[1] DILL-MACKY AS, LEE EN, WERTHEIM JA, et al. Glia in tissue engineering: From biomaterial tools to transplantation. Acta Biomater. 2024;190:24-49.
[2] GUAN Y, REN Z, YANG B, et al. Dual-bionic regenerative microenvironment for peripheral nerve repair. Bioact Mater. 2023; 26:370-386.
[3] QI T, ZHANG X, GU X, et al. Experimental Study on Repairing Peripheral Nerve Defects with Novel Bionic Tissue Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(17): e2203199.
[4] 高欣,孔令驰,史安琪,等.内芯外鞘神经导管的制备及表征[J].东华大学学报(自然科学版),2024,50(6):30-36.
[5] FENG Y, LI Y, SHEN PP, et al. Gene-Modified Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury: a Promising Better Alternative Therapy. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(8):2662-2682.
[6] KONG H, LIU P, LI H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: The Novel Therapeutic Option for Regenerative Dentistry. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(1):46-58.
[7] 王钊鑫,尼加提·吐尔逊,代慧娟,等.巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α对人牙周膜干细胞生物学行为的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(10):1521-1527.
[8] MEAD B, LOGAN A, BERRY M, et al. Concise Review: Dental Pulp Stem Cells: A Novel Cell Therapy for Retinal and Central Nervous System Repair. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):61-67.
[9] 蔡韵竹,朱姝,刘尧,等.牙源性干细胞用于治疗神经系统疾病的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2022,49(3):255-262.
[10] BASABRAIN MS, ZHONG J, LUO H, et al. Formation of Three-Dimensional Spheres Enhances the Neurogenic Potential of Stem Cells from Apical Papilla. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(11):604.
[11] NGAI P, LEE AHC, XU J, et al. Effects of L-Chg10-Teixobactin on Viability, Proliferation, and Osteo/Odontogenic Differentiation of Stem Cells from Apical Papilla. J Endod. 2023;49(2):162-168.
[12] XIAO Y, CHEN L, XU Y, et al. Circ-ZNF236 mediates stem cells from apical papilla differentiation by regulating LGR4-induced autophagy. Int Endod J. 2024;57(4):431-450.
[13] MARTENS W, BRONCKAERS A, POLITIS C, et al. Dental stem cells and their promising role in neural regeneration: an update. Clin Oral Investig. 2013;17(9):1969-1983.
[14] SONGSAAD AT, THAIRAT S, SEEMAUNG P, et al. Characterization of neural stem cells derived from human stem cells from the apical papilla undergoing three-dimensional neurosphere induction. J Appl Oral Sci. 2023;31:e20230209.
[15] MOLINA-HOLGADO E, ESTEBAN PF, AREVALO-MARTIN Á, et al. Endocannabinoid signaling in oligodendroglia. Glia. 2023;71(1):91-102.
[16] SELVARAJ P, TANAKA M, WEN J, et al. The Novel Monoacylglycerol Lipase Inhibitor MJN110 Suppresses Neuroinflammation, Normalizes Synaptic Composition and Improves Behavioral Performance in the Repetitive Traumatic Brain Injury Mouse Model. Cells. 2021;10(12): 3454.
[17] RAMESH K, ROSENBAUM DM. Molecular basis for ligand modulation of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179(14):3487-3495.
[18] MONTEIRO VIANA JC, DA SILVA GOMES GE, DUARTE OLIVEIRA FJ, et al. The Role of Different Types of Cannabinoids in Periodontal Disease: An Integrative Review. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(7):893.
[19] BLANDO S, RAFFAELE I, CHIRICOSTA L, et al. Cannabidiol Promotes Neuronal Differentiation Using Akt and Erk Pathways Triggered by Cb1 Signaling. Molecules. 2022;27(17):5644.
[20] SOUNDARA RAJAN T, GIACOPPO S, SCIONTI D, et al. Cannabidiol Activates Neuronal Precursor Genes in Human Gingival Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(6):1531-1546.
[21] 马玉,段子文,李淑慧,等.牙周膜干细胞与根尖牙乳头干细胞成骨及成牙本质能力比较的实验研究[J].口腔医学,2018,38(1):5-9.
[22] ZIPSER CM, CRAGG JJ, GUEST JD, et al. Cell-based and stem-cell-based treatments for spinal cord injury: evidence from clinical trials. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(7):659-670.
[23] SONGSAAD A, GONMANEE T, RUANGSAWASDI N, et al. Potential of resveratrol in enrichment of neural progenitor-like cell induction of human stem cells from apical papilla. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):542.
[24] SHEN Z, TSAO H, LARUE S, et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and/or Nerve Growth Factor Treatment Induces Expression of Dentinogenic, Neuronal, and Healing Markers in Stem Cells of the Apical Papilla. J Endod. 2021;47(6):924-931.
[25] BLEBEA NM, PRICOPIE AI, VLAD RA, et al. Phytocannabinoids: Exploring Pharmacological Profiles and Their Impact on Therapeutical Use. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(8):4204.
[26] ABIDI AH, ABHYANKAR V, ALGHAMDI SS, et al. Phytocannabinoids regulate inflammation in IL-1β-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts. J Periodontal Res. 2022;57(6):1127-1138.
[27] MARTINEZ RAMIREZ CE, RUIZ-PÉREZ G, STOLLENWERK TM, et al. Endocannabinoid signaling in the central nervous system. Glia. 2023; 71(1):5-35.
