1.1 设计 样品观察性实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2020年8月至2021年6月在天津市天士力研究院实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验用仪器 TENSOR 27傅里叶变换红外光谱分析仪(德国布鲁克);DSC 3+型差示扫描量热仪(瑞士梅特勒-托利多集团);S-3500N型扫描电子显微镜(日本日立);XPR 105型十万分之一天平(瑞士梅特勒-托利多集团);Sorvall Legend Micro 17小型高速冷冻离心机、GenpureXCAD超纯水机、PHARMA11双螺杆热熔挤出机、U3000高效液相色谱仪(美国赛默飞世尔科技有限公司);BPC-250F恒温箱(上海一恒科学仪器有限公司);Qtrap 5500串联三重四级杆质谱仪(美国赛默飞世尔科技公司);KH-851涡旋混合器(上海环宇仪器厂);WIZARD 2.0冷冻干燥机(美国VIRTIS)。
1.3.2 实验用药物与试剂 醋酸亮丙瑞林(杭州信海医药科技有限公司,批号:P20112701,纯度99.63%);聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物(济南岱罡生物工程有限公司,聚乳酸/乙醇酸=50/50);醋酸丙氨瑞林(上海吉尔生化有限公司,批号:P191008-LR061703,纯度≥98%);磷酸二氢钾(分析纯,天津市大茂化学试剂厂);磷酸氢二钠(分析纯,天津市华东试剂厂);柠檬酸、磷酸(分析纯,天津市致远化学试剂有限公司);叠氮化钠(分析纯,天津市大茂化学仪器供应站);甲醇、甲酸、丙酸、乙腈、四氢呋喃为色谱纯(德国默克公司)。
1.3.3 实验动物 10周龄雄性SD大鼠,SPF级,体质量240-260 g,购于北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司。动物许可证号:SCXK(京)2016-0006。普通饲料饲养,自由进食,饲养环境温度20-25℃、相对湿度40%-70%、12 h光照/12 h黑暗交替。动物实验获得天津天士力实验动物管理及福利伦理委员会批准。实验过程遵循了国际兽医学编辑协会《关于动物伦理与福利的作者指南共识》和本地及国家法规。
1.4 方法
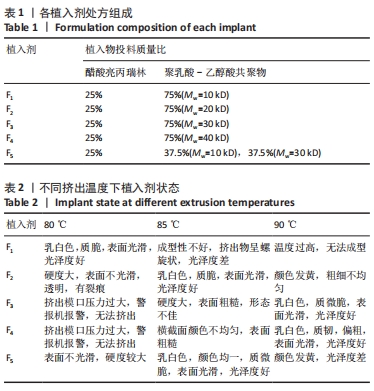
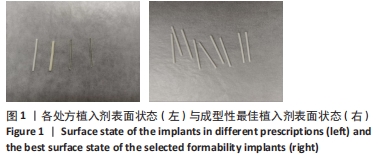
1.4.1 醋酸亮丙瑞林植入剂的制备 采用热熔挤出技术制备醋酸亮丙瑞林缓释植入剂[17-19],不同处方中,醋酸亮丙瑞林的质量分数保持25%不变[20]。按照表1植入物投料比分别称取醋酸亮丙瑞林及聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物于玛瑙研钵中,进行物理研磨均匀混合后过80目筛。热熔挤出技术工序的温度主要由载体基质的玻璃化转变温度(Tg)决定,通常在高于载体基质Tg 20-40 ℃的温度下进行挤出[21],通过对药物和不同辅料熔点和热稳定性分析,分别选择80,85,90 ℃作为挤出温度,其他参数固定,模口直径、加料速度、螺杆转速分别为1 mm、40 r/min、50 r/min。根据挤出物的表面状态确定最佳挤出温度,结果见表2,图1。根据不同处方的辅料特性选用适宜挤出温度,并于室温冷却后收集样品,并将各处方制剂剪切成规格为每支(16.0±0.5) mg备用。
1.4.2 植入剂的理化性质表征
