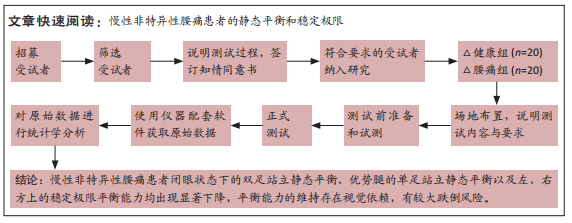
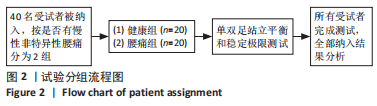
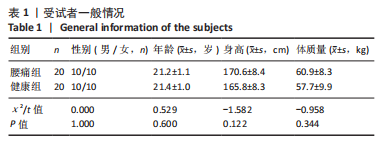
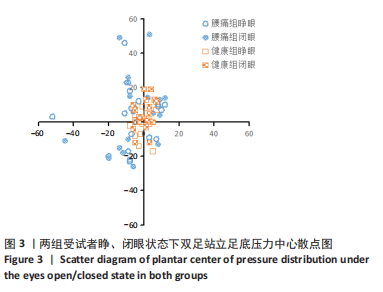
[1] MI J, YE J, ZHAO X, et al. Effects of lumbosacral orthoses on postural control in individuals with or without non-specific low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2018; 27(1):180-186.
[2] MAHER C, UNDERWOOD M, BUCHBINDER R. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet. 2017;389(10070):736-747.
[3] WERTLI MM, STEURER J. Bedeutung prognostischer Faktoren bei unspezifischen, lumbalen Rückenschmerzen. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2017; 106(10):527-531.
[4] 刘红,侯美金,黄武杰,等.基于步态轮廓评分分析青年慢性非特异性腰痛患者的步态模式[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2020,42(3):232-238.
[5] BRUMAGNE S, JANSSENS L, JANSSENS E, et al. Altered postural control in anticipation of postural instability in persons with recurrent low back pain. Gait Posture. 2008;28(4):657-662.
[6] NOGUEIRA JF, CARRASCO AC, PELEGRINELLI ARM, et al. Posturography Comparison and Discriminant Analysis Between Individuals With and Without Chronic Low Back Pain. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2020;43(5):469-475.
[7] CAFFARO RR, FRANÇA FJ, BURKE TN, et al. Postural control in individuals with and without non-specific chronic low back pain: a preliminary case-control study. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(4):807-813.
[8] BROPHY R, SILVERS HJ, GONZALES T, et al. Gender influences: the role of leg dominance in ACL injury among soccer players. Br J Sports Med. 2010; 44(10):694-697.
[9] SUNG PS, SPRATT KF, WILDER DG. A possible methodological flaw in comparing dominant and nondominant sided lumbar spine muscle responses without simultaneously considering hand dominance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(17):1914-1922.
[10] 中国康复医学会脊柱脊髓专业委员会专家组.中国急/慢性非特异性腰背痛诊疗专家共识[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(12):1134-1138.
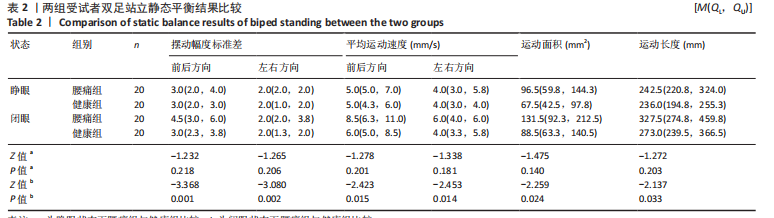
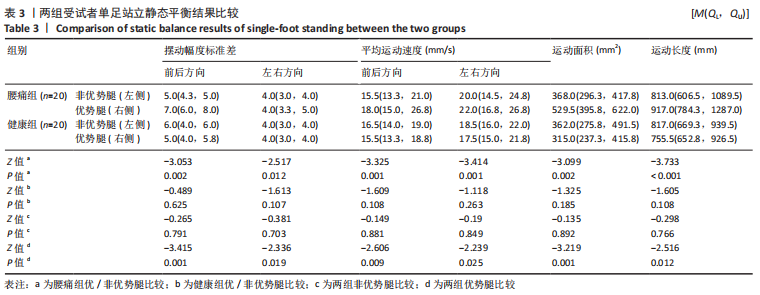
[11] 高敏,梁英,王萍芝,等.动静态平衡仪评定踝关节稳定性的信效度研究[J].中国康复,2015,30(6):451-454.
