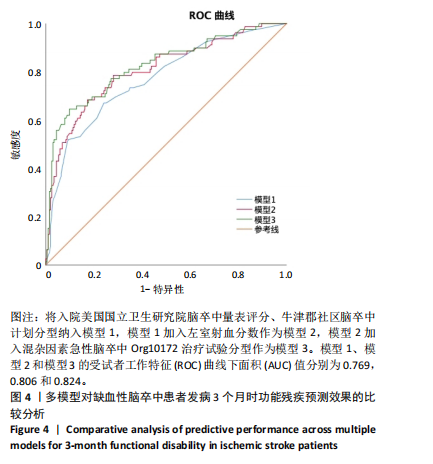
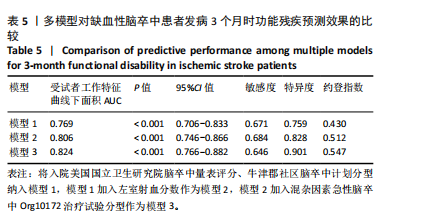
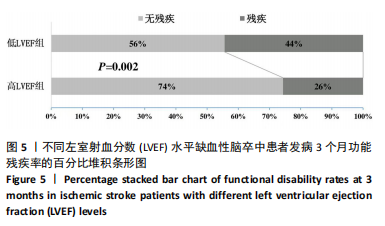
[1] FEIGIN VL, BRAININ M, NORRVING B, et al. World stroke organization (wso): Global stroke fact sheet 2022. Int J Stroke. 2022;17(1):18-29.
[2] KE C, SHI W, ZHOU Z, et al. Overview of evidence-based research on acupuncture for stroke treatment using magnetic resonance imaging technology. Front Neurosci. 2024;18:1495435.
[3] Hernandez-Jimenez M, Abad-Santos F, Cotgreave I, et al. Safety and efficacy of aptoll in patients with ischemic stroke undergoing endovascular treatment: A phase 1/2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2023;80(8):779-788.
[4] MA R, SUN X, LIU Z, et al. Ferroptosis in ischemic stroke and related traditional chinese medicines. Molecules. 2024;29(18):4359.
[5] CHEN J, LI X, HU R, et al. The clinical value of fibrosis indices for predicting the hemorrhagic transformation in patients with acute ischemic stroke after intravenous thrombolysis. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024;16:1492410.
[6] MIKI K, NAKANO M, AIZAWA K, et al. Risk factors and localization of silent cerebral infarction in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2019;16(9):1305-1313.
[7] KELLEY RE, KELLEY BP. Heart-brain relationship in stroke. Biomedicines. 2021;9(12):1835.
[8] EDWARDS JD, HEALEY JS, FANG J, et al. Atrial cardiopathy in the absence of atrial fibrillation increases risk of ischemic stroke, incident atrial fibrillation, and mortality and improves stroke risk prediction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9(11):e013227.
[9] PARK HK, KIM BJ, YOON CH, et al. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in ischemic stroke: Functional and vascular outcomes. J Stroke. 2016; 18:195-202.
[10] RYU WS, PARK JB, KO SB, et al. Diastolic dysfunction and outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;41(3-4):148-155.
[11] MANNINA C, ITO K, JIN Z, et al. Association of left atrial strain with ischemic stroke risk in older adults. JAMA Cardiol. 2023;8:317-325.
[12] OBOKATA M, NEGISHI K, KUROSAWA K, et al. Left atrial strain provides incremental value for embolism risk stratification over cha(2)ds(2)-vasc score and indicates prognostic impact in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014;27(7):709-716. e4.
[13] ZINGALES V, ESPOSITO MR, QUAGLIATA M, et al. Comparative study of spheroids (3d) and monolayer cultures (2d) for the in vitro assessment of cytotoxicity induced by the mycotoxins sterigmatocystin, ochratoxin a and patulin. Foods. 2024;13(4):564.
[14] WU T, GONG L, ZHANG C, et al. Three-dimensional echocardiography and strain cardiac imaging in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023;13(12):7753-7764.
[15] BRAND A, FRUMKIN D, HUBSCHER A, et al. Phasic left atrial strain analysis to discriminate cardiac amyloidosis in patients with unclear thick heart pathology. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021;22(6):680-687.
[16] MARCHESE P, SCALESE M, GIORDANO R, et al. Pediatric ranges of normality for 2d speckle-tracking echocardiography atrial strain: Differences between p- and r-gating and among new (atrial designed) and conventional (ventricular specific) software’s. Echocardiography. 2021;38(12):2025-2031.
[17] REDDIN C, CANAVAN M, HANKEY GJ, et al. Association of vascular risk with severe vs non-severe stroke: An analysis of the interstroke study. Neurology. 2024;103:e210087.
[18] SALIM HA, LAKHANI DA, MEI J, et al. Prolonged venous transit is associated with lower odds of excellent recovery after reperfusion in anterior large-vessel occlusion stroke. Eur J Neurol. 2025;32(1):e16563.
[19] ZEDDE M, LATTANZI S, PILOTTO A, et al. Premorbid frailty, stress hyperglycemia ratio, and functional outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. 2024;15:1463814.
[20] 中国卒中学会,中国卒中学会神经介入分会,中华预防医学会卒中预防与控制专业委员会介入学组.急性缺血性卒中血管内治疗中国指南 2018[J].中国卒中杂志,2018,13(7):706-729.
[21] Correction to: Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke. 2019;50:e440-e441.
[22] WOLF PA, ABBOTT RD, KANNEL WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The framingham study. Stroke. 1991;22:983-988.
[23] VIRK HUH, ESCOBAR J, RODRIGUEZ M, et al. Dual antiplatelet therapy: A concise review for clinicians. Life (Basel). 2023;13(7):1580.
[24] SCHEITZ JF, SPOSATO LA, SCHULZ-MENGER J, et al. Stroke-heart syndrome: Recent advances and challenges. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022; 11:e026528.
[25] QU Y, SUN YY, ABUDUXUKUER R, et al. Heart rate variability parameter changes in patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing intravenous thrombolysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023;12:e028778.
[26] BALINT B, JAREMEK V, THORBURN V, et al. Left atrial microvascular endothelial dysfunction, myocardial inflammation and fibrosis after selective insular cortex ischemic stroke. Int J Cardiol. 2019;292:148-155.
[27] SIMATS A, ZHANG S, MESSERER D, et al. Innate immune memory after brain injury drives inflammatory cardiac dysfunction. Cell. 2024;187: 4637-4655.e26.
[28] JINAWONG K, APAIJAI N, CHATTIPAKORN N, et al. Cognitive impairment in myocardial infarction and heart failure. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021;232: e13642.
[29] HJALMARSSON C, FU M, ZVERKOVA SANDSTROM T, et al. Risk of stroke in patients with heart failure and sinus rhythm: Data from the swedish heart failure registry. ESC Heart Fail. 2021;8(1):85-94.
[30] SHOURAV MMI, GODASI RR, ANISETTI B, et al. Association between heart failure and cerebral collateral flow in large vessel occlusive ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024;33(11):107999.
[31] NAKAO K, DAFAALLA M, NAKAO YM, et al. Comparison of care and outcomes for myocardial infarction by heart failure status between united kingdom and japan. ESC Heart Fail. 2023;10:1372-1384.
[32] CHETAN IM, GERGELY-DOMOKOS B, BEYER R, et al. The role of 3d speckle tracking echocardiography in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea and its severity. Sci Rep. 2022;12:22347.
[33] PARSOVA KE, KELES N, KARATAS M, et al. Assessment of right ventricular sequelae by speckle tracking echocardiography in recovered covid-19 patients. Acta Cardiol. 2024;79:909-914.
[34] WANG C, XING J, ZHAO B, et al. The effects of high-intensity interval training on exercise capacity and prognosis in heart failure and coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Ther. 2022;2022:4273809.
[35] DOCHERTY KF, HENDERSON AD, JHUND PS, et al. Efficacy and safety of finerenone across the ejection fraction spectrum in heart failure with mildly reduced and preserved ejection fraction: A prespecified analysis of the finearts-hf trial. Circulation. 2024. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.072011.
[36] RADAKRISHNAN A, DOKKO J, PASTENA P, et al. Thromboembolism in peripartum cardiomyopathy: A systematic review. J Thorac Dis. 2024;16:645-660.
[37] KANG JB, SON HK, SHAH MA, et al. Retinoic acid attenuates ischemic injury-induced activation of glial cells and inflammatory factors in a rat stroke model. PLoS One. 2024;19:e0300072.
[38] VENKAT P, CUI C, CHEN Z, et al. Cd133+exosome treatment improves cardiac function after stroke in type 2 diabetic mice. Transl Stroke Res. 2021;12:112-124.
[39] KWON HM, PARK JH, KIM JM, et al. Mild left ventricular dysfunction is associated with thrombogenicity in cardioembolic stroke. Eur Neurol. 2006;56:217-221.
[40] SCHAFER A, FLIERL U, BAUERSACHS J. Anticoagulants for stroke prevention in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Clin Res Cardiol. 2022;111(1):1-13.
[41] HERMANNS N, WROBLEWSKI V, BASCUNANA P, et al. Molecular imaging of the brain-heart axis provides insights into cardiac dysfunction after cerebral ischemia. Basic Res Cardiol. 2022;117(1):52.
[42] LIND L, LOADER J, LINDAHL B, et al. A comparison of echocardiographic and circulating cardiac biomarkers for predicting incident cardiovascular disease. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0271835.
[43] SUNG PH, CHEN KH, LIN HS, et al. The correlation between severity of neurological impairment and left ventricular function in patients after acute ischemic stroke. J Clin Med. 2019;8(2):190.
[44] ROJEK A, GASECKI D, FIJALKOWSKI M, et al. Left ventricular ejection fraction and aortic stiffness are independent predictors of neurological outcome in acute ischemic stroke. J Hypertens. 2016;34:2441-2448.
|