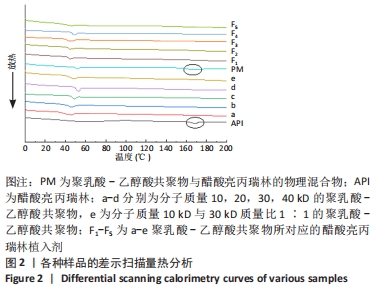
差示扫描量热分析:分别取活性药物成分醋酸亮丙瑞林和各处方中空白载体聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物及活性药物成分和聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物的物理混合物适量,进行药物及辅料的热性能考察。取各处方制剂适量,并与活性药物成分、聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物及其物理混合物的差示扫描量热图谱作比较。测定条件:气氛为氮气,升温速度为10 ℃/ min,温度范围为0-200 ℃。
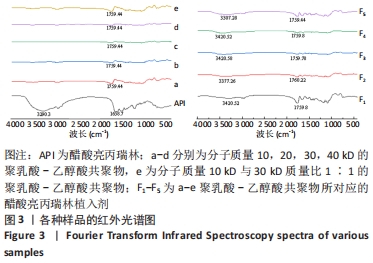
红外光谱分析:分别取活性药物成分醋酸亮丙瑞林和各处方中空白载体聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物适量,用溴化钾压片制备样品,进行红外光谱定性表征分析。取各处方制剂适量,并与活性药物成分、聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物的红外光谱图谱作比较。波数范围为4 000-500 cm-1,分辨率为4 cm-1。
1.4.3 体外分析方法的建立
检测波长的确定:取醋酸亮丙瑞林原料药适量,用85%乙腈水溶液溶解并稀释,配制成质量浓度为0.2 g/L的溶液,以85%乙腈水溶液作为空白对照,按照紫外分光光度法(中国药典 2020 版四部通则0401)在200-400 nm波长范围内进行全波长扫描,结果显示亮丙瑞林在220 nm处有最大吸收波长,故选择220 nm作为含量测定检测波长。
高效液相色谱法的建立:参照高效液相色谱法(中国药典2020年版四部通则0512)检测,确定亮丙瑞林含量测定的高效液相色谱方法如下:色谱柱类型:Waters Spherisorb ODS1(4.6*250 mm,5 µm);流动相:取磷酸二氢钾2.72 g,加水520 mL使溶解,加甲醇480 mL,混匀,用磷酸调节pH值至3.0;流速:1.8 mL/min;紫外检测波长:220 nm;柱温:35 ℃;进样量:10 µL。
方法专属性:取空白辅料约12 mg,精密称定,置20 mL容量瓶中,用85%乙腈水溶液稀释至刻度;取醋酸亮丙瑞林植入剂适量,精密称定,用85%乙腈水溶液溶解并定量配制成质量浓度为0.2 g/L的供试品溶液,空白溶液为85%乙腈水溶液。按高效液相色谱条件进样,结果表明空白溶液及空白辅料在亮丙瑞林的出峰位置无干扰。
标准曲线的制备:精密称取醋酸亮丙瑞林对照品适量,用85%乙腈水溶液溶解并定量配制成质量浓度为0.4 g/L的储备液。分别精密量取该储备液4,4.5,5,5.5,6 mL置于5个不同的10 mL容量瓶中,用85%乙腈水溶液稀释至刻度,摇匀,即得0.16,0.18,0.20,0.22,0.24 g/L的线性标准溶液。按高效液相色谱条件进样,以质量浓度(C)为横坐标,对应峰面积(A)为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线,并进行线性回归分析,得回归方程为 A=12 726.519 2C-31.959 9(R2=0.999 9)。结果表明醋酸亮丙瑞林质量浓度在0.16-0.24 g/L内线性关系良好。
精密度:取0.20 g/L线性标准溶液,连续进样6针,根据峰面积计算相对标准偏差,结果显示相对标准偏差为0.61%,说明方法重复性良好。取醋酸亮丙瑞林对照品适量,精密称定,用85%乙腈水溶液溶解并定量配制成质量浓度为0.2 g/L的对照品溶液,同法配制2份。取醋酸亮丙瑞林植入剂适量,精密称定,用85%乙腈水溶液溶解并定量配制成质量浓度为0.2 g/L的供试品溶液,同法配制6份,按高效液相色谱条件进样,外标法计算相应含量及相对标准偏差值,结果显示相对标准偏差为2.60%,说明方法重复性良好。用相同色谱条件于不同时间、不同人员及不同仪器再次进行重复性实验,计算相对标准偏差值,结果显示相对标准偏差为2.49%,中间精密度良好。综上所述,该方法精密度良好。
回收率:取0.16,0.20,0.24 g/L低、中、高质量浓度的标准溶液,按高效液相色谱条件进样,计算亮丙瑞林的回收率。每个质量浓度平行测定3 次,结果得亮丙瑞林的低、中、高质量浓度的平均回收率分别为 99.24%,99.50%和 99.66%,相对标准偏差为0.26%,说明该方法回收率良好。
1.4.4 植入剂载药量测定 从制备的F1-F5处方植入剂中随机选取10份植入剂样品,精密称定,置于50 mL容量瓶中,加少量 85%乙腈水溶液溶解,随后定容至刻度,摇匀,即得。按高效液相色谱条件进样,计算亮丙瑞林植入剂的含量。
1.4.5 体外药物释放实验 释放介质采用pH=7.4的PBS用于模拟皮下生理环境[22]。释放介质配制方法:无水磷酸氢二钠25.8 g,柠檬酸1.92 g,叠氮化钠0.2 g,加脱气水溶解并稀释至1 000 mL,搅拌至充分溶解,用无水磷酸氢二钠或柠檬酸调节pH值至7.4。
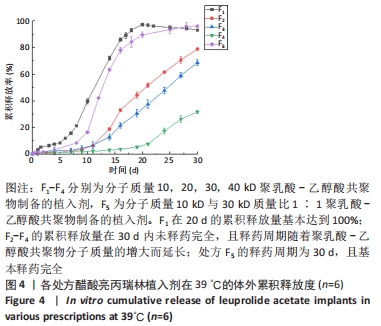
根据美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)对植入剂溶出指导原则及多肽类植入剂的体外释放方法[23],开发体外释放方法:取各处方醋酸亮丙瑞林植入剂1支,精密称定,置于20 mL西林瓶中。加入释放介质10 mL,加盖,放置在(39.0±0.5) ℃恒温箱中保温,在预定时间点取2 mL,并及时补充等温等体积的新鲜释放介质,整个释放过程符合漏槽条件。取出溶液用0.45 µm微孔滤膜滤过后,按高效液相色谱法测定续滤液中亮丙瑞林的含量,计算累计释放度,得到体外释放曲线。每个处方平行6份,结果以x±s表示。最终根据体外释药曲线选择与临床使用释药周期一致为30 d的处方进行研究。
1.4.6 体内药动学研究
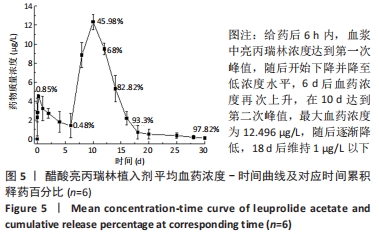
给药方案及血样采集:取雄性SD大鼠6只,每只分别皮下植入释放周期为1个月的植入剂0.45 mg(按亮丙瑞林计),分别在植入后 0.5,1,6 h及1,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,25,28,30 d,采用异氟烷麻醉大鼠,眼眶取血后置于含1 TIU/mL抑肽酶的试管中,4 ℃下13 000 r/min离心10 min,1 h内取上层血清,-80 ℃保存,待测。建立的分析方法按照CFDA颁布的《生物样品定量分析方法验证指导原则》进行验证。采用经过方法学考察合格的液相色谱-串联质谱法测定血浆中亮丙瑞林的浓度[24]。
