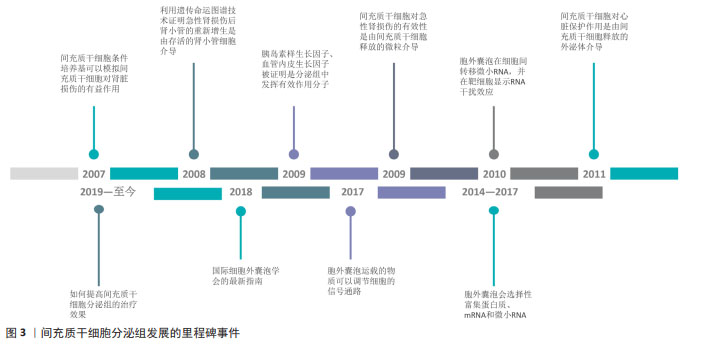
自间充质干细胞通过旁分泌机制发挥作用的假说提出之后,间充质干细胞分泌组的治疗潜力逐步被大量研究所证实,大量的研究证明了间充质干细胞分泌组对各种再生性疾病以及炎症性疾病具有治疗作用。为了确定间充质干细胞分泌组中的有效治疗因子,研究者利用蛋白质组学和基因组学的方法表征间充质干细胞分泌组的物质,并分析相关的生物学功能。在2014-2017年,研究者证明了间充质干细胞的胞外囊泡会选择性富集蛋白质、mRNA和miRNA。在2017年,研究者证明了胞外囊泡运载的物质可以调节细胞的信号通路,改变靶细胞功能[4]。在2018年,国际细胞外囊泡学会的最新指南,确定了胞外囊泡的定义以及制备标准[19]。近年来,研究领域关注于如何提高间充质干细胞分泌组的治疗效果,如通过对间充质干细胞或间充质干细胞来源的分泌组进行工程化改造。文章总结了间充质干细胞分泌组发展的里程碑事件,见图3。
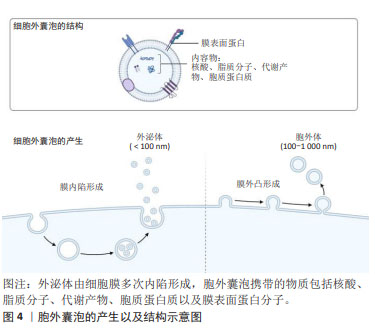
2.2 间充质干细胞分泌组 间充质干细胞分泌组,即间充质干细胞来源的生物活性物质,包括可溶性成分和细胞外囊泡。可溶性成分有可溶血性蛋白质、核酸、脂质等。细胞外囊泡指不可再生的、膜包裹、大多数细胞均可释放到细胞外的一种颗粒[19]。细胞外囊泡是细胞间通讯的有效载体,被受体细胞摄取,可以调节受体细胞的生物学功能[20]。在细胞外介质中存在的可溶性生物分子容易被水解和氧化,而胞外囊泡中的生物分子更稳定。因此,目前认为干细胞分泌组发挥治疗作用,主要是由胞外囊泡所介导的。细胞外囊泡的分类不断发生变化,通常来说,按照直径和来源可以分为外泌体(exosome)和胞外体(ectosome)[21]。外泌体是细胞膜多次内陷形成多泡体,多泡体与细胞内颗粒和细胞器沟通交流,最后形成成分异质性的外泌体。外泌体直径为40-160 nm(平均约100 nm)。胞外体是胞膜外凸形成,包括微粒(microvesicles)和细胞微体(microparticles)以及一些较大颗粒,直径为50 nm-1 μm。胞外囊泡携带的物质包括核酸、脂质分子、代谢产物、胞质蛋白质以及膜表面蛋白分子,见图4。
对于间充质干细胞来源的胞外囊泡,其携带的物质包括多潜能相关转录因子、抗炎症因子、细胞因子、mRNA、非编码RNA等,这些物质对于疾病和组织损伤有再生和修复功能[22-23]。间充质干细胞分泌组来源的胞外囊泡的一大特点——能够携带遗传物质,主要还是RNAs,并且其携带的RNAs能在细胞间传递,以影响受体细胞功能。胞外囊泡携带的遗传物质有mRNA和非编码RNA,如微小RNA(micro RNAs,miRs)。
间充质干细胞分泌组成分复杂,包括免疫调节因子、细胞生长因子、趋化因子、细胞黏附因子、脂质介质、激素、核酸、外泌体和微泡等,且各种生物活性因子之间相互影响,以不同的通路共同发挥作用[1]。有研究应用人工合成的单一因子,其治疗效果没有间充质干细胞分泌组治疗所表现出的多效性[24]。因此,可以明确的是,间充质干细胞分泌组治疗的有效性是多种生物活性因子有效协作共同发挥作用的结果。
2.3 间充质干细胞分泌组发挥治疗作用的分子机制 间充质干细胞分泌组及其成分都具有抑制有害免疫反应、促进组织修复和再生作用。并且研究证明了,间充质干细胞分泌组具有免疫调节、调节血管生成、抗凋亡、促进细胞再生和抗纤维化作用,以此发挥其促进组织再生和修复的作用效果。间充质干细胞分泌组中的生物活性物质包括遗传物质和非遗传物质,以下概述每类物质在免疫调节、促进再生和修复两方面的作用机制。
2.3.1 间充质干细胞分泌组中发挥免疫调节作用的物质 间充质干细胞条件培养基和胞外囊泡包含多种免疫调节因子,通过递送这些免疫调节因子到靶细胞,改变各种免疫细胞的表型和功能,以发挥免疫调节作用,抑制有害免疫反应。间充质干细胞分泌组包含的免疫调节因子有转化生长因子β、肝细胞生长因子、吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶1、白细胞介素10、白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂和前列腺素E2[6]。
间充质干细胞条件培养基或者外泌体通过释放转化生长因子β,依赖Jak-1/Stat-5途径导致受体细胞停滞于G1期,从而抑制辅助性CD4+T细胞和细胞毒性CD8+T细胞的增殖[25-26]。此外,转化生长因子β还可诱导初始CD4+T细胞表达FoxP3,而转变为免疫抑制性的Tregs细胞[27]。肝生长因子和转化生长因子β发挥协同作用抑制免疫反应,含有肝生长因子的间充质干细胞条件培养基和胞外囊泡通过诱导活化的外周单核细胞凋亡,从而抑制活化的外周血单核细胞的扩增[6]。
此外,应用间充质干细胞条件培养基,能抑制炎症反应细胞Th1,Th17的产生,促进免疫抑制性的Tregs细胞的增殖,从而使炎症部位产生免疫抑制微环境。间充质干细胞分泌组主要是通过改变树突状细胞的抗原呈递特性而产生抑制炎症反应细胞Th1,Th17的结果[28]。研究证明,间充质干细胞外泌体通过诱导小鼠树突状细胞产生免疫抑制和耐受性表型,而缓解T细胞驱动的炎症反应[29]。对于诱导Tregs细胞的增殖,除上述转化生长因子β以外,吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶1对于调节Tergs和Th1,Th17的比例也发挥重要作用[30]。在T细胞受体介导的静息Tregs细胞的活化过程,蛋白激酶B(PKB/Akt)和哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)通路的同时激活,诱导Tregs细胞转分化为促炎性的Th17细胞。相反,吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶1通过降解酪氨酸转为犬尿氨酸[31],诱导广泛控制非抑制蛋白2(general control nonderepressible 2,GCN2)的激活,抑制Akt/mTOR信号,进而抑制了Tregs细胞转化成炎性Th17细胞[32]。
白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂对于减轻皮肤的炎症,促进伤口的愈合具有重要作用[33]。并且白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂的分泌受局部炎症因子浓度影响,尤其是肿瘤坏死因子α,肿瘤坏死因子α促进间充质干细胞释放含有白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂的外泌体[33]。白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂通过竞争性抑制作用,阻止白细胞介素1与其相应受体结合,阻止白细胞介素1发挥作用,从而保护组织免受炎症诱导的损伤。
前列腺素E2在间充质干细胞分泌组介导的免疫抑制作用中扮演着重要角色。前列腺素E2发挥免疫抑制作用的机制是多方面的。首先,前列腺素E2直接抑制白细胞介素2的产生,同时减弱T细胞对于白细胞介素2的反应性。应用含有前列腺素E2的间充质干细胞条件培养基和外泌体,其释放的前列腺素E2抑制活化T细胞的克隆性扩增,缓解T细胞介导的炎症,并且有助于选择性激活巨噬细胞,阻止树突状细胞成熟,抑制NK细胞和NKT细胞的细胞毒性,以诱导免疫抑制微环境[6]。
除上述免疫调节因子外,间充质干细胞分泌组也通过传递非编码RNA到靶细胞,发挥免疫调节作用。在2010年,胞外囊泡被证明在细胞间转移miRNA ,并且转移的miRNA在受体细胞中显示RNA干扰效应[34-35]。在胞外囊泡中,外泌体包含的遗传信息主要是小RNA,如miRNA或者其他非编码RNA,而不是在细胞中更丰富存在的mRNA和核糖体RNA[36]。miRNAs被报道是间充质干细胞外泌体通过旁分泌机制发挥治疗作用的最重要成分,其中有一些具有重要的免疫调节特性,例如miR-21,miR-143,miR-146a,miR-147和miR-149等。此处简要阐述miR-146a介导的免疫调节作用,研究证明外泌体介导的miR-146a可转移到巨噬细胞,通过抑制靶蛋白抑制肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6和白细胞介素1受体相关激酶1的表达,下调核转录因子κB p65磷酸化。抑制核转录因子κB的信号通路,从而减少炎症因子的表达,以及抑制了巨噬细胞炎症性M1表型的产生。即巨噬细胞通过内化含miR-146a的外泌体,诱导其自身从M1型促炎表型极化为M2型抗炎表型[37]。近年来大多数研究关注于miRNA的免疫调节作用,但是也有两项研究发现其他非编码RNA也能介导免疫调节作用,如环状RNA mmu_circ_0001295和长链非编码RNA DANCR。
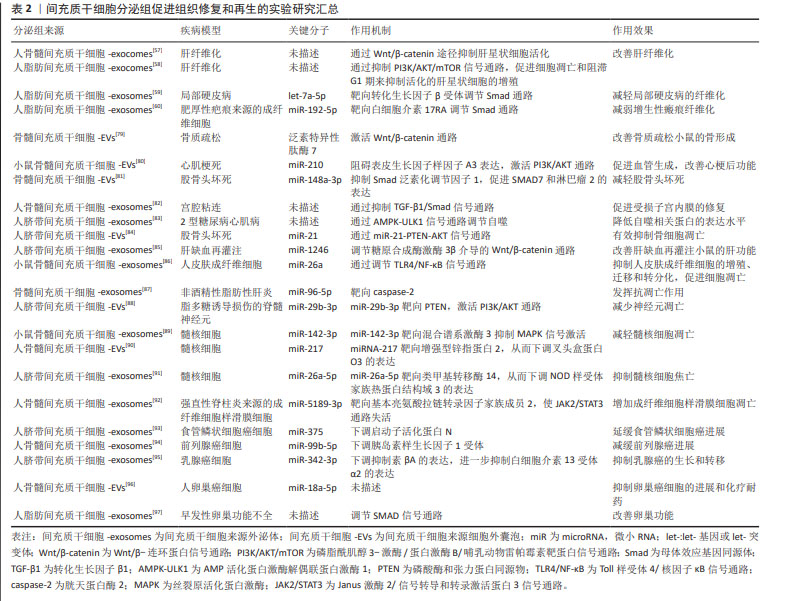
然而,还应该注意的是,间充质干细胞分泌组的免疫调节作用并不总是发挥着免疫抑制作用,间充质干细胞根据其所处环境的炎症状态,改变其分泌组谱和其免疫调节作用[38]。文章列举了间充质干细胞分泌组发挥免疫调节作用的具体实例[39-51],见表1。

2.3.2 间充质干细胞分泌组中促进组织修复和再生的物质 关于间充质干细胞条件培养基和胞外囊泡的促进组织再生和修复功能,大多数研究聚焦于RNA。首先讨论mRNA,mRNA在间充质干细胞分泌组中的丰度不高,研究也很少关注于此。不过仍然有一项研究证明了mRNA的转移与急性肺损伤恢复的相关性。间充质干细胞来源的胞外囊泡对急性肺损伤的有益作用部分是由角质细胞生长因子mRNA所介导的,即胞外囊泡中的mRNA转移到损伤的肺泡Ⅱ型上皮细胞,并翻译为蛋白质;肺泡上皮细胞中的角质细胞生长因子增高,此效应与间充质干细胞来源细胞外囊泡介导的免疫调节作用相协同,共同发挥对损伤肺的保护作用[52]。
