[1] HISANO G, HASHIZUME S, KOBAYASHI T, et al. Unilateral above-knee amputees achieve symmetric mediolateral ground reaction impulse in walking using an asymmetric gait strategy. J Biomech. 2021;115:110201.
[2] CEDIN L, KNOWLTON CB, WIMMER MA. Real-Time Musical Feedback From Pressure-Sensing Insoles For Asymmetric Gait Retraining. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2023.01.024
[3] KULMALA JP, PIIA H, JUSSI N, et al. Asymmetric gait results in symmetric muscular demands in affected versus unaffected side ankle and knee extensors in hemiplegic CP children. Gait Posture. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2020.07.137.
[4] PATCHAY S, GAHÉRY Y. Effect of asymmetrical limb loading on early postural adjustments associated with gait initiation in young healthy adults. Gait Posture. 2003;18(1):85-94.
[5] SATO SD, SCHLECHTER M, PRICE M, et al. Asymmetric shoe height induces reactive changes in gait kinematics but not kinetics in healthy young adults. Gait Posture. 2023;104:70-76.
[6] BANKS JJ, UMBERGER BR, BOYER KA, et al. Lower back kinetic demands during induced lower limb gait asymmetries. Gait Posture. 2022;98: 101-108.
[7] 杨雅琴,王拥军,冯涛,等.功能性步态评价的临床应用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2011,26(12):1186-1189.
[8] FABBRI I, BETTI F, TEDESCHI R. Gait quality after robot therapy compared with physiotherapy in the patient with incomplete spinal cord injured: A systematic review. eNeurologicalSci. 2023;31:100467.
[9] 林英杰,吴建宁,林丽辉.人体步态对称性量化评价方法研究进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2019,38(2):222-232.
[10] 张子华,纪仲秋,庞博,等.老年人步态稳定性,步态评价与跌倒风险的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(7):793-796.
[11] VIENNE A, BARROIS RP, BUFFAT S, et al. Inertial Sensors to Assess Gait Quality in Patients with Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review of Technical and Analytical Challenges. Front Psychol. 2017;8:817.
[12] 吴建宁,伍滨.构建基于小波熵的自训练半监督支持向量机分类模型评价老年人步态[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2013, 32(5):588-594.
[13] YAMAGATA M, NAGAI R, MORIHIRO K, et al. Relation between the kinematic synergy controlling swing foot and visual exploration during obstacle crossing. J Biomech. 2023;157:111702.
[14] HAGOORT I, VUILLERME N, HORTOBÁGYI T, et al. Age and walking conditions differently affect domains of gait. Hum Mov Sci. 2023;89: 103075.
[15] JOHNSON K, LIANG H. Effect of unilateral ankle loading on gait symmetry in young adults. Gait Posture. 2023;104:120-125.
[16] YU X, WANG HJ, ZHEN QX, et al. Added forearm weights for gait pattern normalization in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Neurosci. 2023;114:17-24.
[17] YANG HS, JAMES CR, ATKINS LT, et al. Exploration of arm weight effects on hemiparetic stroke participants’ gait performance. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2023;102:105873.
[18] JEON J, KWON SY, LEE YM, et al. Influence of the Hawthorne effect on spatiotemporal parameters, kinematics, ground reaction force, and the symmetry of the dominant and nondominant lower limbs during gait. J Biomech. 2023;152:111555.
[19] 张宇.基于步态质量指数和雷达图的患者步态评定方法[J].清华大学学报(自然科学版),2008,48(5):785-788.
[20] SHIN SY, LEE RK, SPICER P, et al. Does kinematic gait quality improve with functional gait recovery? A longitudinal pilot study on early post-stroke individuals. J Biomech. 2020;105:109761.
[21] HÖSL M, SCHUPFINGER A, KLICH L, et al. Relationship between kinematic gait quality and caregiver-reported everyday mobility in children and youth with spastic Cerebral Palsy. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2023;42:88-96.
[22] 张宇.运动障碍患者康复评定指标与步态病症诊断方法的研究[D].北京:清华大学,2007.
[23] 杨义勇,王人成,郝智秀,等.人体步态质量主元量化评定方法的研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2005,22(6):1100-1103.
[24] 王人成,张美芹.人体步态时相对称性评价指标的对比研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2011,26(10):957-959.
[25] 吴存书,詹晓萱,赵思怡,等.运用雷达图对脊髓损伤步态训练进行系统评价再评价的质量和效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(14):2287-2296.
[26] ENVELOPE TA. On the fractal geometry of gait dynamics in different neuro-degenerative diseases - ScienceDirect. Phys Med. 2022;14(3): 100050.
[27] ENDO T, SHIRADO O, TOMINAGA R, et al. Maximum gait speed and lumbar spinal mobility can affect quality of life in elderly women with lumbar kyphosis. North Am Spine Soc J. 2022;9:100100.
[28] 朱晓兰,赵芳,周兴龙.老年人步态特征的分析及其评价系统的初步建立[J].北京体育大学学报,2006,29(2):201-203.
[29] LECOMTE C, STARKER F, GUÐNADÓTTIR EÞ, et al. Functional joint center of prosthetic feet during level ground and incline walking. Med Eng Phys. 2020;81:13-21.
[30] THORNING M, NIELSEN HH, FRICH LH, et al. Gait quality and function after fampridine treatment in patients with multiple sclerosis - A prospective cohort study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2022;100: 105826.
[31] PAU M, COGHE G, ATZENI C, et al. Novel characterization of gait impairments in people with multiple sclerosis by means of the gait profile score. J Neurol Sci. 2014;345(1-2):159-163.
[32] PAU M, CORONA F, COGHE G, et al. Quantitative assessment of the effects of 6 months of adapted physical activity on gait in people with multiple sclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil. 2018;40(2):144-151.
[33] GASSNER H, LIST J, MARTINDALE CF, et al. Functional gait measures correlate to fear of falling, and quality of life in patients with Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia: A cross-sectional study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021;209:106888.
[34] HORST F, SLIJEPCEVIC D, SIMAK M, et al. Modeling biological individuality using machine learning: A study on human gait. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023;21:3414-3423.
[35] HASAN MM, MUSTAFA HA. Learning view-invariant features using stacked autoencoder for skeleton-based gait recognition. IET Computer Vision. 2021;(7):15.
[36] PAPAVASILEIOU I, QIAO Z, ZHANG C, et al. GaitCode: Gait-based Continuous Authentication Using Multimodal Learning and Wearable Sensors. Smart Health. 2020;19:100162.
[37] HUANG DD, WU GF, LUO X, et al. Value of muscle quality, strength and gait speed in supporting the predictive power of GLIM-defined malnutrition for postoperative outcomes in overweight patients with gastric cancer. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(6):4201-4208.
[38] FUJITA K, HIYAMA T, WADA K, et al. Machine learning-based muscle mass estimation using gait parameters in community-dwelling older adults: A cross-sectional study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2022;103: 104793. |


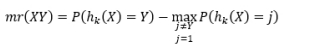 其中,X为随机向量,Y为正确分类的向量,j为不正确分类的向量,P(hk (X)=Y)表示预测正确的概率,
其中,X为随机向量,Y为正确分类的向量,j为不正确分类的向量,P(hk (X)=Y)表示预测正确的概率,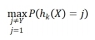 表示判断错误的其他分类概率的最大值。
表示判断错误的其他分类概率的最大值。