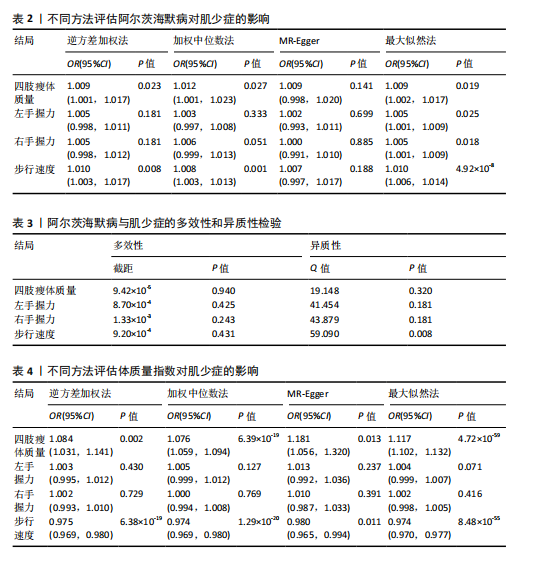
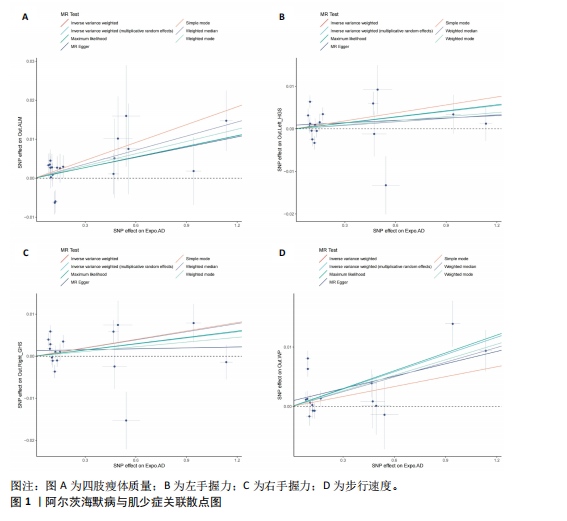
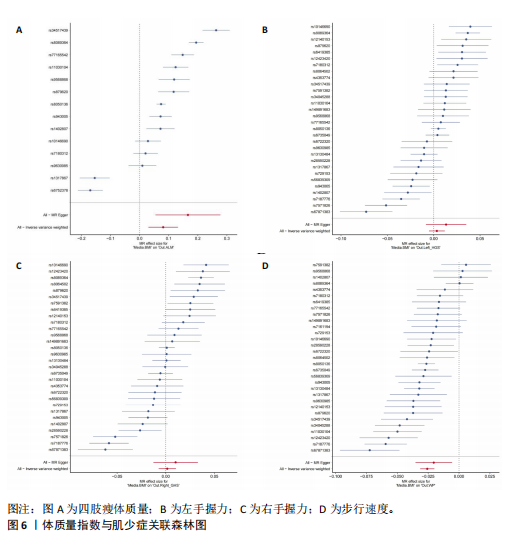
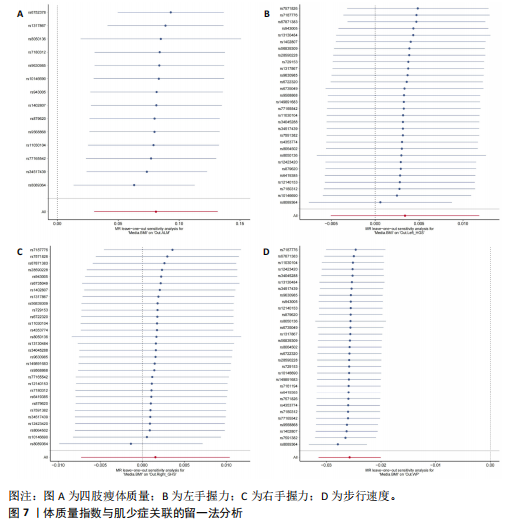
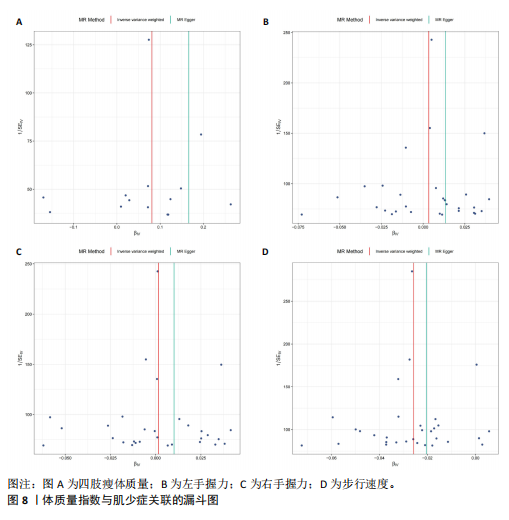
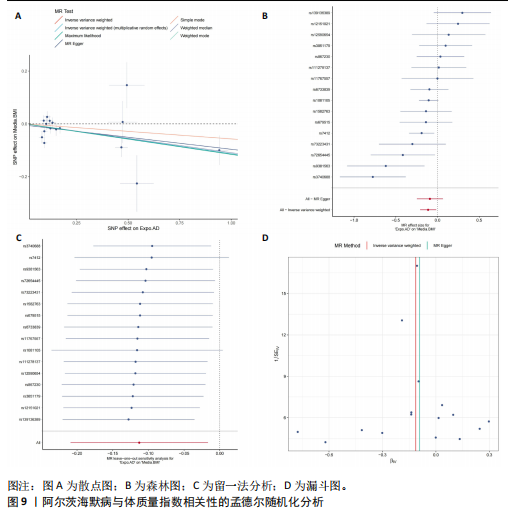
[1] SCHELTENS P, DE STROOPER B, KIVIPELTO M, et al. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2021; 397(10284):1577-1590.