[28] 李永丰,任维,刘一辉.CB1受体通过钾离子通道介导外周镇痛作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(4):660-666.
[29] MADHUBALA D, PATRA A, KHAN MR, et al. Phytomedicine for neurodegenerative diseases: The road ahead. Phytother Res. 2024; 38(6):2993-3019.
[30] 乐明霞,周瑞,黄杜娟,等.大麻素-CB1/CB2受体系统对多巴胺神经元调节作用及其与帕金森病发生的研究进展[J].神经解剖学杂志,2017,33(6):753-757.
[31] 王海军,牛亚凯,陈巍.内源性大麻素系统在运动促进脑健康中的研究进展[J].生命科学,2021,33(9):1096-1103.
[32] MORRIS G, WALDER K, KLOIBER S, et al. The endocannabinoidome in neuropsychiatry: Opportunities and potential risks. Pharmacol Res. 2021;170:105729.
[33] HU M, ZHU D, ZHANG J, et al. Enhancing endocannabinoid signalling in astrocytes promotes recovery from traumatic brain injury. Brain. 2022;145(1):179-193.
[34] MENESES CCB, PIZZATTO LN, SIPERT CR, et al. Endocannabinoids Regulate Stem Cells of the Apical Papilla via a Cannabinoid Receptor and TRPV1-Independent Mechanism. J Endod. 2021;47(10):
1617-1624.
[35] QUE K, HE D, JIN Y, et al. Expression of Cannabinoid Type 1 Receptors in Human Odontoblast Cells. J Endod. 2017;43(2):283-288.
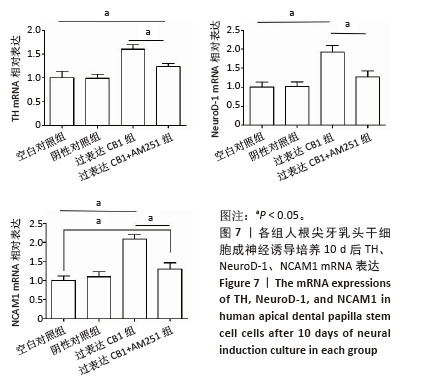
[36] PATASKAR A, JUNG J, SMIALOWSKI P, et al. NeuroD1 reprograms chromatin and transcription factor landscapes to induce the neuronal program. EMBO J. 2016;35(1):24-45.
[37] PARCERISAS A, ORTEGA-GASCÓ A, PUJADAS L, et al. The Hidden Side of NCAM Family: NCAM2, a Key Cytoskeleton Organization Molecule Regulating Multiple Neural Functions. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(18):10021.
[38] 李含章,李亚楠,郭磊,等.电针对帕金森病小鼠肠道NEK7/NLRP3炎症信号通路的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报,2024,47(10): 1466-1473.
[39] FERNÁNDEZ-RUIZ J, GÓMEZ M, HERNÁNDEZ M, et al. Cannabinoids and gene expression during brain development. Neurotox Res. 2004; 6(5):389-401.
[40] VALERI A, CHIRICOSTA L, GUGLIANDOLO A, et al. Cannabinerol and NSC-34 Transcriptomic Analysis: Is the Dose Who Makes Neuronal Differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(14):7541.
[41] SIMONOVIC J, TOLJIC B, LAZAREVIC M, et al. The Effect of Liquid-Phase Exfoliated Graphene Film on Neurodifferentiation of Stem Cells from Apical Papilla. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(18):3116.
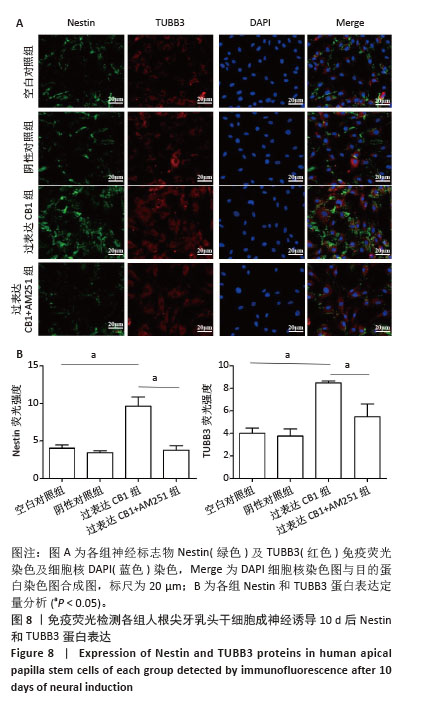
[42] RADWITZ J, HAUSRAT TJ, HEISLER FF, et al. Tubb3 expression levels are sensitive to neuronal activity changes and determine microtubule growth and kinesin-mediated transport. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(11):575.
[43] XAPELLI S, AGASSE F, SARDÀ-ARROYO L, et al. Activation of type 1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1R) promotes neurogenesis in murine subventricular zone cell cultures. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63529.
[44] 孙军,娄雅昕,苏凡,等.花生四烯酸氨基乙醇对人成牙本质细胞样细胞MMP-9表达的影响[J].北京口腔医学,2023,31(6):385-390.
[45] YAN W, CAO Y, YANG H, et al. CB1 enhanced the osteo/dentinogenic differentiation ability of periodontal ligament stem cells via p38 MAPK and JNK in an inflammatory environment. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(6):e12691. |