[1] SMOLEN JS, LANDEWÉ RBM, BERGSTRA SA, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(1):3-18.
[2] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, BARTON A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001.
[3] WINTHROP KL, WEINBLATT ME, CROW MK, et al. Unmet need in rheumatology: reports from the Targeted Therapies meeting 2018. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(7):872-878.
[4] VISSER H, LE CESSIE S, VOS K, et al. How to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis early: a prediction model for persistent (erosive) arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(2):357-365.
[5] FINZEL S, RECH J, SCHMIDT S, et al. Repair of bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors is based on bone apposition at the base of the erosion. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(9):1587-1593.
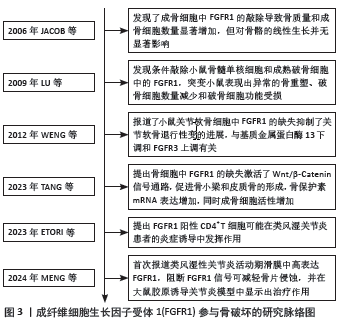
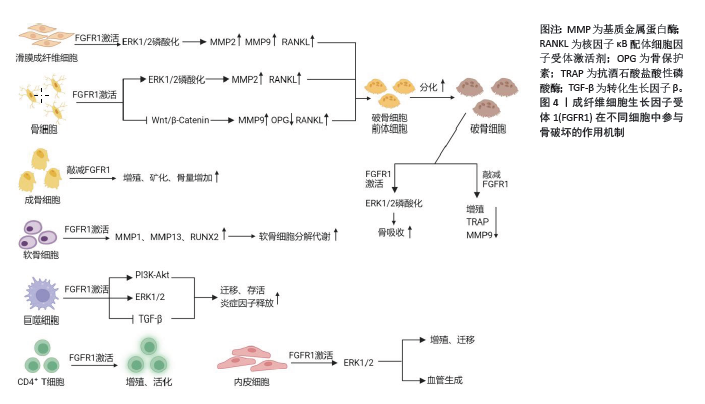
[6] MENG X, CHEN Z, LI T, et al. Role and Therapeutic Potential for Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor 10/FGFR1 in Relapsed Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024;76(1):32-47.
[7] SCHETT G, TANAKA Y, ISAACS JD. Why remission is not enough: underlying disease mechanisms in RA that prevent cure. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(3):135-144.
[8] ORNITZ DM, ITOH N. New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors. WIREs Mech Dis. 2022;14(4):e1549.
[9] XIE Y, SU N, YANG J, et al. FGF/FGFR signaling in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):181.
[10] ORNITZ DM. FGF signaling in the developing endochondral skeleton. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005;16(2):205-213.
[11] TAN Q, CHEN B, WANG Q, et al. A novel FGFR1-binding peptide attenuates the degeneration of articular cartilage in adult mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(12):1733-1743.
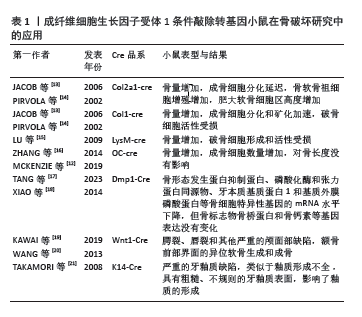
[12] MCKENZIE J, SMITH C, KARUPPAIAH K, et al. Osteocyte Death and Bone Overgrowth in Mice Lacking Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors 1 and 2 in Mature Osteoblasts and Osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(9):1660-1675.
[13] JACOB AL, SMITH C, PARTANEN J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling in the osteo-chondrogenic cell lineage regulates sequential steps of osteoblast maturation. Dev Biol. 2006;296(2):315-328.
[14] PIRVOLA U, YLIKOSKI J, TROKOVIC R, et al. FGFR1 is required for the development of the auditory sensory epithelium. Neuron. 2002;35(4): 671-680.
[15] LU X, SU N, YANG J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 regulates the differentiation and activation of osteoclasts through Erk1/2 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390(3):494-499.
[16] ZHANG Y, SU N, LUO F, et al. Deletion of Fgfr1 in osteoblasts enhances mobilization of EPCs into peripheral blood in a mouse endotoxemia model. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10(9):1064-1071.