[2] WU Y, ZHANG X, LI C, et al. Ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies under influence of climate and land cover change in an afforested semiarid basin, China. Ecol Eng. 2021;159:106083.
[3] ALDRICH L, ISPOGLOU T, PROKOPIDIS K, et al. Acute Sarcopenia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Its Incidence and Muscle Parameter Shifts During Hospitalisation. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13662.
[4] AMINI N, IBN HACH M, LAPAUW L, et al. Meta-analysis on the interrelationship between sarcopenia and mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024;15(4):1240-1253.
[5] 何启旺, 夏宇阳, 卢博雯, 等. 基于生物信息学探讨肌少症与阿尔茨海默病的关系[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2024,17(5):430-445.
[6] WENG X, LIU S, LI M, et al. White matter hyperintensities: a possible link between sarcopenia and cognitive impairment in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Geriatr Med. 2023;14(5): 1037-1047.
[7] BARONE R, BRAMATO G, GNONI V, et al. Sarcopenia in subjects with Alzheimer’s disease: prevalence and comparison of agreement between EGWSOP1, EGWSOP2, and FNIH criteria. BMC Geriatr. 2024;24(1): 278.
[8] CHOI S, CHON J, LEE SA, et al. Central obesity is associated with lower prevalence of sarcopenia in older women, but not in men: a cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1):406.
[9] KANJANAVAIKOON N, SAISIRIVECHAKUN P, CHAIAMNUAY S. Age, body mass index, and function as the independent predictors of sarcopenia in axial spondyloarthritis: a cross-sectional analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2023;42(12):3257-3265.
[10] CHALERMSRI C, AEKPLAKORN W, SRINONPRASERT V. Body Mass Index Combined With Possible Sarcopenia Status Is Better Than BMI or Possible Sarcopenia Status Alone for Predicting All-Cause Mortality Among Asian Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Front Nutr. 2022;9:881121.
[11] GARCíA-MARíN LM, CAMPOS AI, MARTIN NG, et al. Phenome-wide analysis highlights putative causal relationships between self-reported migraine and other complex traits. J Headache Pain. 2021;22(1):66.
[12] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAEYENS JP, BAUER JM, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):412-423.
[13] HU MJ, TAN JS, GAO XJ, et al. Effect of Cheese Intake on Cardiovascular Diseases and Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Nutrients. 2022;14(14):2936.
[14] LIU C, LIU N, XIA Y, et al. Osteoporosis and sarcopenia-related traits: A bi-directional Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:975647.
[15] HE J, HUANG M, LI N, et al. Genetic Association and Potential Mediators between Sarcopenia and Coronary Heart Disease: A Bidirectional Two-Sample, Two-Step Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2023;15(13):3013.
[16] DU Y, XIE B, WANG M, et al. Roles of sex hormones in mediating the causal effect of vitamin D on osteoporosis: A two-step Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1159241.
[17] SU Q, JIN C, YANG Y, et al. Association Between Autoimmune Diseases and Sarcopenia: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Clin Epidemiol. 2023; 15:901-910.
[18] WANG J, YANG M, TIAN Y, et al. Causal associations between common musculoskeletal disorders and dementia: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023;15:1253791.
[19] BOEHM FJ, ZHOU X. Statistical methods for Mendelian randomization in genome-wide association studies: A review. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022;20:2338-2351.
[20] BURGESS S, BOWDEN J, FALL T, et al. Sensitivity Analyses for Robust Causal Inference from Mendelian Randomization Analyses with Multiple Genetic Variants. Epidemiology. 2017;28(1):30-42.
[21] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525.
