中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 898-902.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2428
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
成人无症状前凸型颈椎矢状面平衡影像学参数的相关性特征
曹 斌1,左玉强2,李存瑞3,康伟峰4,于海泉1,苏敬阳1
- 1石家庄市第一医院骨三科,河北省石家庄市 050011;2河北医科大学第二医院体检中心,河北省石家庄市 050000;3张家口市第一医院CT室,河北省张家口市 075041;4石家庄市行唐县中医院骨伤科,河北省石家庄市 050600
Correlation of parameters of lordosis type cervical spine saggital plane in asymptomatic adults
Cao Bin1, Zuo Yuqiang2, Li Cunrui3, Kang Weifeng4, Yu Haiquan1, Su Jingyang1
- 1Third Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital of Shijiazhuang; 2Department of Health Care Center, Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University; 3Department of CT, First Hospital of Zhangjiakou; 4Department of Orthopedics, Xingtang County Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine
摘要:
文题释义:
脊柱矢状面平衡:人体脊柱在矢状面上有4个生理弯曲,即:颈椎前凸、胸椎后凸、腰椎前凸和骶椎后凸,脊柱在矢状面呈S形。人体脊柱整体的矢状面平衡能保证人在站立及行走时以最小的能量消耗来维持视线水平和相对稳定的姿势,若各种原因导致脊柱某节段出现矢状面序列改变时,脊柱需通过其代偿机制来维持脊柱的矢状面平衡。
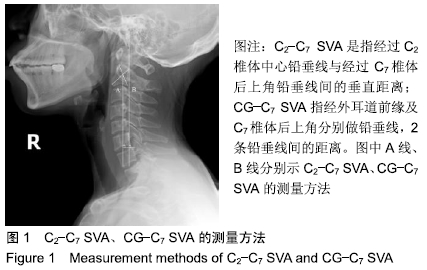
颈椎矢状面力线:主要包括颈椎曲度和颈椎矢状面平衡两个方面,其中颈椎曲度的测量又分为上颈椎曲度(C0-C2角或C1-C2角)和下颈椎曲度(C2-C7角),在X射线片上测量全颈椎曲度或上颈椎曲度多采用Cobb法,测量下颈椎曲度则有多重方法,但Cobb法易用且有良好组内、组间可靠性;颈椎矢状面平衡的测量通常通过C2-C7 SVA来评估,其与健康相关生活质量评分相关。
背景:正常的颈椎矢状面平衡是颈椎矫形手术的关键。由于颈椎解剖结构和生理功能的复杂性,故对颈椎矢状面平衡参数的准确测量及参数间相关性成为制定手术方案及评价疗效的重要参考,现有研究集中在有临床症状的颈椎病患者。
目的:探讨成人无症状前凸型颈椎矢状面平衡影像学参数相关性。
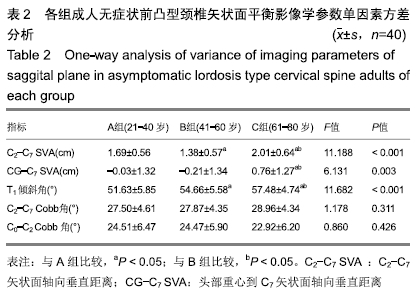
方法:回顾性分析120例成人无症状前凸型颈椎正侧位DR影像,根据研究对象年龄将其分为3组,A组(21-40岁)、B组(41-60岁)、C组(61-80岁),测量其颈椎矢状面平衡影像学参数,包括C2-C7矢状面轴向垂直距离(C2-C7 sagittal vertical axis,C2-C7 SVA)、头部重心到C7矢状面轴向垂直距离(central of gravity to C7 sagittal vertical axis,CG-C7 SVA)、T1倾斜角、C0-C2 Cobb角及C2-C7 Cobb角,分析组间影像学参数差异及不同影像学参数与年龄间相关性。研究通过石家庄市第一医院、河北医科大学第二医院伦理委员会批准,纳入者均签署知情同意书。
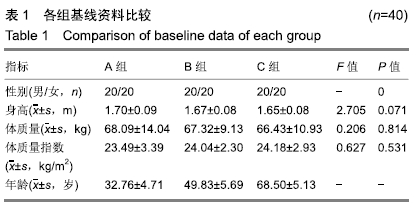
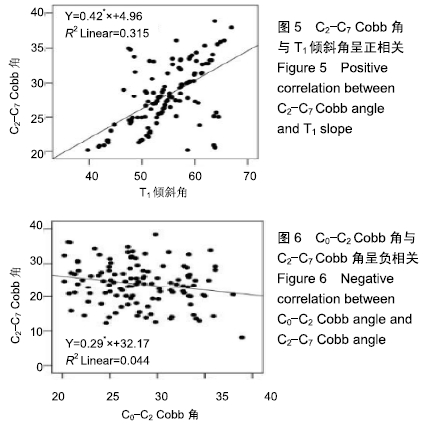
结果与结论:①不同年龄组的C2-C7 SVA(F=11.188,P < 0.001)、CG-C7 SVA(F=6.132,P=0.003)、T1倾斜角(F=11.682,P < 0.001)组间比较差异均有统计学意义,C0-C2 Cobb角(F=1.178,P=0.311)、C2-C7 Cobb角(F=0.860,P=0.426)组间比较差异无统计学意义;②A、B、C组的T1倾斜角分别为(51.63±5.85)°,(54.66±5.58)°,(57.48±4.74)°,线性相关分析显示T1倾斜角与年龄呈正相关(r=0.533,P < 0.001);另T1倾斜角和C2-C7 Cobb角间存在正相关(r=0.561,P < 0.001)。提示:在成人无症状前凸型颈椎者中,T1倾斜角有随着年龄增大而增大的趋势,且T1倾斜角与年龄呈正相关。
ORCID: 0000-0002-2694-3950(曹斌)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: