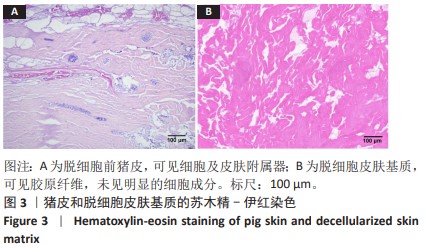
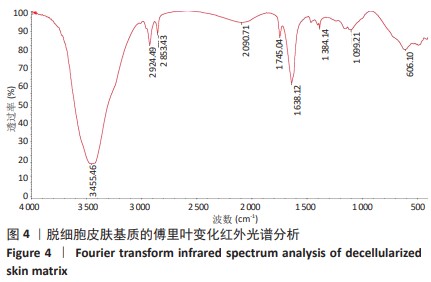
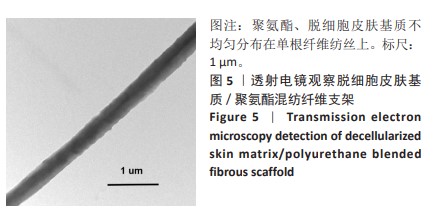
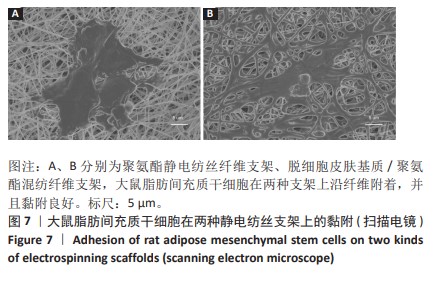
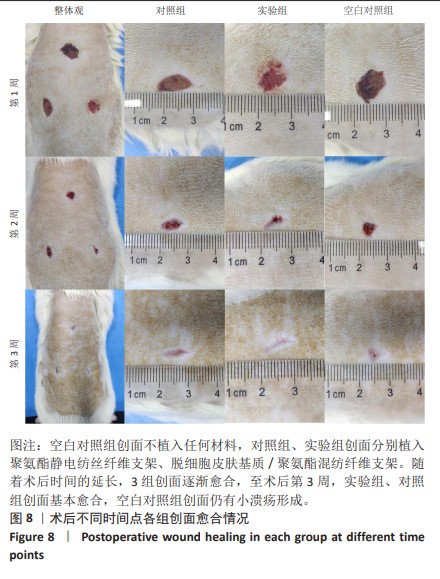
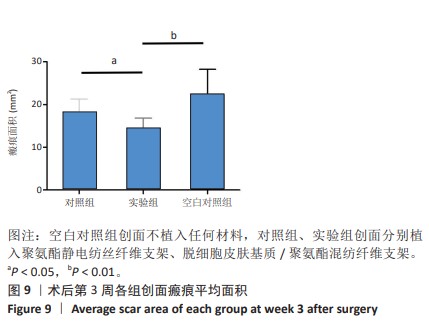
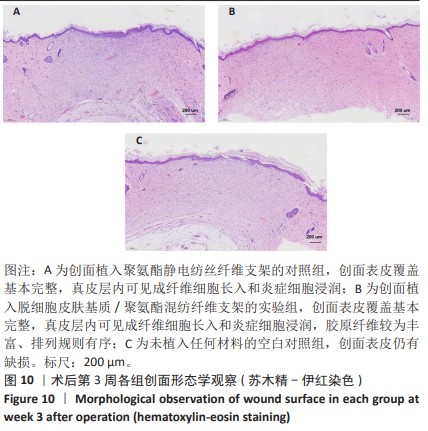
[1] RANI S, RITTER T. The Exosome-A Naturally Secreted Nanoparticle and its Application to Wound Healing. Adv Mater. 2016;28(27):5542-5552.
[2] SCHLOTTMANN F, BUCAN V, VOGT PM, et al. A Short History of Skin Grafting in Burns: From the Gold Standard of Autologous Skin Grafting to the Possibilities of Allogeneic Skin Grafting with Immunomodulatory Approaches. Medicina. 2021;57(3):225.