非编码RNA,尤其是miRNAs被认为是间充质干细胞分泌组促进组织再生和修复作用的重要物质。虽然目前大多数研究认为RNAs是间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的重要介质,但是一项研究通过分析间充质干细胞来源外泌体中蛋白质和RNA的生物学浓度、生化功能和引发合适生化反应的潜力,推测外泌体可能通过它们含有的蛋白质而不是RNA发挥作用[53]。除了RNA,间充质干细胞分泌组还有多种促进组织修复和再生的物质,如生长因子。生长因子能够促进组织修复再生、伤口愈合和新生血管形成。金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂1和2、成纤维细胞生长因子6,7以及肝生长因子的浓度升高被认为是间充质干细胞条件培养基促进角膜上皮伤口愈合的有益因素[54]。含肝生长因子的间充质干细胞-培养基参与肝脏修复和再生[55]。在调节血管形成方面,间充质干细胞分泌组还有一些促血管生成因子,如血管内皮生长因子、β成纤维细胞生长因子、转化生长因子β、血小板衍生生长因子、血管生成素1、胎盘生长因子、白细胞介素6、单核细胞趋化蛋白1、表皮生长因子和肝细胞生长因子,这些促血管生成因子在使用间充质干细胞分泌组治疗缺血性疾病时发挥着有益作用[56]。
下文阐述间充质干细胞分泌组通过调节新生血管生成、调节纤维化、调节凋亡的机制,发挥促进组织修复和再生作用。组织的修复和再生与受损组织处的新生血管形成以及纤维化有着密切相关性。按照常规的病理学观点,理想的再生不应涉及纤维化,但实际情况中损伤通常伴有纤维化的存在。抑制过度纤维化是多种疾病的治疗思路,值得一提的是,间充质干细胞分泌组具有多靶点的抗纤维化作用,尤其是脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞分泌组的抗纤维化作用更显著[57-60]。促进损伤组织处的新生血管形成有利于其修复和再生。在调节受损组织处新生血管生成方面,间充质干细胞分泌组通过传递特定miRNA和生长因子可以介导血管形成。研究发现,促、抗血管形成因子的浓度受间充质干细胞所暴露的缺氧环境和炎症情况影响,当间充质干细胞在高浓度炎症因子的培养条件下,细胞会产生抗血管生成分子,以阻止炎症组织的白细胞的迁移[61]。而缺氧对调节血管生成因子的影响为,缺氧诱导间充质干细胞产生缺氧诱导因子1α,产生的缺氧诱导因子1α诱导血管内皮生长因子的产生,并且缺氧诱导因子1α对于血管内皮生长因子介导的促血管形成作用有重要的影响。在有关骨再生的一项研究中,来自间充质干细胞外泌体的血管内皮生长因子的促血管形成作用可以完全被缺氧诱导因子1α抑制剂所阻止[62]。
此外,间充质干细胞分泌组还通过调控损伤实质细胞的凋亡作用,促进其存活。具体表现为,间充质干细胞分泌组为基础的治疗通过显著降低促凋亡因素,如Bax和caspase-3的表达,增加实质细胞中抗凋亡因素,如Bcl-2的表达,防止实质细胞在持续炎症过程中损失[61]。间充质干细胞分泌组通过miRNA介导的抑制骨细胞、肝脏细胞、神经细胞、髓核细胞的凋亡,促进其存活,从而有利于再生。但是,有趣的是,在应用间充质干细胞分泌组治疗肿瘤细胞、强直性脊柱炎时,表现出截然相反的作用[63]。但间充质干细胞分泌组并不是抑制所有肿瘤细胞的凋亡,缺氧预处理骨髓间充质干细胞产生的细胞外囊泡通过递送miR-21-5p抑制非小细胞肺癌凋亡,从而促进非小细胞肺癌的发展[64]。一些证据表明,间充质干细胞的外泌体还能够诱导自噬激活,进而阻止细胞凋亡,从而促进细胞存活[1]。一项研究表明间充质干细胞外泌体通过递送色素上皮衍生因子增加自噬相关蛋白LC3的表达,并抑制caspase-3驱动的神经元凋亡,从而显著减少缺血/再灌注导致的脑损伤[65],这证实了诱导自噬激活对于间充质干细胞外泌体的抗凋亡作用至关重要。
2.3.3 间充质干细胞分泌组的异质性及应用前景 间充质干细胞的分泌组谱根据其组织来源、供体年龄以及体外培养的环境不同具有明显的异质性[66-68]。显而易见,分泌组的异质性导致其产生的治疗效果也必然不同[67-69]。
尽管间充质干细胞具有共同的表型,但根据起源不同,其分泌组谱有很大程度不同,治疗作用也不同[1]。基于间充质干细胞条件培养基的治疗显著降低了乳腺癌的生长,提高了患瘤小鼠的存活率。但这种治疗作用仅在接受人子宫颈间充质干细胞衍生的条件培养基的患瘤小鼠中观察到,而用人脂肪组织间充质干细胞衍生的条件培养基治疗没有出现抑制肿瘤生长的作用,分析两种间充质干细胞条件培养基成分,发现两者相比,人子宫颈间充质干细胞衍生的条件培养基含有更高水平的诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡的因子和更低水平的促进肿瘤生长的因子[61],这表明间充质干细胞分泌组的作用依赖于其细胞来源。最近,一项广泛的蛋白组学分析揭示了来自骨髓、脂肪组织和脐带的间充质干细胞分泌组的差异[70],未来应该针对不同疾病选择适合的种子细胞来源的分泌组。
间充质干细胞在体外培养和扩增的环境也影响其分泌组谱。在这种意义上,可以通过合适途径预处理间充质干细胞,以刺激用于特定治疗目的的分泌组的产生。通常情况,间充质干细胞应该培养在模拟目标治疗组织微环境的培养基条件,以改变间充质干细胞分泌组的成分为更有价值、更理想的组成,此操作过程为预处理间充质干细胞。常用来预处理间充质干细胞的方法有缺氧条件、暴露于药物化合物等[1]。近年来,一些团队开发了以三维方式培养的间充质干细胞的新方法,更好地模拟体内环境的,并且结果表明有助于增加间充质干细胞分泌的胞外囊泡产量。这些三维系统是使用含有细胞外基质成分的水凝胶,并且水凝胶采用多孔支架的形式,以更好模拟体内环境。研究表明与二维培养的细胞相比,在三维培养的间充质干细胞产生更多的细胞因子和生长因子[71]。
鉴于间充质干细胞分泌组的异质性,确定不同间充质干细胞分泌组的特征,有助于确定其在不同临床条件下的效果。同时,应该为间充质干细胞分泌组的制备建立可扩展的工程策略和标准化的操作流程,同时完善以间充质干细胞分泌组为基础治疗的质量控制与质量分析,以制造出安全有效且标准化的间充质干细胞分泌组。并且,随着越来越多的证据表明间充质干细胞分泌组在治疗疾病和组织再生方面的潜力,对间充质干细胞或间充质干细胞来源的胞外囊泡进行修饰,以提高其治疗效果的特异性及效率,即对间充质干细胞或间充质干细胞来源的胞外囊泡进行工程化改造,这是干细胞分泌组从实验室走向临床的必经之路。间充质干细胞或间充质干细胞来源的胞外囊泡的工程化改造,指通过各种技术对间充质干细胞或间充质干细胞来源的胞外囊泡进行修饰,如基因工程、表面修饰和组织工程,以提高其靶向归巢和治疗效率[72-74]。目前开展较为广泛的是,针对已经明确的治疗靶点,如白细胞介素10,通过基因工程技术获得白细胞介素10过表达的间充质干细胞来源的分泌组,从而提高其免疫调节作用,而有利于改善疾病。因为间充质干细胞来源的胞外囊泡无法自我复制,与细胞相比,胞外囊泡可以相对容易和安全地进行基因操作以携带特定的目标治疗货物。
间充质干细分泌组为基础的治疗,避免了细胞输注,具有更高的安全性。同时与干细胞为基础的方案相比,间充质干细胞分泌组容易获得,生产易扩大和优化,也便于储存和运输;并且评估培养基的安全性和有效性要简单得多,类似于常规药物制剂;如今,随着对间充质干细胞或间充质干细胞来源的胞外囊泡的工程化改造的开展,分泌组的治疗效率会进一步提高。因此间充质干细胞分泌组有望能够像药物一样在临床上广泛应用[1-6]。
2.4 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗潜力的临床研究 尽管在大量的动物模型中的结果证实了间充质干细胞分泌组的有效性,但仅有几项临床研究证实其再生和免疫调节潜力。目前仅注册了17项间充质干细胞分泌组治疗疾病的临床研究,其中有7项研究完成,10项研究正在进行,且研究集中在试探性治疗或者临床1期和2期,仅有一项使用间充质干细胞分泌组治疗COIVD-19重症病例的临床研究为3期临床试验。
目前报道的有关间充质干细胞分泌组治疗疾病的临床研究较少。间充质干细胞分泌组的使用有效改善了患有严重牙槽骨萎缩、骨关节炎患者、COVID-19肺炎和萎缩性痤疮瘢痕的临床症状[75-78],并且在间充质干细胞分泌组治疗组中均未报道不良反应。这表明了局部和全身注射间充质干细胞分泌组是安全的治疗方法。
一项使用间充质干细胞条件培养基进行牙槽骨再生的治疗,结果表明所有病例(8例)均有早期骨形成[75]。另外一项使用脐带间充质干细胞分泌组治疗骨关节炎的开放标签临床试验,结果表明治疗组比对照组膝关节疼痛减轻、生化结果好转且无不良反应[76]。一项使用脐带间充质干细胞衍生外泌体治疗COVID-19肺炎的雾化治疗研究,证明外泌体治疗促进了肺部病变的吸收,缩短了住院时间[77]。在美学研究中,仅报道有一项临床双盲试验表明,实验组在萎缩性痤疮瘢痕方面比点阵激光得到更好的改善[78]。
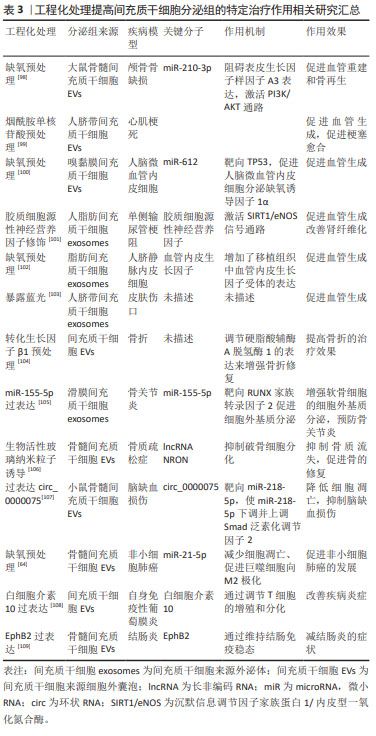
文章最后总结了间充质干细胞分泌组促进组织修复和再生的实验室研究进展[57-60,79-97],工程化处理提高间充质干细胞分泌组的特定治疗作用相关研究进展[98-109],见表2,3。
| [1] KUMAR LP, KANdoi S, MISRA R, et al. The mesenchymal stem cell secretome: a new paradigm towards cell-free therapeutic mode in regenerative medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:1-9. [2] KURIYAN AE, ALBINI TA, TOWNSEND JH, et al. Vision loss after intravitreal injection of autologous “stem cells” for AMD. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(11): 1047-1053. [3] GLASSBERG MK, MINKIEWICZ J, TOONKEL RL, et al. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis via intravenous delivery (AETHER) a phase I safety clinical trial. Chest. 2017; 151(5):971-981. [4] LI JK, YANG C, SU Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: a potential therapeutic strategy for acute kidney injury. Front Immunol. 2021;12:684496. [5] KIM HJ, KIM G, LEE J, et al. Secretome of stem cells: roles of extracellular vesicles in diseases, stemness, differentiation, and reprogramming. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;19(1):19-33. [6] HARRELL CR, FELLABAUM C, JOVICIC N, et al. Molecular mechanisms responsible for therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived secretome. Cells. 2019;8(5):467. [7] HAUSER PV, DE FAZIO R, BRUNO S, et al. Stem cells derived from human amniotic fluid contribute to acute kidney injury recovery. Am J Pathol. 2010;177(4):2011-2021. [8] BI B, SCHMITT R, ISRAILOVA M, et al. Stromal cells protect against acute tubular injury via an endocrine effect. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(9):2486-2496. [9] HUMPHREYS BD, VALERIUS MT, KOBAYASHI A, et al. Intrinsic epithelial cells repair the kidney after injury. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(3):284-291. [10] IMBERTI B, MORIGI M, TOMASONI S, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 sustains stem cell mediated renal repair. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(11): 2921-2928. [11] TöGEL F, ZHANG P, HU Z, et al. VEGF is a mediator of the renoprotective effects of multipotent marrow stromal cells in acute kidney injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(8b):2109-2114. [12] AGGARWAL S, PITTENGER MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105(4):1815-1822. [13] YAGI H, SOTO-GUTIERREZ A, PAREKKADAN B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: Mechanisms of immunomodulation and homing. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(6):667-679. [14] BRUNO S, GRANGE C, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(5):1053-1067. [15] COLLINO F, DEREGIBUS MC, BRUNO S, et al. Microvesicles derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs. PLoS One. 2010;5(7):e11803. [16] TIMMERS L, LIM SK, ARSLAN F, et al. Reduction of myocardial infarct size by human mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium. Stem Cell Res. 2007;1(2):129-137. [17] LAI RC, CHEN TS, LIM SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosome: a novel stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease. Regen Med. 2011;6(4):481-492. [18] BIANCONE L, BRUNO S, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(8):3037-3042. [19] THERY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. [20] RASHED MH, BAYRAKTAR E, HELAL GK, et al. Exosomes: from garbage bins to promising therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):538. [21] COCUCCI E, MELDOLESI J. Ectosomes and exosomes: shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25(6):364-372. [22] RATAJCZAK J, MIEKUS K, KUCIA M, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia. 2006;20(5):847-856. [23] CHEN B, SUN YJ, ZHANG JT, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes promote pressure ulcer healing in aged mice by rejuvenating senescent endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):142. [24] BARTEKOVA M, RADOSINSKA J, JELEMENSKY M, et al. Role of cytokines and inflammation in heart function during health and disease. Heart Fail Rev. 2018;23(5):733-758. [25] CRAIN SK, ROBINSON SR, THANE KE, et al. Extracellular vesicles from wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells suppress CD4 expressing T Cells through transforming growth factor beta and adenosine signaling in a canine model. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(3):212-226. [26] BRIGHT JJ, KERR LD, SRIRAM S. TGF-beta inhibits IL-2-induced tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of Jak-1 and Stat 5 in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1997;159(1):175-183. [27] FU S, ZHANG N, YOPP AC, et al. TGF-beta induces Foxp3+T-regulatory cells from CD4+CD25-precursors. Am J Transplant. 2004;4(10):1614-1627. [28] SHAHIR M, HASHEMI SM, ASADIRADL A, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on the induction of mouse tolerogenic dendritic cells. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(10):7043-7055. [29] HARRELL CR, JOVICIC N, DJONOV V, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and other extracellular vesicles as new remedies in the therapy of inflammatory diseases. Cells. 2019;8(12):1605. [30] ZHANG QY, FU L, LIANG YH, et al. Exosomes originating from MSCs stimulated with TGF- and IFN- promote Treg differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6832-6840. [31] VOLAREVIC V, GAZDIC M, MARKOVIC BS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived factors: Immuno-modulatory effects and therapeutic potential. Biofactors. 