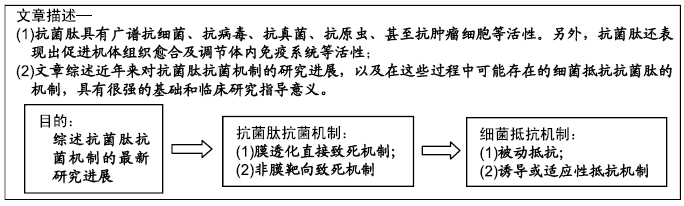
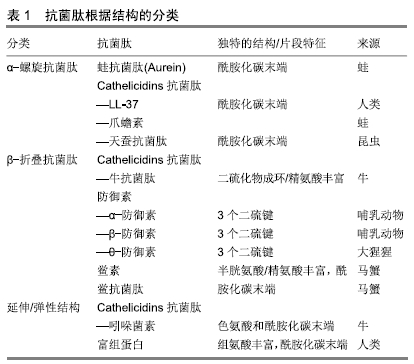
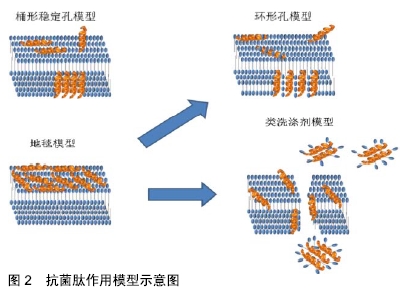
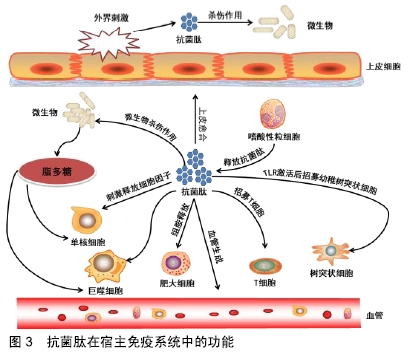
[1] VESTERGAARD M, FREES D, INGMER H. Antibiotic Resistance and the MRSA Problem.Microbiol Spectr. 2019;7(2). doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0057-2018
[2] RELLO J, KALWAJE ESHWARA V, CONWAY-MORRIS A, et al. Perceived differences between intensivists and infectious diseases consultants facing antimicrobial resistance: a global cross-sectional survey.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis.2019;38(7):1235-1240.
[3] CATTOIR V, FELDEN B.Future antibacterial strategies: from basic concepts to clinical challenges.J Infect Dis.2019;220(3):350-360.
[4] BECHINGER B, GORR SU.Antimicrobial Peptides: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance.J Dent Res.2017;96(3):254-260.
[5] NUTI R, GOUD NS, SARASWATI AP, et al.Antimicrobial Peptides: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy in Tackling Antimicrobial Resistance. Curr Med Chem.2017;24(38):4303-4314.
[6] NAWROT R, BARYLSKI J, NOWICKI G, et al.Plant antimicrobial peptides.Folia Microbiol(Praha).2014;59(3):181-96.
[7] ZANJANI NT, MIRANDA-SAKSENA M, CUNNINGHAM AL, et al. Antimicrobial Peptides of Marine Crustaceans: The Potential and Challenges of Developing Therapeutic Agents.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(19):2245-2259.
[8] VINEETH KUMAR TV, SANIL G. A Review of the Mechanism of Action of Amphibian Antimicrobial Peptides Focusing on Peptide-Membrane Interaction and Membrane Curvature.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017; 18(12):1263-1272.
[9] BUONOCORE F, PICCHIETTI S, PORCELLI F, et al. Fish-derived antimicrobial peptides: Activity of a chionodracine mutant against bacterial models and human bacterial pathogens.Dev Comp Immunol. 2019;96:9-17.
[10] WANG X, REN S, GUO C, et al. Identification and functional analyses of novel antioxidant peptides and antimicrobial peptides from skin secretions of four East Asian frog species. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).2017;49(6):550-559.