[3] ZHANG X, XU W, HU X. Tissue-Engineered Skin Regenerative Units for Epidermal Keratinocytes Expansion and Wound Healing. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e932978.
[4] WANG YC, ZHANG Y, LI T, et al. Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Promote Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Embedded in Collagen/Platelet-Rich Plasma Scaffold and Accelerate Wound Healing. Adv Mater. 2023;35(40):e2303642.
[5] ZHOU GY, ZHU JY, INVERARITY C, et al. Fabrication of Fibrin/Polyvinyl Alcohol Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering via Emulsion Templating. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(5):1151.
[6] MA PF, LI MY, HU JL, et al. New skin tissue engineering scaffold with sulfated silk fibroin/chitosan/hydroxyapatite and its application. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;640:117-124.
[7] GSIB O, EGGERMONT LJ, EGLES C, et al. Engineering a macroporous fibrin-based sequential interpenetrating polymer network for dermal tissue engineering. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(24):7106-7116.
[8] ALAM MR, ALIMUZZAMAN S, SHAHID MA, et al. Collagen/ Nigella sativa/chitosan inscribed electrospun hybrid bio-nanocomposites for skin tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2023;34(11):1517-1538.
[9] SU T, ZHANG MY, ZENG QK, et al. Mussel-inspired agarose hydrogel scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):579-588.
[10] VARGAS M, MARTINEZ-GARCIA F, OFFENS F, et al. Viscoelastic properties of plasma-agarose hydrogels dictate favorable fibroblast responses for skin tissue engineering applications. Biomater Adv. 2022; 139:212967.
[11] MOLINA MI, CHEN CA, MARTINEZ J, et al. Novel Electrospun Polycaprolactone/Calcium Alginate Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering. Materials (Basel). 2022;16(1):136.
[12] GUO YJ, WANG XY, LI BB, et al. Oxidized sodium alginate crosslinked silk fibroin composite scaffold for skin tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022;110(12):2667-2675.
[13] SALESA B, LLORENS-GÁMEZ M, SERRANO-AROCA Á. Study of 1D and 2D carbon nanomaterial in alginate films. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(2):206.
[14] XU J, FANG H, SU Y, et al. A 3D bioprinted decellularized extracellular matrix/gelatin/quaternized chitosan scaffold assembling with poly (ionic liquid)s for skin tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;220: 1253-1266.
[15] XU J, FANG H, ZHENG SS, et al. A biological functional hybrid scaffold based on decellularized extracellular matrix/gelatin/chitosan with high biocompatibility and antibacterial activity for skin tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;187:840-849.
[16] XIA B, KIM DH, BANSAL S, et al. Development of A Decellularized Meniscus Matrix-Based Nanofibrous Scaffold for Meniscus Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2021;128:175-185.
[17] BASARA G, OZCEBE SG, ELLIS BW, et al. Tunable human myocardium derived decellularized extracellular matrix for 3D bioprinting and cardiac tissue engineering. Gels. 2021;7(2):70.
[18] GAO X, WEN ML, LIU Y, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of PU/PLCL/CMCS Electrospun Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(22):5029.
[19] HAJIKHANI M, EMAM-DJOMEH Z, ASKARI G. Fabrication and characterization of mucoadhesive bioplastic patch via coaxial polylactic acid (PLA) based electrospun nanofibers with an- timicrobial and wound healing application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;172:143-153.
[20] CHENG CC, YANG XJ, FAN WL, et al. Cytosine-Functionalized Supramolecular Polymer-Mediated Cellular Behavior and Wound Healing. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(9):3857-3866.
[21] MOVAHEDI M, ASEFNEJAD A, RAFIENIA M, et al. Potential of novel electrospun core-shell structured polyurethane/starch (hyaluronic acid) nanofibers for skin tissue engineering: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;146:627-637.
