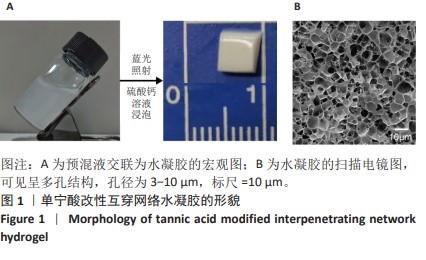
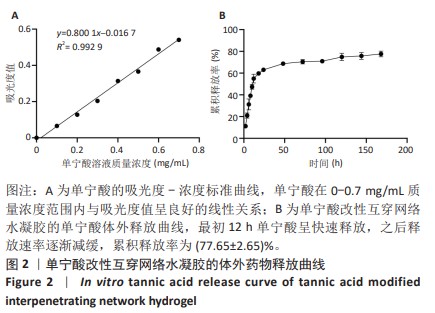
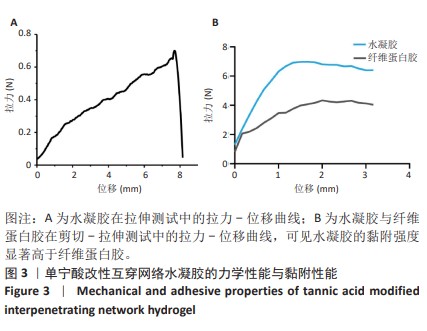
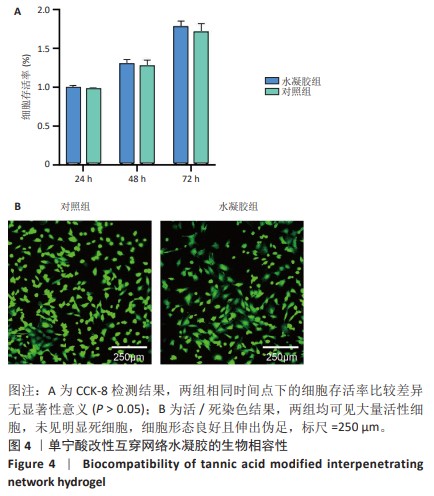
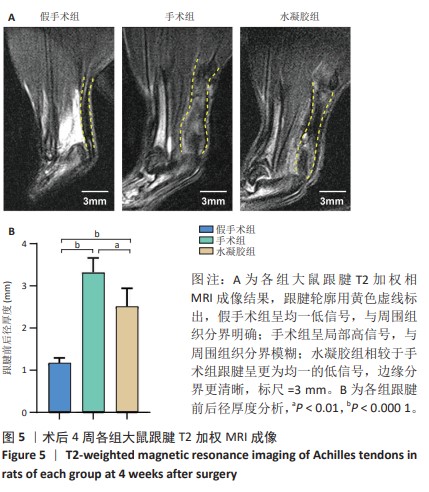
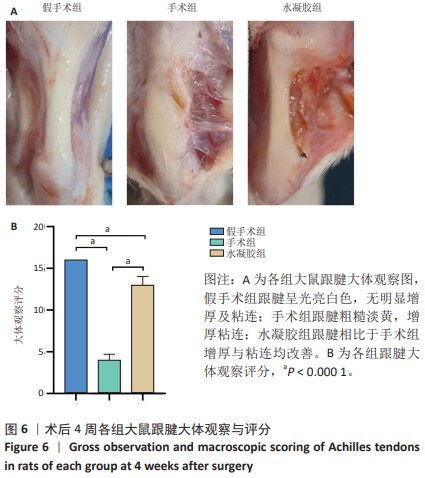
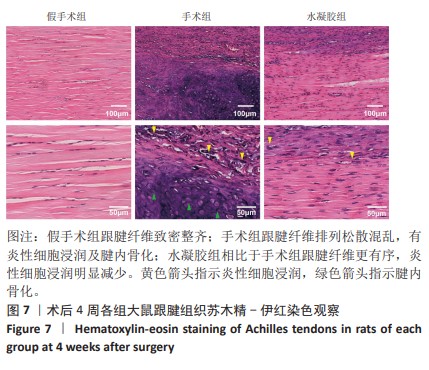
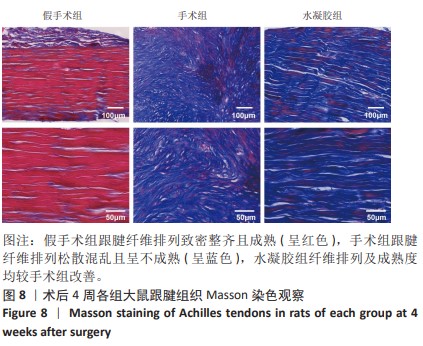
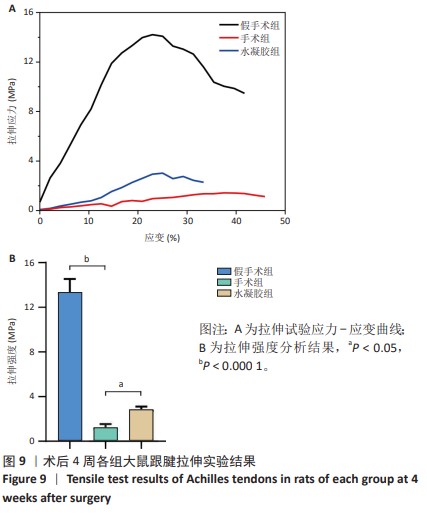
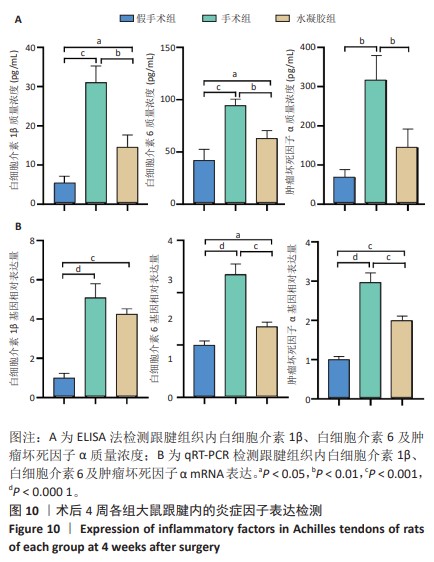
[1] MYHRVOLD SB, BROUWER EF, ANDRESEN TKM, et al. Nonoperative or Surgical Treatment of Acute Achilles’ Tendon Rupture. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1409-1420.
[2] HOLM C, KJAER M, ELIASSON P. Achilles tendon rupture--treatment and complications: a systematic review. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(1):e1-10.
[3] KULICK MI, BRAZLOW R, SMITH S, et al. Injectable Ibuprofen: Preliminary Evaluation of Its Ability to Decrease Peritendinous Adhesions. Ann Plast Surg. 1984;13(6):459.
[4] YAN Z, MENG X, SU Y, et al. Double layer composite membrane for preventing tendon adhesion and promoting tendon healing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;123:111941.
[5] CHOI HJ, CHOI S, KIM JG, et al. Enhanced tendon restoration effects of anti-inflammatory, lactoferrin-immobilized, heparin-polymeric nanoparticles in an Achilles tendinitis rat model. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;241:116284.
[6] TU T, SHEN Y, WANG X, et al. Tendon ECM modified bioactive electrospun fibers promote MSC tenogenic differentiation and tendon regeneration. Appl Mater Today. 2020;18:100495.
[7] CAI C, ZHANG X, LI Y, et al. Self-Healing Hydrogel Embodied with Macrophage-Regulation and Responsive-Gene-Silencing Properties for Synergistic Prevention of Peritendinous Adhesion. Adv Mater. 2022;34(5):e2106564.
[8] ZHANG Q, YANG Y, YILDIRIMER L, et al. Advanced technology-driven therapeutic interventions for prevention of tendon adhesion: Design, intrinsic and extrinsic factor considerations. Acta Biomater. 2021;124:15-32.
