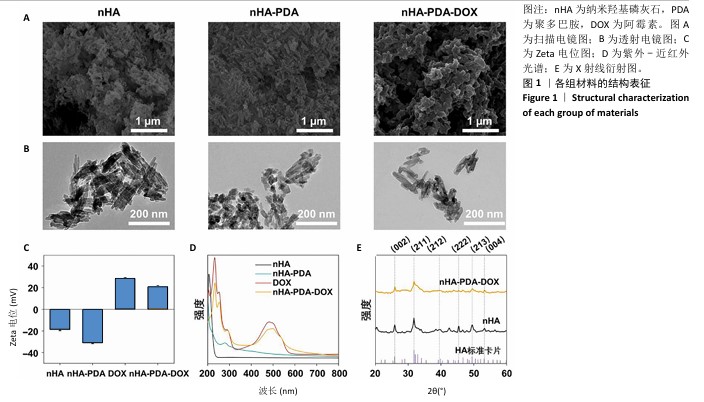
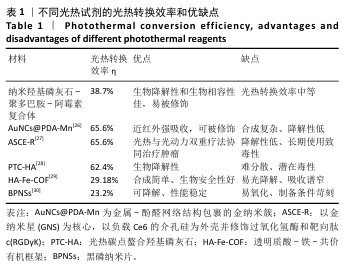
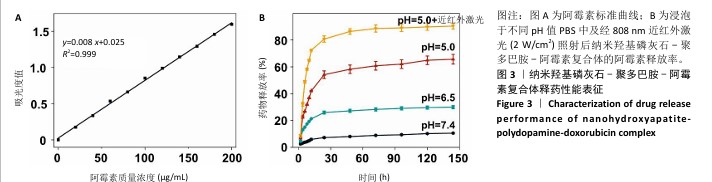
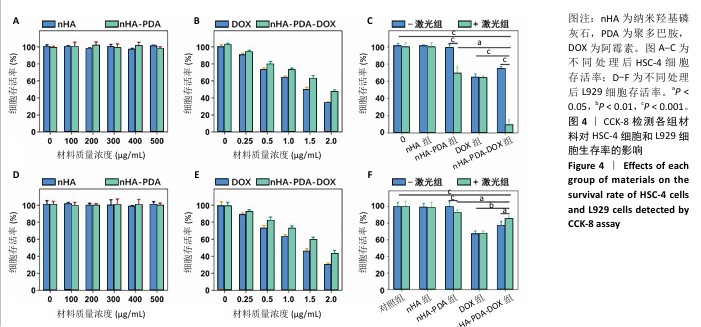
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249.
[2] TANG Q, XIE M, YU S, et al. Periodic Oxaliplatin Administration in Synergy with PER2-Mediated PCNA Transcription Repression Promotes Chronochemotherapeutic Efficacy of OSCC. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6(21):1900667.
[3] SMYTH EC, LAGERGREN J, FITZGERALD RC, et al. Oesophageal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17048.
[4] TIAN Y, TANG C, SHI G, et al. Novel fluorescent GLUT1 inhibitor for precision detection and fluorescence image-guided surgery in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2022;151(3):450-462.
[5] PIETZSCH S, WOHLAN K, THACKERAY JT, et al. Anthracycline-free tumor elimination in mice leads to functional and molecular cardiac recovery from cancer-induced alterations in contrast to long-lasting doxorubicin treatment effects. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021;116(1):61.
[6] LIU T, ZHU M, CHANG X, et al. Tumor-Specific Photothermal-Therapy-Assisted Immunomodulation via Multiresponsive Adjuvant Nanoparticles. Adv Mater. 2023;35(18):e2300086.
[7] REN Y, YAN Y, QI H. Photothermal conversion and transfer in photothermal therapy: From macroscale to nanoscale. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;308:102753.
[8] PALMER LC, NEWCOMB CJ, KALTZ SR, et al. Biomimetic systems for hydroxyapatite mineralization inspired by bone and enamel. Chem Rev. 2008;108(11):4754-4783.
[9] WANG R, HUA Y, WU H, et al. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles promote TLR4 agonist-mediated anti-tumor immunity through synergically enhanced macrophage polarization. Acta Biomater. 2023;164:626-640.
[10] ZHANG K, ZHOU Y, XIAO C, et al. Application of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in tumor-associated bone segmental defect. Sci Adv. 2019;5(8):eaax6946.
[11] YANG Y, YANG J, ZHU N, et al. Tumor-targeting hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for remodeling tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) by activating mitoDNA-pyroptosis pathway in cancer. J Nanobiotechnol. 2023;21(1):470.
[12] KANG Y, SUN W, LI S, et al. Oligo Hyaluronan-Coated Silica/Hydroxyapatite Degradable Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Treatment. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6(13):1900716.
[13] CHENG X, XU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Glucose-Targeted Hydroxyapatite/Indocyanine Green Hybrid Nanoparticles for Collaborative Tumor Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(31):37665-37679.