[22] LAKRA R, KIRAN MS, KORRAPATI PS, et al. Electrospun gelatin-polyethylenimine blend nanofibrous scaffold for biomedical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(12):129.
[23] JOY J, AID-LAUNAIS R, PEREIRA J, et al. Gelatin-polytrimethylene carbonate blend based electrospun tubular construct as a potential vascular biomaterial. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;106:110178.
[24] PATEL KH, TALOVIC M, DUNN AJ, et al. Aligned nanofibers of decellularized muscle extracellular matrix for volumetric muscle loss. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(6):2528-2537.
[25] GAO S, GUO WM, CHEN MX, et al. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun nanofibers composed of decellularized meniscus extracellular matrix and polycaprolactone for meniscus tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(12):2273-2285.
[26] LIU C, JIN ZX, GE X, et al. Decellularized Annulus Fibrosus Matrix/Chitosan hydrogels for annulus fibrous tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2019;25(23-24):1605-1613.
[27] NAMVIRIYACHOTE N, MUANGMAN P, CHINAROONCHAI K, et al. Polyurethanebiomacromolecule combined foam dressing containing asiattcoside: fabricatton, characterizatton and clinical efffcacy for traumattc dermal wound treatment. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;143: 510-520.
[28] SADEGHIANMARYAN A, KARIMI Y, NAGHIEH S, et al. Electrospinning of Scaffolds from the Polycaprolactone/Polyurethane Composite with Graphene Oxide for Skin Tissue Engineering. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2020;191(2):567-578.
[29] SOLARTE DAVID VA, GÜIZA-ARGÜELLO VR, ARANGO-RODRÍGUEZ ML,
et al. Decellularized Tissues for Wound Healing: Towards Closing the Gap Between Scaffold Design and Effective Extracellular Matrix Remodeling. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:821852.
[30] CHAUDHARI AA, VIG K, BAGANIZI DR, et al. Future Prospects for Scaffolding Methods and Biomaterials in Skin Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):1974.
[31] SHEIKHOLESLAM M, WRIGHT MEE, CHENG N, et al. Electrospun Polyurethane-Gelatin Composite: A New Tissue-Engineered Scaffold for Application in Skin Regeneration and Repair of Complex Wounds. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(1):505-516.
[32] PRASAD T, SHABEENA EA, VINOD D, et al. Characterization and in vitro evaluation of electrospun chitosan/polycaprolactone blend fibrous mat for skin tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(1):5352.
[33] PEREIRA AL, SEMITELA Â, GIRÃO AF, et al. Three-dimensional nanofibrous and porous scaffolds of poly(ε-caprolactone)-chitosan blends for musculoskeletal tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023;111(7):950-961.
[34] HERNÁNDEZ-RANGEL A, MARTIN-MARTINEZ ES. Collagen based electrospun materials for skin wounds treatment.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(9):1751-1764.
[35] GIL-CIFUENTES L, JIMÉNEZ RA, FONTANILLA MR. Evaluatton of collagen type I scaffolds including gelattn-collagen microparttcles and Aloe vera in a model of full-thickness skin wound. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019;9(1):25-36.
[36] GILPIN A, YANG Y. Decellularization Strategies for Regenerative Medicine: From Processing Techniques to Applications. Biomed Res Int. 2017:2017:9831534.
[37] 郭宝林,陈志强,王术勇,等.猪皮细胞外基质促进创伤小鼠再表皮化的实验研究[J].军事医学,2018,42(3):169-175,181.
[38] CARVALHO J, ZANATA F, ALOISE AC, et al. Acellular dermal matrix in skin wound healing in rabbits - histological and histomorphometric analyses. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021;76:e2066.
[39] QI YJ, DONG ZX, CHU HZ, et al. Denatured acellular dermal matrix seeded with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for wound healing in mice. Burns. 2019;45(7):1685-1694.
[40] GHORBANI F, MORADI L, SHADMEHR MB, et al. In-vivo characterization of a 3D hybrid scaffold based on PCL/decellularized aorta for tracheal tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;81:74-83.
|