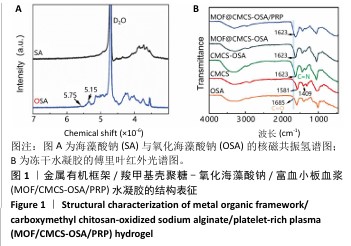
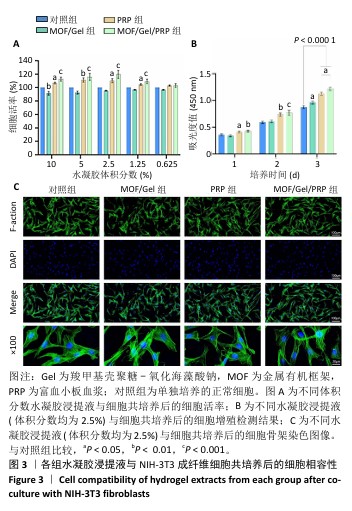
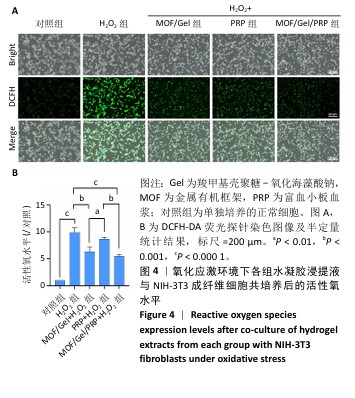
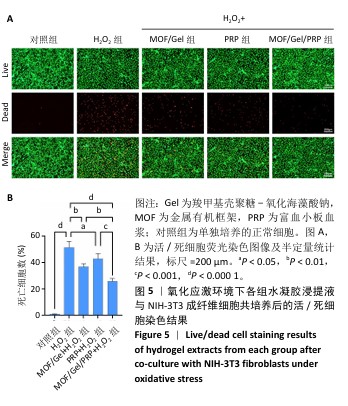
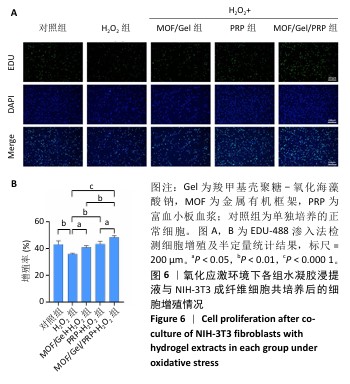
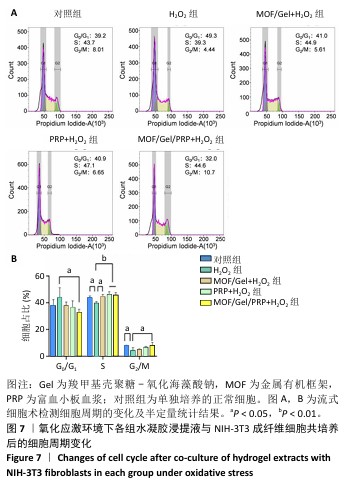
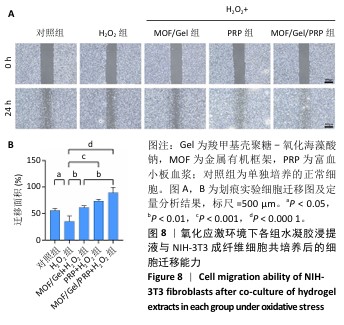
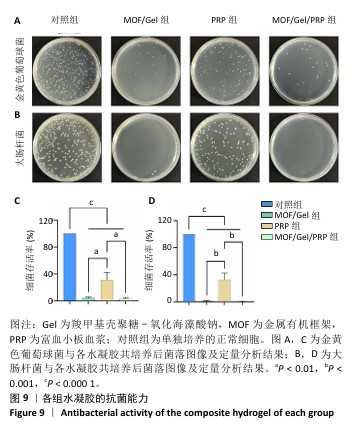
[1] XIONG Y, CHU X, YU T, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species-Scavenging Nanosystems in the Treatment of Diabetic Wounds. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(25):2300779.
[2] DUNNILL C, PATTON T, BRENNAN J, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and wound healing: the functional role of ROS and emerging ROS-modulating technologies for augmentation of the healing process. Int Wound J. 2017; 14(1):89-96.