[14] CHANG L, HUANG S, ZHAO X, et al. Preparation of ROS active and photothermal responsive hydroxyapatite nanoplatforms for anticancer therapy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;125:112098.
[15] ALFIERI ML, WEIL T, NG DYW, et al. Polydopamine at biological interfaces. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;305:102689.
[16] FU Y, YANG L, ZHANG J, et al. Polydopamine antibacterial materials.Mater Horiz. 2021;8(6):1618-1633.
[17] LIAO J, LI W, PENG J, et al. Combined cancer photothermal-chemotherapy based on doxorubicin/gold nanorod-loaded polymersomes. Theranostics. 2015;5(4):345-356.
[18] NI W, WU J, FANG H, et al. Photothermal-Chemotherapy Enhancing Tumor Immunotherapy by Multifunctional Metal-Organic Framework Based Drug Delivery System. Nano Lett. 2021;21(18):7796-7805.
[19] YANG G, LI M, SONG T, et al. Polydopamine-Engineered Theranostic Nanoscouts Enabling Intracellular HSP90 mRNAs Fluorescence Detection for Imaging-Guided Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(23):e2201615.
[20] DING T, XIAO Y, SAIDING Q, et al. Capture and Storage of Cell-Free DNA via Bio-Informational Hydrogel Microspheres. Adv Mater. 2024; 36(33):e2403557.
[21] LIU L, ZHAO X. Preparation of environmentally responsive PDA&DOX@LAC live drug carrier for synergistic tumor therapy. Sci Rep.2024;14(1):15927.
[22] CHEN Z, SUN Y, WANG J, et al. Dual-Responsive Triple-Synergistic Fe-MOF for Tumor Theranostics. ACS Nano. 2023;17(10):9003-9013.
[23] ZHANG Y, KONG F, WU D, et al. Hydrothermal Extraction and Characterization of Natural Hydroxyapatite from Waste Bovine Femur Bone. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2023;29(11): 535-544.
[24] HE S, ZHENG Q, MA L, et al. Mucin-Triggered Osmium Nanoclusters as Protein-Corona-Like Nanozymes with Photothermal-Enhanced Peroxidase-Like Activity for Tumor-Specific Therapy. Nano Lett. 2024; 24(45):14337-14345.
[25] WU J, LIU J, LIN B, et al. Met-Targeted Dual-Modal MRI/NIR II Imaging for Specific Recognition of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(4):1640-1650.
[26] YANG T, DAI L, LIU J, et al. Metal-phenolic-network-coated gold nanoclusters for enhanced photothermal/chemodynamic/immunogenic cancer therapy. Bioact Mater. 2025;44:447-460.
[27] ZHANG L, YANG XQ, WEI JS, et al. Intelligent gold nanostars for in vivo CT imaging and catalase-enhanced synergistic photodynamic & photothermal tumor therapy. Theranostics. 2019;9(19):5424-5442.
[28] LIU G, LI B, LI J, et al. Photothermal Carbon Dots Chelated Hydroxyapatite Filler: High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency and Enhancing Adhesion of Hydrogel. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023; 15(48):55335-55345.
[29] CHEN Y, FENG T, ZHU X, et al. Ambient Synthesis of Porphyrin-Based Fe-Covalent Organic Frameworks for Efficient Infected Skin Wound Healing. Biomacromolecules. 2024;25(6): 3671-3684.
[30] LI S, ZHANG Y, WEN W, et al. A high-sensitivity thermal analysis immunochromatographic sensor based on au nanoparticle-enhanced two-dimensional black phosphorus photothermal-sensing materials. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;133:223-229.
[31] KATO K, MACHIDA R, ITO Y, et al. Doublet chemotherapy, triplet chemotherapy, or doublet chemotherapy combined with radiotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment for locally advanced oesophageal cancer (JCOG1109 NExT): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2024;404(10447):55-66.
[32] ZHANG Z, SUN D, TANG H, et al. PER2 binding to HSP90 enhances immune response against oral squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting IKK/NF-κB pathway and PD-L1 expression. J Immunother Cancer. 2023;11(11):e007627.
[33] FAROKHI M, MOTTAGHITALAB F, SAEB MR, et al. Functionalized theranostic nanocarriers with bio-inspired polydopamine for tumor imaging and chemo-photothermal therapy. J Control Release. 2019; 309:203-219.
[34] POUSTCHI F, AMANI H, AHMADIAN Z, et al. Combination Therapy of Killing Diseases by Injectable Hydrogels: From Concept to Medical Applications. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(3):e2001571.
[35] RATZIU V, CHARLTON M. Rational combination therapy for NASH: Insights from clinical trials and error. J Hepatol. 2023;78(5):1073-1079.
[36] FANE M, WEERARATNA AT. How the ageing microenvironment influences tumour progression. Nature reviews Cancer 2020;20(2):89-106.
[37] CHEN J, XIANG Y, BAO R, et al. Combined Photothermal Chemotherapy for Effective Treatment Against Breast Cancer in Mice Model. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:9973-9987.