[11] SANG M, WU Q, XI X, et al. Identification and target-modifications of temporin-PE: A novel antimicrobial peptide in the defensive skin secretions of the edible frog, Pelophylax kl. esculentus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2018;495(4):2539-2546.
[12] FINDLAY F, PROUDFOOT L, STEVENS C, et al. Cationic host defense peptides; novel antimicrobial therapeutics against Category A pathogens and emerging infections.Pathog Glob Health. 2016;110 (4-5):137-147.
[13] KHURSHID Z, NASEEM M, SHEIKH Z, et al.Oral antimicrobial peptides: Types and role in the oral cavity.Saudi Pharm J.2016;24(5):515-524.
[14] MEADE KG, O'FARRELLY C.beta-Defensins: Farming the Microbiome for Homeostasis and Health. Frontiers in immunology.Front Immunol. 2019;9:3072.
[15] HANCOCK RE, HANEY EF, GILL EE.The immunology of host defence peptides: beyond antimicrobial activity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16(5): 321-334.
[16] HANEY EF, HANCOCK RE. Peptide design for antimicrobial and immunomodulatory applications. Biopolymers.2013;100(6):572-583.
[17] VELDHUIZEN EJ, SCHNEIDER VA, AGUSTIANDARI H, et al. Antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities of PR-39 derived peptides.PLoS One.2014;9(4):e95939.
[18] ZHANG LJ, GALLO RL. Antimicrobial peptides.Curr Biol. 2016;26(1): R14-19.
[19] FARKAS A, MAROTI G, KERESZT A, et al.Comparative analysis of the bacterial membrane disruption effect of two natural plant antimicrobial peptides.Front Microbiol.2017;8:51-62.
[20] GUILHELMELLI F, VILELA N, ALBUQUERQUE P, et al. Antibiotic development challenges: the various mechanisms of action of antimicrobial peptides and of bacterial resistance.Front Microbiol. 2013;9(4):353-364.
[21] YANG H, BIERMANN MH, BRAUNER JM, et al. New Insights into Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Mechanisms of Formation and Role in Inflammation.Front Immunol.2016;12(7):302-309.
[22] FOX JL.Antimicrobial peptides stage a comeback. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31(5):379-382.
[23] MADANCHI H, AKBARI S, SHABANI AA, et al. Alignment-based design and synthesis of new antimicrobial Aurein-derived peptides with improved activity against Gram-negative bacteria and evaluation of their toxicity on human cells.Drug Dev Res.2019;80(1):162-170.
[24] WENZEL M, SENGES CH, ZHANG J, et al. Antimicrobial Peptides from the Aurein Family Form Ion-Selective Pores in Bacillus subtilis. Chembiochem.2015;16(7):1101-1108.
[25] MURA M, WANG J, ZHOU Y, et al. The effect of amidation on the behaviour of antimicrobial peptides. Eur Biophys J. 2016;45(3):195-207.
[26] BAYER A, LAMMEL J, TOHIDNEZHAD M, et al.The Antimicrobial Peptide Human Beta-Defensin-3 Is Induced by Platelet-Released Growth Factors in Primary Keratinocytes.Mediators Inflamm. 2017; 2017:6157491.
[27] LEE TH, HALL KN, AGUILAR MI. Antimicrobial Peptide Structure and Mechanism of Action: A Focus on the Role of Membrane Structure. Curr Top Med Chem.2016;16(1):25-39.
[28] KHANAL N, GAYE MM, CLEMMER DE.Multiple solution structures of the disordered peptide indolicidin from IMS-MS analysis.Int J Mass Spectrom.2018;427:52-58.
[29] TAJBAKHSH M, KARIMI A, FALLAH F, et al.Overview of ribosomal and non-ribosomal antimicrobial peptides produced by Gram positive bacteria.Cell Mol Biol(Noisy-le-grand). 2017;63(10):20-32.
