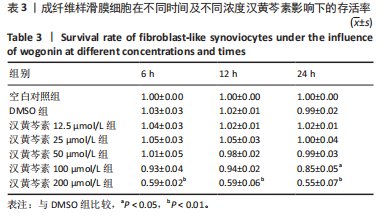
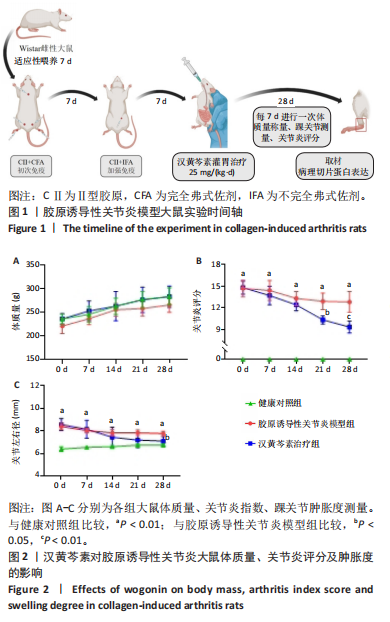
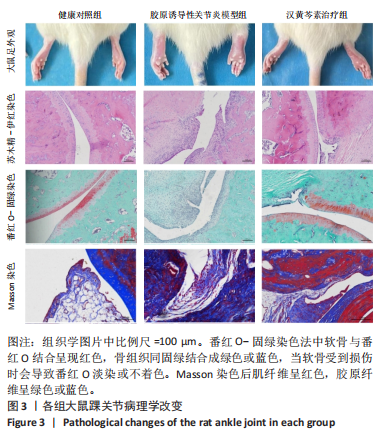
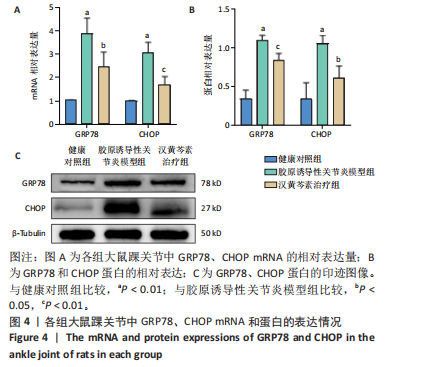
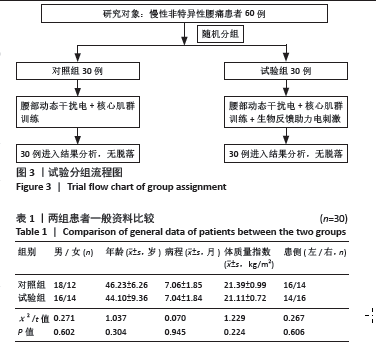
[1] NYGAARD G, FIRESTEIN GS. Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(6):316-333.
[2] DAIKH DI. Rheumatoid arthritis: Evolving recognition of a common disease. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2022;36(1):101740.
[3] SPARKS JA. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(1): ITC1-ITC16.
[4] BARTOK B, FIRESTEIN GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010;233(1):233-255.
[5] ZHANG Q, LIU J, ZHANG M, et al. Apoptosis induction of fibroblast-like synoviocytes is an important molecular-mechanism for herbal medicine along with its active components in treating rheumatoid arthritis. Biomolecules. 2019;9(12):795.
[6] TU J, HONG W, ZHANG P, et al. Ontology and function of fibroblast-like and macrophage-like synoviocytes: how do they talk to each other and can they be targeted for rheumatoid arthritis therapy? Front Immunol. 2018;9:1467.
[7] BOTTINI N, FIRESTEIN GS. Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: passive responders andimprinted aggressors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013;9(1):24-33.
[8] SCHWARZ DS, Blower MD. The endoplasmic reticulum: structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:79-94.
[9] LI WY, YANG F, LI X, et al. Stress granules inhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis during hypoxia-induced injury in acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol. 2023;29(8):1315.
[10] RAHMATI M, MOOSAVI MA, MCDERMOTT MF. ER stress: a therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis?. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018;39(7):610-623.
[11] DE SEABRA RODRIGUES DIAS IR, LO HH, ZHANG K, et al. Potential therapeutic compounds from traditional Chinese medicine targeting endoplasmic reticulum stress to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Res. 2021;170:105696.
[12] DESENY D, BIANCHI E, BAIWIR D, et al. Proteins involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress are modulated in synovitis of osteoarthritis, chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy and rheumatoid arthritis, and correlate with the histological inflammatory score. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14159.
[13] LI W, CAO T, LUO C, et al. Crosstalk between ER stress, NLRP3 inflammasome, and inflammation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020, 104: 6129-6140.