[9] JAFARI H, GHAFFARI-BOHLOULI P, NIKNEZHAD SV, et al. Tannic acid: a versatile polyphenol for design of biomedical hydrogels. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(31):5873-5912.
[10] GUO S, YAO M, ZHANG D, et al. One-Step Synthesis of Multifunctional Chitosan Hydrogel for Full-Thickness Wound Closure and Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(4):2101808.
[11] LI Q, XIAO W, ZHANG F, et al. Tannic acid-derived metal-phenolic networks facilitate PCL nanofiber mesh vascularization by promoting the adhesion and spreading of endothelial cells. J Mater Chem B. 2018; 6(18):2734-2738.
[12] NAGESH PKB, CHOWDHURY P, HATAMI E, et al. Tannic acid inhibits lipid metabolism and induce ROS in prostate cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):980.
[13] DHAND AP, GALARRAGA JH, BURDICK JA. Enhancing Biopolymer Hydrogel Functionality through Interpenetrating Networks. Trends Biotechnol. 2021;39(5):519-538.
[14] HU M, YANG J, XU J. Structural and biological investigation of chitosan/hyaluronic acid with silanized-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as an injectable reinforced interpenetrating network hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):607-619.
[15] ZHANG Y, DOU X, ZHANG L, et al. Facile fabrication of a biocompatible composite gel with sustained release of aspirin for bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;11:130-139.
[16] THANKAM FG, DIAZ C, CHANDRA I, et al. Hybrid interpenetrating hydrogel network favoring the bidirectional migration of tenocytes for rotator cuff tendon regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022;110(2):467-477.
[17] FAN X, WANG S, FANG Y, et al. Tough polyacrylamide-tannic acid-kaolin adhesive hydrogels for quick hemostatic application. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;109:110649.