[30] TATARKIEWICZ J, STANISZEWSKA A, BUJALSKA-ZADROZNY M. New agents approved for treatment of acute staphylococcal skin infections.Arch Med Sci.2016;12(6):1327-1336.
[31] ZHAO P, XUE Y, LI X, et al.Fungi-derived lipopeptide antibiotics developed since 2000. Peptides.2019;113:52-65.
[32] JOO HS, FU CI, OTTO M. Bacterial strategies of resistance to antimicrobial peptides. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.2016; 371(1695).pii: 20150292. doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0292.
[33] MITCHELL SA, TRUSCOTT F, DICKMAN R, et al.Simplified lipid II-binding antimicrobial peptides: Design, synthesis and antimicrobial activity of bioconjugates of nisin rings A and B with pore-forming peptides. Bioorg Med Chem.2018;26(21):5691-5700.
[34] LEE EY, ZHANG C, DI DOMIZIO J, et al.Helical antimicrobial peptides assemble into protofibril scaffolds that present ordered dsDNA to TLR9. Nat Commun.2019;10(1):1012-1021.
[35] FELICIO MR, SILVA ON, GONCALVES S, et al.Peptides with Dual Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Front Chem.2017;5:5-14.
[36] JOUHET J.Importance of the hexagonal lipid phase in biological membrane organization. Front Plant Sci.2013;4:494-499.
[37] ALVARES DS, RUGGIERO NETO J, AMBROGGIO EE. Phosphatidylserine lipids and membrane order precisely regulate the activity of Polybia-MP1 peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017;1859(6):1067-1074.
[38] STROMSTEDT AA, KRISTIANSEN PE, GUNASEKERA S, et al. Selective membrane disruption by the cyclotide kalata B7: complex ions and essential functional groups in the phosphatidylethanolamine binding pocket.Biochim Biophys Acta.2016;1858(6):1317-1327.
[39] PHOENIX DA, HARRIS F, MURA M, et al.The increasing role of phosphatidylethanolamine as a lipid receptor in the action of host defence peptides.Prog Lipid Res.2015;59:26-37.
[40] SCHMIDT NW, WONG GC. Antimicrobial peptides and induced membrane curvature: geometry, coordination chemistry,and molecular engineering.Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2013;17(4):151-163.
[41] EPAND RM,WALKER C,EPAND RF,et al.Molecular mechanisms of membrane targeting antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1858(5): 980-987.
[42] ANDERSSON DI, HUGHES D, KUBICEK-SUTHERLAND JZ. Mechanisms and consequences of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides.Drug Resist Updat.2016;26:43-57.
[43] KRAUSON AJ, HE J, WIMLEY AW, et al.Synthetic molecular evolution of pore-forming peptides by iterative combinatorial library screening. ACS Chem Biol.2013;8(4):823-831.
[44] KUMAR P, KIZHAKKEDATHU JN, STRAUS SK. Antimicrobial Peptides: Diversity, Mechanism of Action and Strategies to Improve the Activity and Biocompatibility In Vivo. Biomolecules.2018;8(1).pii: E4. doi:10.3390/biom8010004.
[45] PAZDERKOVA M, MALON P, ZIMA V, et al.Interaction of Halictine-Related Antimicrobial Peptides with Membrane Models.Int J Mol Sci.2019;20(3).pii: E631.doi:10.3390/ijms20030631.
[46] KRISHNAN RS, SATHEESAN R, PUTHUMADATHIL N, et al. Autonomously Assembled Synthetic Transmembrane Peptide Pore.J Am Chem Soc.2019;141(7):2949-2959.
[47] MANZINI MC, PEREZ KR, RISKE KA, et al.Peptide:lipid ratio and membrane surface charge determine the mechanism of action of the antimicrobial peptide BP100.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1838(7): 1985-1999.
[48] MALANOVIC N, LOHNER K. Antimicrobial Peptides Targeting Gram-Positive Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals(Basel).2016;9(3).pii: E59. doi:10.3390/ph9030059.