2017;43(5):633-644. [32] ACOVIC A, GAZDIC M, JOVICIC N, et al. Role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2018. doi: 10.1177/1756284818815334. [33] KOU XX, XU XT, CHEN C, et al. The Fas/Fap-1/Cav-1 complex regulates IL-1RA secretion in mesenchymal stem cells to accelerate wound healing. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(432):eaai8524. [34] PEGTEL DM, COSMOPOULOS K, THORLEY-LAWSON DA, et al. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107(14):6328-6333. [35] ZHANG YJ, LIU DQ, CHEN X, et al. Secreted Monocytic miR-150 enhances targeted endothelial cell migration. Mol Cell. 2010;39(1):133-144. [36] CHEN TS, LAI RC, LEE MM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell secretes microparticles enriched in pre-microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(1):215-224. [37] SONG YX, DOU H, LI XJ, et al. Exosomal miR-146a contributes to the enhanced therapeutic efficacy of interleukin-1-primed mesenchymal stem cells against sepsis. Stem Cells. 2017;35(5):1208-1221. [38] GAZDIC M, VOLAREVIC V, ARSENIJEVIC N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: a friend or foe in immune-mediated diseases. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015;11(2):280-287. [39] WANG D, XUE H, TAN J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes containing miR-539-5p inhibit pyroptosis through NLRP3/caspase-1 signalling to alleviate inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Res. 2022;71(7-8):833-846. [40] WANG X, LIU D, ZHANG X, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate sepsis-induced lung injury in mice by inhibiting the secretion of IL-27 in macrophages. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):18. [41] ZHANG C, LIAO W, LI W, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles alleviate salpingitis by promoting M1-to-M2 transformation. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1131701. [42] ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, ZHANG H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles alleviate traumatic hemorrhagic shock induced hepatic injury via IL-10/PTPN22-mediated M2 Kupffer cell polarization. Front Immunol. 2021;12:811164. [43] DONG B, WANG C, ZHANG J, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the inflammation of severe steroid-resistant asthma by reshaping macrophage polarization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):204. [44] CAO L, XU H, WANG G, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis by promoting M2 macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;72:264-274. [45] ZHANG L, YUAN J, KOFI WIREDU OCANSEY D, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate lymphangiogenesis via the miR-302d-3p/VEGFR3/AKT axis to ameliorate inflammatory bowel disease. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:109066. [46] ZHOU H, SHEN X, YAN C, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis of the knee in mice model by interacting with METTL3 to reduce m6A of NLRP3 in macrophage. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):322. [47] HE Y, ZHANG Z, YAO T, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells relieves diabetic retinopathy through a microRNA-30c-5p-dependent mechanism. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;190:109861. [48] CAO S, HUANG Y, DAI Z, et al. Circular RNA mmu_circ_0001295 from hypoxia pretreated adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) exosomes improves outcomes and inhibits sepsis-induced renal injury in a mouse model of sepsis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):6323-6331. [49] WU X, WANG Z, WANG J, et al. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells induce immune tolerance to mouse kidney transplantation via transporting LncRNA DANCR. Inflammation. 2022;45(1):460-475. [50] GUO L, LAI P, WANG Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells prevent contact hypersensitivity through the suppression of Tc1 and Th1 cells and expansion of regulatory T cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;74:105663. [51] DENG S, ZHOU X, GE Z, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;114:105564. [52] ZHU YG, FENG XM, ABBOTT J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of escherichia coli endotoxin- induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 2014;32(1):116-125. [53] TOH WS, LAI RC, ZHANG B, et al. MSC exosome works through a protein-based mechanism of action. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018;46(4):843-853. [54] BERMUDEZ MA, SENDON-LAGO J, EIRO N, et al. Corneal epithelial wound healing and bactericidal effect of conditioned medium from human uterine cervical stem cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(2):983-992. [55] ZAGOURA DS, ROUBELAKIS MG, BITSIKA V, et al. Therapeutic potential of a distinct population of human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells and their secreted molecules in mice with acute hepatic failure. Gut. 2012;61(6):894-906. [56] TAO HY, HAN ZB, HAN ZC, et al. Proangiogenic features of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic applications. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016:1314709. [57] RONG X, LIU J, YAO X, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):98. [58] ZHANG Z, SHANG J, YANG Q, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and remodeling choline metabolism. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):29. [59] WANG L, LI T, MA X, et al. Exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate localized scleroderma fibrosis by the let-7a-5p/TGF-βR1/Smad axis. J Dermatol Sci. 2023;112(1):31-38. [60] LI Y, ZHANG J, SHI J, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hypertrophic scar fibrosis by miR-192-5p/IL-17RA/Smad axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):221. [61] VIZOSO FJ, EIRO N, CID S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome: toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):1852. [62] ZHANG YT, HAO ZC, WANG PF, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through HIF-1 alpha-mediated promotion of angiogenesis in a rat model of stabilized fracture. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12570. [63] EIRO N, SENDON-LAGO J, SEOANE S, et al. Potential therapeutic effect of the secretome from human uterine cervical stem cells against both cancer and stromal cells compared with adipose tissue stem cells. Oncotarget. 2014;5(21):10692-10708. [64] REN W, HOU J, YANG C, et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by hypoxia pre-challenged mesenchymal stem cells promote non-small cell lung cancer cell growth and mobility as well as macrophage M2 polarization via miR-21-5p delivery. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):62. [65] HUANG X, DING J, LI YF, et al. Exosomes derived from PEDF modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulation of autophagy and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2018;371(1):269-277. [66] PIRES AO, MENDES-PINHEIRO B, TEIXEIRA FG, et al. Unveiling the differences of secretome of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, adipose tissue-derived stem cells, and human umbilical cord perivascular cells: a proteomic analysis. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(14):1073-1083. [67] ASSONI A, COATTI G, VALADARES MC, et al. Different donors mesenchymal stromal cells secretomes reveal heterogeneous profile of relevance for therapeutic use. Stem Cells Dev. 2017;26(3):206-214. [68] LEUNING DG, BEIJER NRM, DU FOSSE NA, et al. The cytokine secretion profile of mesenchymal stromal cells is determined by surface structure of the microenvironment. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7716. [69] CUNHA FF, MARTINS L, MARTIN PKM, et al. A comparison of the reparative and angiogenic properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from the bone marrow of BALB/c and C57/BL6 mice in a model of limb ischemia. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(4):86. [70] WANG ZG, HE ZY, LIANG S, et al. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of exosomes derived from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):511. [71] SU N, GAO PL, WANG K, et al. Fibrous scaffolds potentiate the paracrine function of mesenchymal stem cells: a new dimension in cell-material interaction. Biomaterials. 2017;141:74-85. [72] ZHU X, MA D, YANG B, et al. Research progress of engineered mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes and their application in autoimmune/inflammatory diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):71. [73] HAIDER KH, ARAMINI B. Mircrining the injured heart with stem cell-derived exosomes: an emerging strategy of cell-free therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):23. [74] REDONDO-CASTRO E, CUNNINGHAM CJ, MILLER J, et al. Changes in the secretome of tri-dimensional spheroid-cultured human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro by interleukin-1 priming. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):11. [75] KATAGIRI W, OSUGI M, KAWAI T, et al. First-in-human study and clinical case reports of the alveolar bone regeneration with the secretome from human mesenchymal stem cells. Head Face Med. 2016;12:5. [76] PARTAN RU, PUTRA KM, KUSUMA NF, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell secretome improves clinical outcomes and changes biomarkers in knee osteoarthritis. J Clin Med. 2023;12(22):7138. [77] CHU M, WANG H, BIAN L, et al. Nebulization therapy with umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for COVID-19 pneumonia. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(6):2152-2163. [78] HARTMAN N, LOYAL J, FABI S. Update on exosomes in aesthetics. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48(8):862-865. [79] WANG X, ZOU C, HOU C, et al. Extracellular vesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoporosis in mice through USP7-mediated YAP1 protein stability and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;217:115829. [80] WANG N, CHEN C, YANG D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles, via miR-210, improve infarcted cardiac function by promotion of angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017; 1863(8):2085-2092. [81] HUANG S, LI Y, WU P, et al. microRNA-148a-3p in extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppresses SMURF1 to prevent osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(19): 11512-11523. [82] YAO Y, CHEN R, WANG G, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells reverse EMT via TGF-β1/Smad pathway and promote repair of damaged endometrium. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):225. [83] ZHANG Z, CHEN L, CHEN X, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUCMSC-EXO) regulate autophagy through AMPK-ULK1 signaling pathway to ameliorate diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;632:195-203. [84] KUANG MJ, HUANG Y, ZHAO XG, et al. Exosomes derived from Wharton’s jelly of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce osteocyte apoptosis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats via the miR-21-PTEN-AKT signalling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2019; 15(9):1861-1871. [85] XIE K, LIU L, CHEN J, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells improve hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury via delivering miR-1246. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(24):3491-3501. [86] LI Q, HUANG P, CHEN W, et al. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells secreting miR-26a exosomes affecting high glucose-induced skin fibroblasts function by regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Inflamm Res. 2021;70(7):811-821. [87] EL-DERANY MO, ABDELHAMID SG. Upregulation of miR-96-5p by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes alleviate non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: emphasis on caspase-2 signaling inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;190:114624. [88] XIAO X, LI W, XU Z, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce lipopolysaccharide-induced spinal cord injury neuronal apoptosis by mediating miR-29b-3p/PTEN. Connect Tissue Res. 2022;63(6):634-649. [89] ZHU L, SHI Y, LIU L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes ameliorate nucleus pulposus cells apoptosis via delivering miR-142-3p: therapeutic potential for intervertebral disc degenerative diseases. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(14):1727-1739. [90] HAO Y, ZHU G, YU L, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells confer protection against intervertebral disc degeneration through a microRNA-217-dependent mechanism. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(11):1455-1467. [91] YUAN X, LI T, SHI L, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-26a-5p via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis through METTL14/NLRP3. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):91. [92] ZHANG Y, TU B, SHA Q, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes suppress miRNA-5189-3p to increase fibroblast-like synoviocyte apoptosis via the BATF2/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):6767-6780. [93] HE Z, LI W, ZHENG T, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes deliver microRNA-375 to downregulate ENAH and thus retard esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):140. [94] JIANG S, CHEN H, HE K, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes attenuated prostate cancer progression via the miR-99b-5p/IGF1R axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):2004-2016. [95] LIU Q, ZHANG J, LIU Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles extracted from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells carrying MicroRNA-342-3p inhibit the INHBA/IL13Rα2 axis to suppress the growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Transl Oncol. 