[22] ZENG Y, GUO R, CAO S, et al. CSF N-acylethanolamine acid amidase level and Parkinson’s disease risk: A mendelian randomization study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2024;123:106953.
[23] ZHAO W, ZHANG X, LI F, et al. Mendelian Randomization Estimates the Effects of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Proteins on Intelligence, Fluid Intelligence Score, and Cognitive Performance. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04542-5.
[24] LONGO S, MESSI ML, WANG ZM, et al. Accelerated sarcopenia precedes learning and memory impairments in the P301S mouse model of tauopathies and Alzheimer’s disease. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024;15(4):1358-1375.
[25] XU H, BHASKARAN S, PIEKARZ KM, et al. Age Related Changes in Muscle Mass and Force Generation in the Triple Transgenic (3xTgAD) Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:876816.
[26] WU MY, ZOU WJ, LEE D, et al. APP in the Neuromuscular Junction for the Development of Sarcopenia and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):7809.
[27] KARIM A, IQBAL MS, MUHAMMAD T, et al. Elevated plasma zonulin and CAF22 are correlated with sarcopenia and functional dependency at various stages of Alzheimer’s diseases. Neurosci Res. 2022;184:47-53.
[28] AUDOUARD E, VAN HEES L, SUAIN V, et al. Motor deficit in a tauopathy model is induced by disturbances of axonal transport leading to dying-back degeneration and denervation of neuromuscular junctions. Am J Pathol. 2015;185(10):2685-2697.
[29] TORCINARO A, RICCI V, STRIMPAKOS G, et al. Peripheral Nerve Impairment in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2021;11(9):1245.
[30] WEN Y, ZHENG Y, HUA S, et al. Mechanisms of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 in Respiratory Diseases. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024;25(1):1.
[31] SARTORI R, MILAN G, PATRON M, et al. Smad2 and 3 transcription factors control muscle mass in adulthood. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;296(6):C1248-1257.
[32] WANG S, GUSTAFSON S, DECKELMAN C, et al. Dysphagia Profiles Among Inpatients with Dementia Referred for Swallow Evaluation. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;89(1):351-358.
[33] SAARI T, HALLIKAINEN I, HINTSA T, et al. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and activities of daily living in Alzheimer’s disease: ALSOVA 5-year follow-up study. Int Psychogeriatr. 2020;32(6):741-751.
[34] DZIEWAS R, ALLESCHER HD, AROYO I, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of neurogenic dysphagia - S1 guideline of the German Society of Neurology. Neurol Res Pract. 2021;3(1):23.
[35] JUN L, ROBINSON M, GEETHA T, et al. Prevalence and Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy in Metabolic Conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):2973.
[36] LIGUORI C, CHIARAVALLOTI A, NUCCETELLI M, et al. Hypothalamic dysfunction is related to sleep impairment and CSF biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol. 2017;264(11):2215-2223.
[37] STEINBACH S, HUNDT W, VAITL A, et al. Taste in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol. 2010;257(2): 238-246.
[38] KOPP KO, GLOTFELTY EJ, LI Y, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and neuroinflammation: Implications for neurodegenerative disease treatment. Pharmacol Res. 2022;186:106550.
[39] YU X, CHEN S, FUNCKE JB, et al. The GIP receptor activates futile calcium cycling in white adipose tissue to increase energy expenditure and drive weight loss in mice. Cell Metab. 2024:S1550-4131(24)00449-2.
[40] DODDS RM, GRANIC A, DAVIES K, et al. Prevalence and incidence of sarcopenia in the very old: findings from the Newcastle 85+ Study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017;8(2):229-237.
[41] NASIMI N, DABBAGHMANESH MH, SOHRABI Z. Nutritional status and body fat mass: Determinants of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2019; 122:67-73.
[42] FAN Y, ZHANG B, HUANG G, et al. Sarcopenia: Body Composition and Gait Analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14: 909551.
[43] MESINOVIC J, MCMILLAN LB, SHORE-LORENTI C, et al. Metabolic Syndrome and Its Associations with Components of Sarcopenia in Overweight and Obese Older Adults. J Clin Med. 2019;8(2):145.
[44] YOO MC, WON CW, SOH Y. Association of high body mass index, waist circumference, and body fat percentage with sarcopenia in older women. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1): 937.
[45] TOMLINSON DJ, ERSKINE RM, MORSE CI, et al. The impact of obesity on skeletal muscle strength and structure through adolescence to old age. Biogerontology. 2016;17(3): 467-483.
[46] MORGAN PT, SMEUNINX B, BREEN L. Exploring the Impact of Obesity on Skeletal Muscle Function in Older Age. Front Nutr. 2020;7:569904.
[47] BAHNIWAL RK, SADR N, SCHINDERLE C, et al. Obesity Paradox and the Effect of NT‐proBNP on All‐Cause and Cause‐Specific Mortality. Clin Cardiol. 2024;47(11):e70044.