[17] TANG Y, YANG P, JIN M, et al. Fgfr1 deficiency in osteocytes leads to increased bone mass by enhancing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Bone. 2023;174:116817.
[18] XIAO Z, HUANG J, CAO L, et al. Osteocyte-specific deletion of Fgfr1 suppresses FGF23. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e104154.
[19] KAWAI M, HERRMANN D, FUCHS A, et al. Fgfr1 conditional-knockout in neural crest cells induces heterotopic chondrogenesis and osteogenesis in mouse frontal bones. Med Mol Morphol. 2019;52(3):156-163.
[20] WANG C, CHANG JY, YANG C, et al. Type 1 fibroblast growth factor receptor in cranial neural crest cell-derived mesenchyme is required for palatogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(30):22174-22183.
[21] TAKAMORI K, HOSOKAWA R, XU X, et al. Epithelial fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 regulates enamel formation. J Dent Res. 2008;87(3): 238-243.
[22] COMPTON JT, LEE FY. A review of osteocyte function and the emerging importance of sclerostin. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(19):1659-1668.
[23] WANG K, JI W, YU Y, et al. FGFR1-ERK1/2-SOX2 axis promotes cell proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastasis in FGFR1-amplified lung cancer. Oncogene. 2018;37(39):5340-5354.
[24] CHEN LC, SHIBU MA, LIU CJ, et al. ERK1/2 mediates the lipopolysaccharide-induced upregulation of FGF-2, uPA, MMP-2, MMP-9 and cellular migration in cardiac fibroblasts. Chem Biol Interact. 2019;306:62-69.
[25] SALHOTRA A, SHAH HN, LEVI B, et al. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(11):696-711.
[26] WILKIE AO. Bad bones, absent smell, selfish testes: the pleiotropic consequences of human FGF receptor mutations. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005;16(2):187-203.
[27] RICE DP, RICE R, THESLEFF I. Fgfr mRNA isoforms in craniofacial bone development. Bone. 2003;33(1):14-27.
[28] LEE Y, BAE KJ, CHON HJ, et al. A Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Dovitinib (TKI-258), Enhances BMP-2-Induced Osteoblast Differentiation In Vitro. Mol Cells. 2016;39(5):389-394.
[29] WU AL, FENG B, CHEN MZ, et al. Antibody-mediated activation of FGFR1 induces FGF23 production and hypophosphatemia. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57322.
[30] KAWAGUCHI H, CHIKAZU D, NAKAMURA K, et al. Direct and indirect actions of fibroblast growth factor 2 on osteoclastic bone resorption in cultures. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(3):466-473.
[31] CHIKAZU D, HAKEDA Y, OGATA N, et al. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 directly stimulates mature osteoclast function through activation of FGF receptor 1 and p42/p44 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(40): 31444-31450.
[32] NAKAJIMA A, NAKAJIMA F, SHIMIZU S, et al. Spatial and temporal gene expression for fibroblast growth factor type I receptor (FGFR1) during fracture healing in the rat. Bone. 2001;29(5):458-466.
[33] AUKES K, FORSMAN C, BRADY NJ, et al. Breast cancer cell-derived fibroblast growth factors enhance osteoclast activity and contribute to the formation of metastatic lesions. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0185736.
[34] ORNITZ DM, ITOH N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2015;4(3):215-266.
[35] KAROLAK MR, YANG X, ELEFTERIOU F. FGFR1 signaling in hypertrophic chondrocytes is attenuated by the Ras-GAP neurofibromin during endochondral bone formation. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(9):2552-2564.
[36] TUZON CT, RIGUEUR D, MERRILL AE. Nuclear Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Skeletal Development and Disease. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019;17(3):138-146.
[37] WANG Z, HUANG Y, HE Y, et al. Myocardial protection by heparin-based coacervate of FGF10. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(7):1867-1877.
[38] YAN D, CHEN D, COOL SM, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 is principally responsible for fibroblast growth factor 2-induced catabolic activities in human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(4):R130.
[39] TANG J, SU N, ZHOU S, et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 3 Inhibits Osteoarthritis Progression in the Knee Joints of Adult Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(10):2432-2443.