[18] SMAJILAGIĆ A, ALJIČEVIĆ M, REDŽIĆ A, et al. Rat bone marrow stem cells isolation and culture as a bone formative experimental system. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2013;13(1):27-30.
[19] YANG S, SHI X, LI X, et al. Oriented collagen fiber membranes formed through counter-rotating extrusion and their application in tendon regeneration. Biomaterials. 2019;207:61-75.
[20] FREEDMAN BR, MOONEY DJ. Biomaterials to Mimic and Heal Connective Tissues. Adv Mater. 2019;31(19):e1806695.
[21] LI J, FENG X, LIU B, et al. Polymer materials for prevention of postoperative adhesion. Acta Biomater. 2017;61:21-40.
[22] ZHANG J, XIAO C, ZHANG X, et al. An oxidative stress-responsive electrospun polyester membrane capable of releasing anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory agents for postoperative anti-adhesion. J Control Release. 2021;335:359-368.
[23] EVROVA O, BÜRGISSER GM, EBNÖTHER C, et al. Elastic and surgeon friendly electrospun tubes delivering PDGF-BB positively impact tendon rupture healing in a rabbit Achilles tendon model. Biomaterials. 2020;232:119722.
[24] LIU C, TIAN S, BAI J, et al. Regulation of ERK1/2 and SMAD2/3 Pathways by Using Multi-Layered Electrospun PCL-Amnion Nanofibrous Membranes for the Prevention of Post-Surgical Tendon Adhesion. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:927-942.
[25] YANG Y, XU T, ZHANG Q, et al. Biomimetic, Stiff, and Adhesive Periosteum with Osteogenic-Angiogenic Coupling Effect for Bone Regeneration. Small. 2021;17(14):e2006598.
[26] COOMBES BK, BISSET L, VICENZINO B. Efficacy and safety of corticosteroid injections and other injections for management of tendinopathy: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 2010;376(9754):1751-1767.
[27] GUO Z, XIE W, LU J, et al. Tannic acid-based metal phenolic networks for bio-applications: a review. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(20):4098-4110.
[28] GRACEY E, BURSSENS A, CAMBRÉ I, et al. Tendon and ligament mechanical loading in the pathogenesis of inflammatory arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(4):193-207.
[29] CHOI S, CHOI Y, KIM J. Anisotropic Hybrid Hydrogels with Superior Mechanical Properties Reminiscent of Tendons or Ligaments. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(38):1904342.
[30] TANG Y, WANG Z, XIANG L, et al. Functional biomaterials for tendon/ligament repair and regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2022;9:rbac062.
[31] CHEN C, YANG H, YANG X, et al. Tannic acid: a crosslinker leading to versatile functional polymeric networks: a review. RSC Adv. 2022; 12(13):7689-7711.
[32] REN L, GONG P, GAO X, et al. Metal-phenolic networks acted as a novel bio-filler of a barrier membrane to improve guided bone regeneration via manipulating osteoimmunomodulation. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(48):10128-10138.
[33] WU F, NERLICH M, DOCHEVA D. Tendon injuries: Basic science and new repair proposals. EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(7):332-342.
[34] MILLAR NL, MURRELL GAC, MCINNES IB. Inflammatory mechanisms in tendinopathy - towards translation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(2): 110-122.
[35] JUNEJA SC, SCHWARZ EM, O’KEEFE RJ, et al. Cellular and molecular factors in flexor tendon repair and adhesions: a histological and gene expression analysis. Connect Tissue Res. 2013;54(3):218-226.
[36] VOLETI PB, BUCKLEY MR, SOSLOWSKY LJ. Tendon healing: repair and regeneration. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;14:47-71.
[37] HOU J, YANG R, VUONG I, et al. Biomaterials strategies to balance inflammation and tenogenesis for tendon repair. Acta Biomater. 2021;130:1-16.
[38] NICHOLS AEC, BEST KT, LOISELLE AE. The cellular basis of fibrotic tendon healing: challenges and opportunities. Transl Res. 2019;209: 156-168.
[39] JING W, XIAOLAN C, YU C, et al. Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of tannic acid. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;154:113561.
[40] CHEN Y, TIAN L, YANG F, et al. Tannic Acid Accelerates Cutaneous Wound Healing in Rats Via Activation of the ERK 1/2 Signaling Pathways. Adv Wound Care. 2019;8(7):341-354.
[41] XI Q, HOTH-HANNIG W, DENG S, et al. The effect of polyphenol-containing solutions on in situ biofilm formation on enamel and dentin. J Dent. 2020;102:103482.
[42] HU F, ZHANG R, GUO W, et al. PEGylated-PLGA Nanoparticles Coated with pH-Responsive Tannic Acid–Fe(III) Complexes for Reduced Premature Doxorubicin Release and Enhanced Targeting in Breast Cancer. Mol Pharmaceutics. 2021;18(6):2161-2173.
|