[12] BICKLEY C, LINTON J, SULLIVAN E, et al. Comparison of simultaneous static standing balance data on a pressure mat and force plate in typical children and in children with cerebral palsy. Gait Posture. 2019;67:91-98.
[13] 王露,蔡蕊琳,张宽,等.肥胖儿童短时间静态平衡特征[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(6):957-962.
[14] 罗卫,黄志锐,曹志贤,等.颈性眩晕患者的静态平衡和稳定极限特征[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022,28(2):165-169.
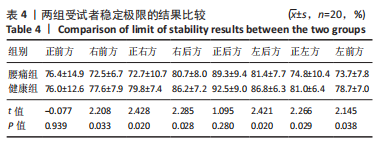
[15] JOHANSSON J, JAROCKA E, WESTLING G, et al. Predicting incident falls: Relationship between postural sway and limits of stability in older adults. Hum Mov Sci. 2019;66:117-123.
[16] QASEEM A, WILT TJ, MCLEAN RM, et al. Noninvasive Treatments for Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Low Back Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(7):514-530.
[17] OZCAN KAHRAMAN B, KAHRAMAN T, KALEMCI O, et al. Gender differences in postural control in people with nonspecific chronic low back pain. Gait Posture. 2018;64:147-151.
[18] DA SILVA RA, VIEIRA ER, FERNANDES KBP, et al. People with chronic low back pain have poorer balance than controls in challenging tasks. Disabil Rehabil. 2018;40(11):1294-1300.
[19] SAGGINI R, ANASTASI GP, BATTILOMO S, et al. Consensus paper on postural dysfunction: recommendations for prevention, diagnosis and therapy. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021;35(2):441-456.
[20] KUO YL, HUANG KY, CHIANG PT, et al. Steadiness of Spinal Regions during Single-Leg Standing in Older Adults with and without Chronic Low Back Pain. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0128318.
[21] SHIGAKI L, VIEIRA ER, DE OLIVEIRA GIL AW, et al. Effects of Holding an External Load on the Standing Balance of Older and Younger Adults With and Without Chronic Low Back Pain. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017; 40(4):284-292.
[22] ZHANG C, ZHANG Z, LI Y, et al. Pain Catastrophizing Is Related to Static Postural Control Impairment in Patients with Nonspecific Chronic Low Back Pain: A Cross-Sectional Study. Pain Res Manag. 2020;2020:9629526.
[23] BUSSEY MD, ALDABE D, SHEMMELL J, et al. Anticipatory postural control differs between low back pain and pelvic girdle pain patients in the absence of visual feedback. Hum Mov Sci. 2020;69:102529.
[24] CAO Z, ZHU C, ZHOU Y, et al. Risk factors related balance disorder for patients with dizziness/vertigo. BMC Neurol. 2021;21(1):186.
[25] MEIER ML, STÄMPFLI P, VRANA A, et al. Neural Correlates of Fear of Movement in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain vs. Pain-Free Individuals. Front Hum Neurosci. 2016;10:386.
[26] SIPKO T, KUCZYŃSKI M. Intensity of chronic pain modifies postural control in low back patients. Eur J Pain. 2013;17(4):612-620.
[27] TEICHTAHL AJ, URQUHART DM, WANG Y, et al. Fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles is associated with low back pain, disability, and structural abnormalities in community-based adults. Spine J. 2015;15(7):1593-1601.
[28] MUEHLBAUER T, SCHWIERTZ G, BRUECKNER D, et al. Limb Differences in Unipedal Balance Performance in Young Male Soccer Players with Different Ages. Sports (Basel). 2019;7(1):20.
[29] SŁOMKA KJ, PAWŁOWSKI M, MICHALSKA J, et al. Effects of 8-Week Complex Balance Training in Young Alpine Skiers: A Pilot Study. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:6804534. |