[40] WENG T, YI L, HUANG J, et al. Genetic inhibition of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 in knee cartilage attenuates the degeneration of articular cartilage in adult mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(12):3982-3992.
[41] SHEN J, LI J, WANG B, et al. Deletion of the transforming growth factor β receptor type II gene in articular chondrocytes leads to a progressive osteoarthritis-like phenotype in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(12):3107-3119.
[42] ZHOU YX, XU X, CHEN L, et al. A Pro250Arg substitution in mouse Fgfr1 causes increased expression of Cbfa1 and premature fusion of calvarial sutures. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9(13):2001-2008.
[43] WANG Z, HUANG J, ZHOU S, et al. Loss of Fgfr1 in chondrocytes inhibits osteoarthritis by promoting autophagic activity in temporomandibular joint. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(23):8761-8774.
[44] YAO X, ZHANG J, JING X, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 18 exerts anti-osteoarthritic effects through PI3K-AKT signaling and mitochondrial fusion and fission. Pharmacol Res. 2019;139:314-324.
[45] DELUCCHI Á, TORO L, ALZAMORA R, et al. Glucocorticoids Decrease Longitudinal Bone Growth in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients by Stimulating the FGF23/FGFR3 Signaling Pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(10):1851-1861.
[46] DAVIDSON D, BLANC A, FILION D, et al. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 18 signals through FGF receptor 3 to promote chondrogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(21):20509-20515.
[47] VALVERDE-FRANCO G, BINETTE JS, LI W, et al. Defects in articular cartilage metabolism and early arthritis in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 deficient mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(11):1783-1792.
[48] TAKASE N, KOMA Y, URAKAWA N, et al. NCAM- and FGF-2-mediated FGFR1 signaling in the tumor microenvironment of esophageal cancer regulates the survival and migration of tumor-associated macrophages and cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2016;380(1):47-58.
[49] REED JR, STONE MD, BEADNELL TC, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 activation in mammary tumor cells promotes macrophage recruitment in a CX3CL1-dependent manner. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45877.
[50] ZHAO YN, LIU ZD, YAN T, et al. Macrophage-specific FGFR1 deletion alleviates high-fat-diet-induced liver inflammation by inhibiting the MAPKs/TNF pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024;45(5):988-1001.
[51] BOHRER LR, SCHWERTFEGER KL. Macrophages promote fibroblast growth factor receptor-driven tumor cell migration and invasion in a CXCR2-dependent manner. Mol Cancer Res. 2012;10(10):1294-1305.
[52] DAVIDSON S, COLES M, THOMAS T, et al. Fibroblasts as immune regulators in infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21(11):704-717.
[53] MARSH LJ, KEMBLE S, REIS NISA P, et al. Fibroblast pathology in inflammatory joint disease. Immunol Rev. 2021;302(1):163-183.
[54] BUCKLEY CD, OSPELT C, GAY S, et al. Author Correction: Location, location, location: how the tissue microenvironment affects inflammation in RA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(4):246.
[55] KOMATSU N, TAKAYANAGI H. Mechanisms of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis - immune cell-fibroblast-bone interactions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(7):415-429.
[56] DANKS L, KOMATSU N, GUERRINI MM, et al. RANKL expressed on synovial fibroblasts is primarily responsible for bone erosions during joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(6):1187-1195.
[57] BARTOK B, FIRESTEIN GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010;233(1):233-255.
[58] NYGAARD G, FIRESTEIN GS. Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(6):316-333.
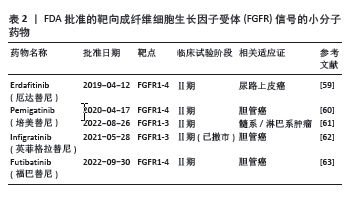
[59] SIEFKER-RADTKE AO, NECCHI A, PARK SH, et al. Efficacy and safety of erdafitinib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: long-term follow-up of a phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(2):248-258.
[60] ABOU-ALFA GK, SAHAI V, HOLLEBECQUE A, et al. Pemigatinib for previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(5):671-684.