[3] LIANG Y, HE J, GUO B. Functional hydrogels as wound dressing to enhance wound healing. ACS Nano. 2021;15(8):12687-12722.
[4] SILVA JC, PITTA MG, PITTA IR, et al. New peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist (GQ-11) improves wound healing in diabetic mice. Adv Wound Care. 2019;8(9):417-428.
[5] LIU K, ZHANG H, WANG Z, et al. Carrier-Free, Injectable Hydrogel Formed by Self-Assembled Nanofibers of Antimicrobial and Anti-inflammatory Peptide for Wound Healing. ACS App Nano Mater. 2024;7(14):16585-16598.
[6] CHEN J, LIU Y, CHENG G, et al. Tailored hydrogel delivering niobium carbide boosts ROS‐scavenging and Antimicrobial activities for diabetic wound healing. Small. 2022;18(27):2201300.
[7] ZHENG SY, WAN XX, KAMBEY PA, et al. Therapeutic role of growth factors in treating diabetic wound. World J Diabetes. 2023;14(4):364.
[8] XU D, WU L, YAO H, et al. Catalase‐like nanozymes: Classification, catalytic mechanisms, and their applications. Small. 2022;18(37):2203400.
[9] WU A, LI M, CHEN Y, et al. Multienzyme Active Manganese Oxide Alleviates Acute Liver Injury by Mimicking Redox Regulatory System and Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(11):2302556.
[10] HU S, WANG L, LI J, et al. Catechol-modified and MnO2-nanozyme-reinforced hydrogel with improved antioxidant and antibacterial capacity for periodontitis treatment. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(9):5332-5346.
[11] SUN H, YU X, MA X, et al. MnOx-CeO2 catalyst derived from metal-organic frameworks for toluene oxidation. Catal Today. 2020;355:580-586.
[12] PAN W, WANG W, WANG P, et al. Sustained delivery of extracellular vesicles using UiO-66-NH2 crosslinked hydrogel for accelerating chronic diabetic wound-healing. Mater Design. 2024;238:112688.
[13] ZHU J, QIU W, YAO C, et al. Water-stable zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks armed polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous membrane with enhanced antibacterial therapy for wound healing. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2021;603:243-251.
[14] FAN YL, LIU HJ, WANG ZL, et al. A One-Nano MOF-Two-Functions Strategy Toward Self-healing, Anti-inflammatory, and Antibacterial Hydrogels for Infected Wound Repair. Chem Eng J. 2024;497:155037.
[15] BI X, BAI Q, LIANG M, et al. Silver peroxide nanoparticles for combined antibacterial sonodynamic and photothermal therapy. Small. 2022;18(2): 2104160.
[16] ZHANG Y, KANG J, CHEN X, et al. Ag nanocomposite hydrogels with immune and regenerative microenvironment regulation promote scarless healing of infected wounds. J Nanobiotechnol. 2023;21(1):435.
[17] EVERTS P, ONISHI K, JAYARAM P, et al. Platelet-rich plasma: new performance understandings and therapeutic considerations in 2020. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(20):7794.
[18] FANG J, WANG X, JIANG W, et al. Platelet-rich plasma therapy in the treatment of diseases associated with orthopedic injuries. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(6):571-585.
[19] CL K, JEYARAMAN M, JEYARAMAN N, et al. Antimicrobial Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Scoping Review. Cureus. 2023;15(12):e51360.
[20] ZHANG Y, WANG ZL, DENG ZP, et al. An extracellular matrix-inspired self-healing composite hydrogel for enhanced platelet-rich plasma-mediated chronic diabetic wound treatment. Carbohyd Polym. 2023;315:120973.
[21] SHANG S, ZHUANG K, CHEN J, et al. A bioactive composite hydrogel dressing that promotes healing of both acute and chronic diabetic skin wounds. Bioact Mater. 2024;34:298-310.
[22] KŁOSIŃSKI KK, WACH RA, KRUCZKOWSKA W, et al. Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogels for Effective Wound Healing—An Animal Study. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(9):473.
[23] JIANG Y, GUO S, JIAO J, et al. A biphasic hydrogel with self-healing properties and a continuous layer structure for potential application in osteochondral defect repair. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(12):2744.
[24] KIRK T, AHMED A, ROGNONI E. Fibroblast memory in development, homeostasis and disease. Cells. 2021;10(11):2840.