[14] KHAN NM, HASEEB A, ANSARI MY, et al. Dataset of effect of Wogonin, a natural flavonoid, on the viability and activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in IL-1β-stimulated human OA chondrocytes. Data Brief. 2017;12:150-155.
[15] FAN L, QIU D, HUANG G, et al. Wogonin Suppresses IL-10 Production in B Cells via STAT3 and ERK Signaling Pathway. J Immunol Res. 2020; 2020: 3032425.
[16] HUYNH DL, NGAU TH, NGUYEN NH, et al. Potential therapeutic and pharmacological effects of Wogonin: an updated review. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(12):9779-9789.
[17] BANIK K, KHATOON E, HARSHA C, et al. Wogonin and its analogs for the prevention and treatment of cancer: A systematic review. Phytother Res. 2022;36(5):1854-1883.
[18] 陆璐, 刘宇婧, 李瑗,等. 基于NLRP3相关炎症反应和肠道黏膜屏障功能探究汉黄芩素治疗溃疡性结肠炎小鼠的作用机制[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2022,37(10):5992-5999.
[19] 沈晓庆, 王晶, 李婷君. 汉黄芩素对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠的治疗作用及对NLRP3炎症小体的影响[J]. 中医药导报,2021,27(8):26-30.
[20] 王慧莲, 孟庆良, 李松伟,等. 汉黄芩素通过激活活性氧簇介导的p38MAPK信号通路诱导类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞凋亡[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(7):890-895.
[21] 李玉彤, 刘静淑, 李振. ChAT/α7nAChR/核因子κB信号途径在类风湿关节炎发病中的免疫调控[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(35): 5596-5602.
[22] 姬霄霄, 李振, 郝慧琴,等. 防己黄芪汤对CIA大鼠关节PI3K-Akt通路的调控作用研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2023,39(2):291-296.
[23] HUANG Y, GUO L, CHITTI R, et al. Wogonin ameliorate complete Freund’s adjuvant induced rheumatoid arthritis via targeting NF‐κB/MAPK signaling pathway. BioFactors. 2020;46(2):283-291.
[24] KABALA PA, ANGIOLILLI C, YEREMENKO N, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress cooperates with Toll-like receptor ligation in driving activation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):207.
[25] COMBE B, RINCHEVAL N, BERENBAUM F, et al. Current favourable 10-year outcome of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: data from the ESPOIR cohort. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2021;60(11):5073-5079.
[26] WANG J, CHEN S, ZHANG J, et al. Scutellaria baicalensis georgi is a promising candidate for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:946030.
[27] PARK YJ, YOO SA, KIM WU. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. J Korean Med Sci. 2014;29(1):2-11.
[28] CHOI Y, LEE EG, JEONG JH, et al. 4-Phenylbutyric acid, a potent endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibitor, attenuates the severity of collagen-induced arthritis in mice via inhibition of proliferation and inflammatory responses of synovial fibroblasts. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2021;37(7):604-615.
[29] LI X, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. Inhibition of transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) channel induces RA FLSs apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33: 1565-1574.
[30] BETTIGOLE SE, GLIMCHER LH. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:107-138.
[31] PENG YW, ZHANG M, HU JK. Non-coding RNAs involved in fibroblast-like synoviocyte functioning in arthritis rheumatoid: From pathogenesis to therapy. Cytokine. 2024;173:156418.
[32] LU Q, WANG J, ZHANG X, et al. TXNDC5 protects synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis from the detrimental effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2020;9(1):23-29.
[33] MARCINIAK SJ, CHAMBERS JE, RON D. Pharmacological targeting of endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022; 21(2):115-140.
[34] MIGLIORANZA SCAVUZZI B, HOLOSHITZ J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress, and rheumatic diseases. Antioxidants(Basel). 2022; 11(7):1306.
[35] KIM EK, KIM Y, YANG JY, et al. Prx1 Regulates Thapsigargin-Mediated UPR Activation and Apoptosis. Genes(Basel). 2022;13(11):2033.
[36] HU H, TIAN M, DING C, et al. The C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) transcription factor functions in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and microbial infection. Front Immunol. 2019;9:3083.
[37] WISEMAN RL, MESGARZADEH JS, HENDERSHOT LM. Reshaping endoplasmic reticulum quality control through the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell. 2022;82(8):1477-1491.
[38] SO JS. Roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress in immune responses. Mol Cells. 2018;41(8):705-716.
[39] AHMADIANY M, ALAVI-SAMANI M, HASHEMI Z, et al. The Increased RNase Activity of IRE1α in PBMCs from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Adv Pharm Bull. 2019;9(3):505-509.
|