[61] GOTLIB J, KILADJIAN J, VANNUCCHI A, et al. A Phase 2 Study of Pemigatinib (FIGHT-203; INCB054828) in Patients with Myeloid/Lymphoid Neoplasms (MLNs) with Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 (FGFR1) Rearrangement (MLN FGFR1). Blood. 2021;138(Supplement 1):385.
[62] JAVLE MM, ROYCHOWDHURY S, KELLEY RK, et al. Final results from a phase II study of infigratinib (BGJ398), an FGFR-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with previously treated advanced cholangiocarcinoma harboring an FGFR2 gene fusion or rearrangement. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(3_suppl):265.
[63] GOYAL L, MERIC-BERNSTAM F, HOLLEBECQUE A, et al. Futibatinib for FGFR2-Rearranged Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(3):228-239.
[64] SHODA J, TANAKA S, ETORI K, et al. Semaphorin 3G exacerbates joint inflammation through the accumulation and proliferation of macrophages in the synovium. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):134.
[65] ZHAO XM, BYRD VM, MCKEEHAN WL, et al. Costimulation of human CD4+ T cells by fibroblast growth factor-1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor). J Immunol. 1995;155(8):3904-3911.
[66] MANABE N, ODA H, NAKAMURA K, et al. Involvement of fibroblast growth factor-2 in joint destruction of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999;38(8):714-720.
[67] SATO H, KAZAMA JJ, MURASAWA A, et al. Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Intern Med. 2016;55(2):121-126.
[68] GOULD PW, ZEMEL BS, TARATUTA EG, et al. Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Associations With Disease Characteristics, Body Composition, and Physical Functioning. J Rheumatol. 2021;48(4):504-512.
[69] ETORI K, TANAKA S, TAMURA J, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 as a potential marker of terminal effector peripheral T helper cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(11):3763-3769.
[70] BYRD V, ZHAO XM, MCKEEHAN WL, et al. Expression and functional expansion of fibroblast growth factor receptor T cells in rheumatoid synovium and peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39(6):914-922.
[71] BALOGH E, BINIECKA M, FEARON U, et al. Angiogenesis in Inflammatory Arthritis. Isr Med Assoc J. 2019;21(5):345-352.
[72] LEBLOND A, ALLANORE Y, AVOUAC J. Targeting synovial neoangiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2017; 16(6):594-601.
[73] WANG Y, WU H, DENG R. Angiogenesis as a potential treatment strategy for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;910:174500.
[74] ZHANG YF, GAO SS, LI JL, et al. Comparison and correlation study of synovial ultrasound indices and serum VEGF in rheumatoid wrist arthritis before and after treatment. Clin Rheumatol. 2022;41(9): 2677-2683.
[75] LEE C, CHEN R, SUN G, et al. VEGF-B prevents excessive angiogenesis by inhibiting FGF2/FGFR1 pathway. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):305.
[76] ZHU X, QIU C, WANG Y, et al. FGFR1 SUMOylation coordinates endothelial angiogenic signaling in angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(26):e2202631119.
[77] TAN Q, WANG Z, WANG Q, et al. A novel FGFR1-binding peptide exhibits anti-tumor effect on lung cancer by inhibiting proliferation and angiogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14(10):1389-1398.
[78] WANG Y, WU H, GUI BJ, et al. Geniposide alleviates VEGF-induced angiogenesis by inhibiting VEGFR2/PKC/ERK1/2-mediated SphK1 translocation. Phytomedicine. 2022;100:154068.
[79] WU Q, HAN L, GUI W, et al. MiR-503 suppresses fibroblast activation and myofibroblast differentiation by targeting VEGFA and FGFR1 in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(24): 14339-14348.
[80] GAO M, LI X, YANG M, et al. TNFAIP3 mediates FGFR1 activation-induced breast cancer angiogenesis by promoting VEGFA expression and secretion. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022;24(12):2453-2465.
[81] OBERKERSCH RE, PONTARIN G, ASTONE M, et al. Aspartate metabolism in endothelial cells activates the mTORC1 pathway to initiate translation during angiogenesis. Dev Cell. 2022;57(10):1241-1256.e8.
[82] NOURSE MB, ROLLE MW, PABON LM, et al. Selective control of endothelial cell proliferation with a synthetic dimerizer of FGF receptor-1. Lab Invest. 2007;87(8):828-835.
|