血样处理及测定:所有冷冻血浆样品在室温下解冻,移取100 µL血浆样品、100 µL内标液(250 µg/L丙氨瑞林)、100 µL甲醇∶水∶甲酸=60∶40∶0.08(体积比)及500 µL甲醇于2 mL 离心管中。涡旋混合10 min,取上清液于离心管中,加入500 µL水后,轻轻加载到用1 mL甲醇及去离子水进行预处理的HLB固相萃取柱(1 mL,30 mg)。然后用1 mL去离子水及1 mL甲醇∶水=60∶40(体积比)洗杂质,再用1 mL甲醇(含0.01%甲酸)洗脱。洗脱液收集在微型管中,在氮气保护下于50 ℃干燥10 min。在浓缩液中加入100 µL甲醇∶水∶甲酸=60∶40∶0.08(体积比)复溶,取上清液于自动进样瓶中,涡旋后取10 µL进样至液质系统。
色谱柱类型:ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18柱(50 mm×2.1 mm,1.8 µm);流动相为甲醇(A)和体积比0.02%的丙酸水(B);流速为0.4 mL/min;柱温40 ℃;质谱条件离子源:电喷雾离子化源;极性:正离子;CE电压:30 eV;DP电压为40 V;离子喷射电压:5 500 V;温度:600 ℃;源内气体1(N2)为344.74 kPa;气体2(N2)为413.69 kPa;气帘气(N2)为206.84 kPa;碰撞气为55.16 kPa;用于定量分析的离子反应为:亮丙瑞林(605.5/249.1),内标丙氨瑞林(584.5/249.1)。
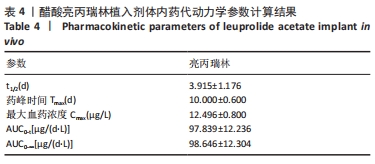
数据经DAS 2.0版软件进行处理,采用非房室模型方法计算获得药动学参数。
1.4.7 药物释放动力学与热力学相关性
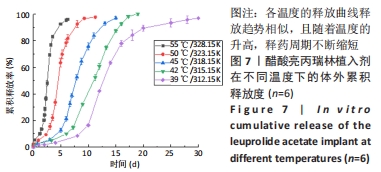
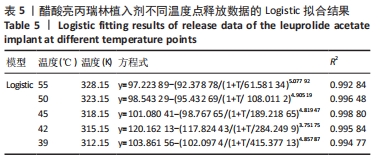
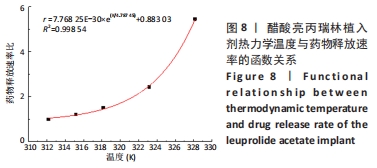
体外加速释放实验:取释放周期为1个月的植入剂1支,精密称定,置于20 mL西林瓶中,加入释放介质10 mL,加盖,并分别放入(39.0±0.5),(42.0±0.5),(45.0±0.5),(50.0±0.5),(55.0±0.5)℃恒温箱中,在预定时间点取2 mL,并及时补充等温等体积的新鲜释放介质,取出溶液用0.45 µm微孔滤膜滤过后,按高效液相色谱法测量滤过液中亮丙瑞林的体外累计释放度,得到体外释放曲线。每个温度点平行6份,结果以x±s表示。
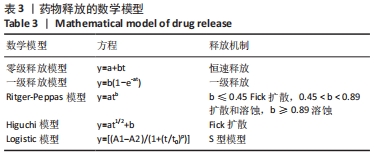
体外释药模型的建立:缓控释制剂药物的释放模型较为常用的有零级释放、一级释放、Ritger-Peppas模型、Higuchi模型和Logistic模型等[25],见表3。用OriginPro 2019对体外释放数据进行拟合,确定体外释放的最佳模型,考察释药机制。
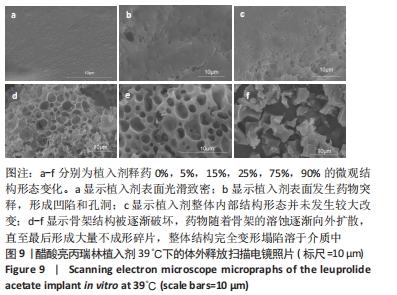
扫描电镜观察:取体外释药过程中预定时间的植入剂,在液氮环境中迅速冷冻15 min后,置于冷冻干燥机中24 h,切片,将样品置于导电胶上,真空下喷金,在超高分辨率场发射扫描电镜下观察样品的微观结构。
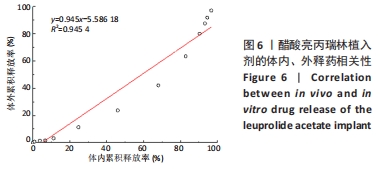
1.4.8 体内释放和体外释放相关性评价 根据文献报道[26],将植入剂在SD大鼠体内的血药浓度转化为体内药物吸收百分数,与体外释放的累积释放百分数进行线性回归,考察二者的相关性。
1.5 主要观察指标 植入剂初始形态、体外释药行为、体内药动学参数、体外加速释放动力学行为及释药过程中微观形态。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 22.0统计软件进行分析,数据以x±s表示。相关性分析采用Origin的线性回归分析。