[38] 李璐,刘怡萌,李楠楠,等.多功能19F磁共振/CT成像及光热/化学联合治疗纳米平台用于肿瘤诊疗[J]. 化学试剂,2023,45(9):47-55.
[39] CHEN T, ZHUANG B, HUANG Y, et al. Inhaled curcumin mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles against radiation pneumonitis. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12(5):2522-2532.
[40] YUAN Z, LIN C, HE Y, et al. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Nitric-Oxide-Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy and Low-Temperature Photothermal Therapy for Biofilm Elimination. ACS Nano. 2020;14(3):3546-3562.
[41] WANG Z, LI Z, SHI Y, et al. Mesoporous polydopamine delivery system for intelligent drug release and photothermal-enhanced chemodynamic therapy using MnO(2) as gatekeeper. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbad087.
[42] NIEZNI D, HARRIS Y, SASON H, et al. Polydopamine Copolymers for Stable Drug Nanoprecipitation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12420.
[43] VIGER ML, SANKARANARAYANAN J, DE GRACIA LUX C, et al. Collective activation of MRI agents via encapsulation and disease-triggered release. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(21):7847-7850.
[44] HANH L, VAN HAI L, THE HOANG N, et al. In vitro biodegradation behavior of biodegradable hydroxyapatite coated AZ31 alloy treated at various pH values. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2021;19: 22808000211010037.
[45] LI D, HUANG X, WU Y, et al. Preparation of pH-responsive mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for intracellular controlled release of an anticancer drug. Biomater Sci. 2016;4(2):272-280.
[46] CHEN W, MENG F, CHENG R, et al. pH-Sensitive degradable polymersomes for triggered release of anticancer drugs: a comparative study with micelles. J Control Release. 2010;142(1):40-46.
[47] LIU J, HUANG Y, KUMAR A, et al. pH-sensitive nano-systems for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32(4):693-710.
[48] ESKANDANI M, JAHANBAN-ESFAHLAN R, SADUGHI MM, et al. Thermal-responsive β-cyclodextrin-based magnetic hydrogel as a de novo nanomedicine for chemo/hyperthermia treatment of cancerous cells. Heliyon. 2024;10(11):e32183.
[49] WU D, JI W, XU S, et al. Near-infrared Light-Triggered Size-Shrinkable theranostic nanomicelles for effective tumor targeting and regression. Int J Pharm. 2024;658:124203.
[50] ZHOU T, WU L, MA N, et al. Photothermally responsive theranostic nanocomposites for near-infrared light triggered drug release and enhanced synergism of photothermo-chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;8(1):e10368.
[51] SHIN HH, CHOI HW, LIM JH, et al. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Thermo-responsive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Pyrrole Nanocomposites for Chemo-photothermal Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2020; 15(1):214.
[52] BAE Y, FUKUSHIMA S, HARADA A, et al. Design of environment-sensitive supramolecular assemblies for intracellular drug delivery: polymeric micelles that are responsive to intracellular pH change. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2003;42(38):4640-4643.
[53] GE R, LIN M, LI X, et al. Cu(2+)-Loaded Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided pH- and Near-Infrared-Light-Stimulated Thermochemotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(23):19706-19716.
[54] WANG H, HAN Z, LIU Y, et al. Recyclable Composite Membrane of Polydopamine and Graphene Oxide-Modified Polyacrylonitrile for Organic Dye Molecule and Heavy Metal Ion Removal. Membranes (Basel). 2022;12(10):938.
[55] RENNICK JJ, JOHNSTON APR, PARTON RG. Key principles and methods for studying the endocytosis of biological and nanoparticle therapeutics. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021;16(3):266-276.
[56] ZHANG S, GAO H, BAO G. Physical Principles of Nanoparticle Cellular Endocytosis. ACS Nano. 2015;9(9):8655-8671.
[57] BATTAGLINI M, CARMIGNANI A, CIOBANU DZ, et al. Detailed Profiling of Protein Corona Formed by Polydopamine Nanoparticles in Human Plasma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025;17(7):10485-10498.
[58] HAN M, LI Y, LU S, et al. Amyloid Protein-Biofunctionalized Polydopamine Nanoparticles Demonstrate Minimal Plasma Protein Fouling and Efficient Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(11):13743-13757.
[59] ZHU Z, SU M. Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Combined Chemo- and Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017;7(7):160.
[60] LI X, YANG C, TAO Y, et al. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Thermosensitive Liposomes Modified with Membrane Peptides for the Local Chemo/Photothermal Therapy of Melanoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;14:1317-1329.
[61] BORDAT A, BOISSENOT T, NICOLAS J, et al. Thermoresponsive polymer nanocarriers for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019; 138:167-192.
[62] XU C, ZHANG J, ZHANG J, et al. Near Infrared-Triggered Nitric Oxide-Release Nanovesicles with Mild-Photothermal Antibacterial and Immunomodulation for Healing MRSA-Infected Diabetic Wounds. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(31):e2402297. |