[48] SWAN L, WARTERS A, O’SULLIVAN M. Socioeconomic Inequality and Risk of Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Clin Interv Aging. 2021;16:1119-1129.
[49] STUDENSKI S, PERERA S, PATEL K, et al. Gait speed and survival in older adults. JAMA. 2011;305(1):50-58.
[50] GONG Z, FAULKNER ME, AKHONDA M, et al. White matter integrity and motor function: a link between cerebral myelination and longitudinal changes in gait speed in aging. Geroscience. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01392-w.
[51] NEWMAN AB, VISSER M, KRITCHEVSKY SB, et al. The Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) Study-Ground-Breaking Science for 25 Years and Counting. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023;78(11): 2024-2034.
[52] LIU H, JIN M, HAO H, et al. Association between relative fat mass and kidney stones in American adults. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1): 27045.
[53] PRIETO J, WILSON J, TINGLE A, et al. Strategies for older people living in care homes to prevent urinary tract infection: the StOP UTI realist synthesis. Health Technol Assess. 2024;28(68):1-139.
[54] CAO H, ZHANG D, WANG P, et al. Gut microbiome: a novel preventive and therapeutic target for prostatic disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024;14: 1431088.
[55] HENTZEN C, TURMEL N, CHESNEL C, et al. Effect of a strong desire to void on walking speed in individuals with multiple sclerosis and urinary disorders. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2020;63(2):106-110.
[56] BAUER SR, PARKER-AUTRY C, LU K, et al. Skeletal Muscle Health, Physical Performance, and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Older Adults: The Study of Muscle, Mobility, and Aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024;79(6):glad218.
[57] HAN P, ZHAO J, GUO Q, et al. Incidence, Risk Factors, and the Protective Effect of High Body Mass Index against Sarcopenia in Suburb-Dwelling Elderly Chinese Populations. J Nutr Health Aging, 2016;20(10):1056-1060.
[58] LI C, KANG B, ZHANG T, et al. High Visceral Fat Area Attenuated the Negative Association between High Body Mass Index and Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Chinese People. Healthcare (Basel). 2020;8(4):479.
[59] ZHAO X, LIU D, ZHANG H, et al. Associations of physical activity intensity, frequency, duration, and volume with the incidence of sarcopenia in middle-aged and older adults: a 4-year longitudinal study in China. BMC Geriatr. 2024;24(1):258.
[60] SENIOR HE, HENWOOD TR, BELLER EM, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of sarcopenia among adults living in nursing homes. Maturitas. 2015;82(4):418-423.
[61] LUO S, CHEN X, HOU L, et al. The accuracy of body mass index and calf circumference values when assessing sarcopenia in a multi-ethnic cohort of middle-aged and older adults: West China health and aging trend study results. Heliyon. 2023;9(4):e15027.
[62] BARDON LA, STREICHER M, CORISH CA, et al. Predictors of Incident Malnutrition in Older Irish Adults from the Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing Cohort-A MaNuEL study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020;75(2): 249-256.
[63] CURTIS M, SWAN L, FOX R, et al. Associations between Body Mass Index and Probable Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Nutrients. 2023;15(6):1505.
[64] DíAZ-AMAYA MJ, ROSALES-ARREOLA LF, HERNáNDEZ-LICONA J, et al. Postoperative complications in the pediatric population. Malnutrition or phase angle? Which one do we use? Front Nutr. 2024;11:1474616.
[65] SCHNEIDER SM, CORREIA M. Epidemiology of weight loss, malnutrition and sarcopenia: A transatlantic view. Nutrition. 2020;69: 110581.
[66] AI D, DING N, WU H. The impact of sarcopenia on nutritional status in elderly patients with gastrointestinal tumors. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):10308.
[67] PRADO CM, BATSIS JA, DONINI LM, et al. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: a clinical overview. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2024;20(5): 261-277.
[68] CEDERHOLM T, JENSEN GL, CORREIA M, et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition - A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019;10(1): 207-217.
[69] NAHMIAS BLANK D, HERMANO E, SONNENBLICK A, et al. Macrophages Upregulate Estrogen Receptor Expression in the Model of Obesity-Associated Breast Carcinoma. Cells. 2022;11(18):2844.
[70] MORYA VK, SHAHID H, LANG J, et al. Advancements in Therapeutic Approaches for Degenerative Tendinopathy: Evaluating Efficacy and Challenges. Int J Mol Sci. 2024; 25(21):11846.
[71] HO PY, KOH YC, LU TJ, et al. Purple Napiergrass (Pennisetum purpureum Schumach) Hot Water Extracts Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Metabolic Disorders in Mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2023;71(51):20701-20712. |