[25] WOODLEY JP, LAMBERT DW, ASENCIO IO. Reduced Fibroblast Activation on Electrospun Polycaprolactone Scaffolds. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023; 10(3):348.
[26] WOODLEY JP, LAMBERT DW, ASENCIO I O. Understanding fibroblast behavior in 3D biomaterials. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022;28(3):569-578.
[27] 梅和平,石孟琼,陈茂华,等.地连二心颗粒对H2O2 致小鼠成纤维细胞损伤的保护作用研究[J].中药药理与临床,2017,33(1):139-144.
[28] WU M, TU J, HUANG J, et al. Exosomal IRF1-loaded rat adipose-derived stem cell sheet contributes to wound healing in the diabetic foot ulcers. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):60.
[29] 胡晶晶 . 具有 ROS 清除作用的水凝胶包裹小檗碱 @ NMOF 促进糖尿病足创面愈合 [D]. 广州 : 南方医科大学 ,2022.
[30] DENG L, DU C, SONG P, et al. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetic wound healing. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021(1):8852759.
[31] LONG M, ROJO DE LA VEGA M, WEN Q, et al. An essential role of NRF2 in diabetic wound healing. Diabetes. 2016;65(3):780-793.
[32] YAN R, ZHANG X, XU W, et al. ROS-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Aging Dis. 2024;16(1):250-268.
[33] WANG Y, XIE R, LI Q, et al. A self-adapting hydrogel based on chitosan/oxidized konjac glucomannan/AgNPs for repairing irregular wounds. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(7):1910-1922.
[34] ZHENG Z, LI M, SHI P, et al. Polydopamine-modified collagen sponge scaffold as a novel dermal regeneration template with sustained release of platelet-rich plasma to accelerate skin repair: a one-step strategy. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(8):2613-2628.
[35] ZHOU J, CHEN N, LIAO J, et al. Ag-activated metal-organic framework with peroxidase-like activity synergistic Ag+ release for safe bacterial eradication and wound healing. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(22):4058.
[36] DASTNESHAN A, RAHIMINEZHAD S, MEZAJIN M N, et al. Cefazolin encapsulated UIO-66-NH2 nanoparticles enhance the antibacterial activity and biofilm inhibition against drug-resistant S. aureus: In vitro and in vivo studies. Chem Eng J. 2023;455:140544.
[37] KESHK WA, ZAHRAN SM. Mechanistic role of cAMP and hepatocyte growth factor signaling in thioacetamide-induced nephrotoxicity: Unraveling the role of platelet rich plasma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1078-1084.
[38] RANIA N, ISLAM IH, ATEF M, et al. Effect of platelet rich plasma on an experimental rat model of adriamycin induced chronic kidney disease. Med J Cairo Univ. 2019;87:2207-2217.
[39] BURANASIN P, MIZUTANI K, IWASAKI K, et al. High glucose-induced oxidative stress impairs proliferation and migration of human gingival fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2018;13(8):e0201855.
[40] ELMONGY NF, MEAWAD SB, ELSHORA SZ, et al. Platelet-rich plasma ameliorates neurotoxicity induced by silver nanoparticles in male rats via modulation of apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress. J Biochem Mol Toxicl. 2023;37(9):e23420.
[41] ZHENG WQ, ZHANG JH, LI ZH, et al. Mammalian mitochondrial translation infidelity leads to oxidative stress–induced cell cycle arrest and cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(37):e2309714120.
[42] THANGAPAZHAM RL, DARLING TN, MEYERLE J. Alteration of skin properties with autologous dermal fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(5):8407-8427.
[43] YI W, BAO Q, XU D, et al. ETS1 Expression in Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Implications for Fibroblast Phenotype and Wound Healing Through the PP2A/YAP Pathway. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:7373-7388.
[44] DEVEREAUX J, NURGALI K, KIATOS D, et al. Effects of platelet-rich plasma and platelet-poor plasma on human dermal fibroblasts. Maturitas. 2018;117: 34-44.
[45] WEI S, WANG Z, LIANG X, et al. A composite hydrogel with antibacterial and promoted cell proliferation dual properties for healing of infected wounds. AM J Transl Res. 2023;15(7):4467.
[46] HUANG P, HE Y, HUANG C, et al. MOF@platelet-rich plasma antimicrobial GelMA dressing: structural characterization, bio-compatibility, and effect on wound healing efficacy. RSC Adv. 2024;14(41):30055-30069. |