2022;18:101333. [96] WANG X, JIANG L, LIU Q. miR-18a-5p derived from mesenchymal stem cells-extracellular vesicles inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and chemotherapy resistance. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):258. [97] HUANG B, LU J, DING C, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mesenchymal stem cells improve ovary function of premature ovarian insufficiency by targeting SMAD. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):216. [98] ZHUANG Y, CHENG M, LI M, et al. Small extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells promote vascularized bone regeneration through the miR-210-3p/EFNA3/PI3K pathway. Acta Biomater. 2022;150:413-426. [99] PU Y, LI C, QI X, et al. Extracellular vesicles from NMN preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells ameliorated myocardial infarction via miR-210-3p promoted angiogenesis. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(4):1051-1066. [100] GE L, XUN C, LI W, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxia-preconditioned olfactory mucosa mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis via miR-612. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):380. [101] CHEN L, WANG Y, LI S, et al. Exosomes derived from GDNF-modified human adipose mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate peritubular capillary loss in tubulointerstitial fibrosis by activating the SIRT1/eNOS signaling pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(20):9425-9442. [102] HAN Y, REN J, BAI Y, et al. Exosomes from hypoxia-treated human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis through VEGF/VEGF-R. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;109:59-68. [103] YANG K, LI D, WANG M, et al. Exposure to blue light stimulates the proangiogenic capability of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):358. [104] ZHOU Z, GUO C, SUN X, et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by tgf-β1-treated mesenchymal stem cells promote fracture healing by SCD1-regulated transference of LRP5. Stem Cells Int. 2023;2023:4980871. [105] WANG Z, YAN K, GE G, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-155-5p-overexpressing synovial mesenchymal stem cells prevent osteoarthritis via enhancing proliferation and migration, attenuating apoptosis, and modulating extracellular matrix secretion in chondrocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021;37(1):85-96. [106] YANG Z, LIU X, ZHAO F, et al. Bioactive glass nanoparticles inhibit osteoclast differentiation and osteoporotic bone loss by activating lncRNA NRON expression in the extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2022;283:121438. [107] LIU Y, LI YP, XIAO LM, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from bone mesenchymal stem cells carrying circ_0000075 relieves cerebral ischemic injury by competitively inhibiting miR-218-5p and up-regulating E3 ubiquitin ligase SMURF2. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(5):2801-2818. [108] LI Y, REN X, ZHANG Z, et al. Effect of small extracellular vesicles derived from IL-10-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells on experimental autoimmune uveitis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):100. [109] YU T, CHU S, LIU X, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from EphB2-overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate DSS-induced colitis by modulating immune balance. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):181. |
| [1] | 赖鹏宇, 梁 冉, 沈 山. 组织工程技术修复颞下颌关节:问题与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | 杨治航, 孙祖延, 黄文良, 万 喻, 陈仕达, 邓 江. 神经生长因子促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化并抑制肥大分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [3] | 胡涛涛, 刘 兵, 陈 诚, 殷宗银, 阚道洪, 倪 杰, 叶凌霄, 郑祥兵, 严 敏, 邹 勇. 过表达神经调节蛋白1的人羊膜间充质干细胞促进小鼠皮肤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [4] | 金 凯, 唐 婷, 李美乐, 谢裕安. 人脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基及外泌体对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [5] | 李帝均, 酒精卫, 刘海峰, 闫 磊, 李松岩, 王 斌. 明胶三维微球装载人脐带间充质干细胞修复慢性肌腱病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [6] | 刘 琪, 李林臻, 李玉生, 焦泓焯, 杨 程, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清促进3种细胞共培养体系中软骨细胞增殖和干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [7] | 艾克帕尔·艾尔肯, 陈晓涛, 吾凡别克·巴合提. 