[49] MUNCH D, SAHL HG. Structural variations of the cell wall precursor lipid II in Gram-positive bacteria - Impact on binding and efficacy of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1848(11 Pt B): 3062-3071.
[50] SHARMA H, NAGARAJ R. Human beta-defensin 4 with non-native disulfide bridges exhibit antimicrobial activity.PLoS One. 2015;10(3): e0119525.
[51] KANG KM, PARK JH, KIM SH, et al.Potential role of host defense antimicrobial peptide resistance in increased virulence of health care-associated MRSA strains of sequence type (ST) 5 versus livestock-associated and community-associated MRSA strains of ST72.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis.2019;62:13-18.
[52] KOPRIVNJAK T, PESCHEL A. Bacterial resistance mechanisms against host defense peptides.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(13): 2243-2254.
[53] COATES-BROWN R, MORAN JC, PONGCHAIKUL P, et al. Comparative Genomics of Staphylococcus Reveals Determinants of Speciation and Diversification of Antimicrobial Defense.Front Microbiol. 2018;9:2753.
[54] NAWROCKI KL, CRISPELL EK, MCBRIDE SM. Antimicrobial Peptide Resistance Mechanisms of Gram-Positive Bacteria.Antibiotics(Basel). 2014;3(4):461-492.
[55] SUAREZ JM, EDWARDS AN, MCBRIDE SM. The Clostridium difficile cpr locus is regulated by a noncontiguous two-component system in response to type A and B lantibiotics.J Bacteriol.2013;195(11):2621-2631.
[56] ISHAQ N, BILAL M, IQBAL HMN. Medicinal Potentialities of Plant Defensins: A Review with Applied Perspectives.Medicines(Basel). 2019;6(1).pii: E29.doi:10.3390/medicines6010029.
[57] GOUR S, KUMAR V, SINGH A, et al. Mammalian antimicrobial peptide protegrin-4 self assembles and forms amyloid-like aggregates: Assessment of its functional relevance.J Pept Sci. 2019;25(3):e3151.
[58] MORAVEJ H, MORAVEJ Z, YAZDANPARAST M, et al. Antimicrobial Peptides: Features, Action, and Their Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria. Microb Drug Resist.2018;24(6):747-767.
[59] ZHAO L, LU W. Defensins in innate immunity.Curr Opin Hematol. 2014;21(1):37-42.
[60] HOLLY MK, DIAZ K, SMITH JG. Defensins in Viral Infection and Pathogenesis.Annu Rev Virol. 2017;4(1):369-391.
[61] AL-RAYAHI IA, SANYI RH.The overlapping roles of antimicrobial peptides and complement in recruitment and activation of tumor-associated inflammatory cells.Front Immunol.2015;6:2.
[62] STEPHAN A, BATINICA M, STEIGER J, et al.LL37:DNA complexes provide antimicrobial activity against intracellular bacteria in human macrophages.Immunology.2016;148(4):420-432.
[63] AGEITOS JM, SANCHEZ-PEREZ A, CALO-MATA P, et al. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): Ancient compounds that represent novel weapons in the fight against bacteria.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;133:117-138.
[64] MOJSOSKA B, JENSSEN H. Peptides and Peptidomimetics for Antimicrobial Drug Design. Pharmaceuticals(Basel). 2015;8(3): 366-415.
[65] AMANI J, BARJINI KA, MOGHADDAM MM, et al. In vitro synergistic effect of the CM11 antimicrobial peptide in combination with common antibiotics against clinical isolates of six species of multidrug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. Protein Pept Lett.2015;22(10):940-951.
[66] MOHAMMADI AZAD Z, MORAVEJ H, FASIHI-RAMANDI M, et al. In vitro synergistic effects of a short cationic peptide and clinically used antibiotics against drug-resistant isolates of Brucella melitensis. J Med Microbiol.2017;66(7):919-926.
|