成骨诱导人牙周膜干细胞来源外泌体促进炎症微环境下人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [8] | 章镇宇, 梁秋健, 杨 军, 韦相宇, 蒋 捷, 黄林科, 谭 桢. 新橙皮苷治疗骨质疏松症的靶点及对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [9] | 吕丽婷, 于 霞, 张金梅, 高巧婧, 刘仁凡, 李 梦, 王 璐. 脑衰老与外泌体研究进程及现状的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [10] | 常金霞, 刘羽飞, 牛少辉, 王 唱, 曹建春. 巨噬细胞极化在组织修复过程中的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [11] | 何 波, 陈 文, 马岁录, 何志军, 宋 渊, 李金鹏, 刘 涛, 魏晓涛, 王威威, 谢 婧. 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的发病机制及治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [12] | 孙现娟, 王秋花, 张锦艺, 杨杨杨, 王文双, 张晓晴. 不同静电纺丝膜上骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附、增殖与成血管平滑肌分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [13] | 张 煜, 徐睿安, 方 蕾, 历龙飞, 刘姝妍, 丁凌雪, 王悦熹, 郭子琰, 田 丰, 薛佳佳. 梯度人工骨修复支架调控骨骼系统组织的修复与再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 846-855. |
| [14] | 王思凡, 何惠宇, 杨 泉, 韩祥祯. miRNA-378a过表达巨噬细胞株复合胶原蛋白海绵:抗炎及促进组织修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 789-799. |
| [15] | 郑伊桐, 汪永新, 刘 文, 阿木吉特, 秦 虎. 神经内镜下人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体鞘内移植修复脊髓损伤的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
不过,目前公认输注干细胞发挥治疗作用不是通过干细胞取代受损组织,而是通过其旁分泌作用。即输注的干细胞通过释放外泌体等胞外囊泡或者细胞因子,这些物质作用于靶细胞,改变靶细胞的功能,进而促进靶细胞的再生活性[4]。间充质干细胞的分泌组是指间充质干细胞来源的生物活性因子,包括可溶性蛋白质、核酸、脂类和细胞外囊泡。在实验室条件下培养间充质干细胞时,细胞会向培养基中释放一系列的生物活性因子,这种培养基被称为间充质干细胞条件培养基或间充质干细胞分泌组[1]。
间充质干细胞的条件培养基具有间充质干细胞的全分泌组,因此常被用于研究间充质干细胞分泌组的治疗效果。大量研究证实了间充质干细胞分泌组的有效治疗作用,即组织保护性作用(抗凋亡、抗炎症和抗纤维化)、免疫调节作用、促血管形成和组织再生以及抗肿瘤作用,且发挥着与移植间充质干细胞相似的疗效[5-6]。因此,基于干细胞分泌组治疗方案的有效性,以及其无细胞输注的特点规避了基于细胞治疗的安全问题,这种新型的利用分泌组的治疗方案成为再生医学领域的关注热点。虽然已有大量研究证实间充质干细胞分泌组治疗的有效性,但是由于间充质干细胞分泌组的异质性和复杂性,其从实验室走向临床的道路仍然漫长。
文章基于有关间充质干细胞分泌组治疗机制的最新研究,根据生物活性物质发挥作用的机制将间充质干细胞分泌组分为两大类,即调控免疫的物质和促进组织再生和修复的物质。目前虽然已经有一些关于间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的分子机制的综述,但是该文以间充质干细胞的异质性为出发点,结合近年来间充质干细胞分泌组的组织工程化进展,指出间充质干细胞分泌组的发展前景。分析间充质干细胞分泌组的成分,研究各成分的生物学作用,这有助于评估间充质干细胞分泌组治疗疾病的效力,这为基于分泌组治疗疾病的研究提供了一种研究思路,也符合当下精准医学的理念。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2023年11月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库至2023年11月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“exosomes,mesenchymal stem cells secrete,extracellular vesicles,mesenchymal stem cells,mechanism”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述和述评。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 在PubMed数据库检索,初步共检索到209篇。同时结合追溯法,以检索到的高质量文献为依据进行文献追踪。在中国知网数据库检索,共检索到39篇文献。
1.2 入组标准1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与间充质干细胞分泌组发挥治疗作用机制相关的研究;②权威杂志在同领域内近期发表的文章;③具有原创性、文章论点可靠的文章。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与主题无关的文章;②重复性研究;③缺乏可靠数据及不严谨的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 文献质量评价由第一作者独立完成。共检索到文献209篇,通过阅读文章题目、摘要进行初步筛选,排除与研究主题无关的文章、重复性研究及缺乏可靠数据的文章,纳入49篇研究性文章。同时结合文献追溯法,以纳入的文章为基础,利用文献所列的参考文献,逐一追查原文,以扩大文献信息范围,最终纳入PubMed数据库的109篇英文文献进行综述。见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 目前已经有文献对间充质干细胞分泌组进行综述,但是文章在详细介绍间充质干细胞分泌组在免疫调节和修复再生方面的分子机制的同时,基于间充质干细胞分泌组的异质性,结合近年来关于间充质干细胞分泌组工程化改造的内容为间充质干细胞分泌组的发展前景提出了见解。并且,文章的主题是间充质干细胞分泌组对各个器官发挥治疗作用的机制,其特点是所涵盖范围广泛,可以为不同专业的研究人员提供间充质干细胞分泌组的研究进展,便于研究者们对比分析间充质干细胞分泌组在不同疾病治疗的差异。最后,文章在论述间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的分子机制的同时,还补充了间充质干细胞分泌组纵向性的历史发展以及其在临床上的试探性应用情况。因此,该综述对间充质干细胞分泌组的研究进展进行了全面论述。
3.3 综述的局限性 由于文献筛选标准不同,存在主观因素引起的偏倚。同时文章所论述的内容为间充质干细胞分泌组对各个器官系统疾病发挥治疗作用的机制,所涵盖范围之广导致文章是按照各个系统共同的机制展开论述的,即是介绍间充质干细胞分泌组在免疫调节和修复再生两大方面的分子机制,而未针对单独疾病展开论述。不过文章已经囊括了间充质干细胞分泌组发挥治疗作用的绝大部分机制类型,因此虽然没有对特定一个疾病的研究进展详细论述,文章依旧能够给研究者提供间充质干细胞分泌组的研究进展,并且给不同研究方向研究者提供看待间充质干细胞分泌组的新视角。
3.4 综述的重要意义 该综述在间充质干细胞分泌组领域所发表的高质量文献中提取自己认为有价值的信息,对最新的研究现状、动态、技术、发现、观点进行归纳和总结。首先总结出间充质干细胞分泌组发展里程碑,帮助相关领域研究者快速了解间充质干细胞分泌组的前世今生;最后通过对分泌组的异质性、工程化的分泌组以及其临床应用3方面的阐述,展望了间充质干细胞分泌组的发展前景。通过阅读此综述,研究者能够在较短的时间内基本了解间充质干细胞分泌组的研究进展,为研究者节约大量时间,同时为后续在该领域的研究提供理论依据。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 间充质干细胞分泌组对多种疾病的有效性吸引着研究人员开展对此领域的研究。并且与细胞疗法相比,间充质干细胞分泌组具有更经济、安全的特点,是间充质干细胞有前景的替代方案。鉴于间充质干细胞分泌组的异质性,未来应针对不同疾病选择合适来源的间充质干细胞分泌组,确定具有最高治疗潜力的分泌组。同时,应建立特定疾病的间充质干细胞分泌组质量标准和控制体系,以提高大规模制备高纯度和明确治疗活性的间充质干细胞分泌组。更重要的是,深入研究间充质干细胞分泌组发挥治疗作用的机制,明确发挥作用的关键靶点,这有助于其成为关键的干预措施,并可能改善其治疗活性。未来应结合工程化和基因工程技术等,研发出具有创新性的特异型、增强型间充质干细胞分泌组。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
间充质干细胞分泌组:是指间充质干细胞来源的生物活性物质,包括可溶性成分和细胞外囊泡。可溶性成分有可溶血性蛋白质、核酸和脂质等。与移植间充质干细胞相比,应用间充质干细胞分泌组具有相似的治疗效果。#br#胞外囊泡:是指不可再生的、膜包裹和大多数细胞均可释放到细胞外的一种颗粒。细胞外囊泡最初被认为是“垃圾车”,运输无用的物质到细胞外,现在细胞外囊泡被认为是细胞间通信的有效载体,被受体细胞摄取,可以调节受体细胞的生物学功能。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
早期研究认为移植到体内的间充质干细胞通过再生、分化、取代损伤组织,而发挥治疗作用。然而目前研究表明,间充质干细胞的治疗作用得益于其产生的大量生物活性物质。大量研究证实间充质干细胞分泌组的治疗有效性与间充质干细胞相当,但对于其发挥作用的机制尚不清楚。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||