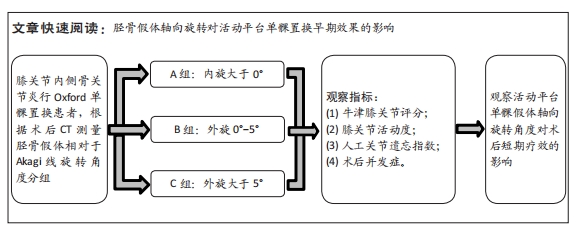
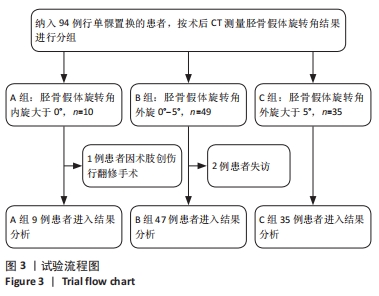
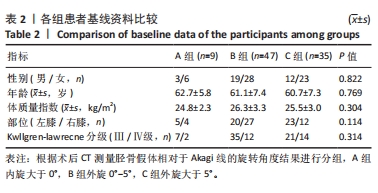
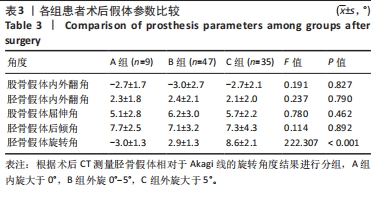
[1] REN Y, HU J, TAN J, et al. Incidence and risk factors of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis among the Chinese population: analysis from a nationwide longitudinal study. BMC Public Health. 2020; 20(1):1491.
[2] ROSSI SMP, SANGALETTI R, NESTA F, et al. A well performing medial fixed bearing UKA with promising survivorship at 15 years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(5):2693-2699.
[3] PONGCHAROEN B, LIENGWATTANAKOL P, BOONTANAPIBUL K, et al. Comparison of functional recovery between unicompartmental and total knee arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2023;105(3):191-201.
[4] BANDI M, BENAZZO F, BATAILLER C, et al. A morphometric fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty can reproduce normal knee kinematics. Arthroplasty Today. 2022;16:151-157.
[5] GHOMRAWI HM, EGGMAN AA, PEARLE AD, et al. Effect of age on cost-effectiveness of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty compared with total knee arthroplasty in the U.S. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015; 97(5):396-402.
[6] CASPER DS, FLEISCHMAN AN, PAPAS PV, et al. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty provides significantly greater improvement in function than total knee arthroplasty despite equivalent satisfaction for isolated medial compartment osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(8):1611-1616.
[7] GUERREIRO JPF, SANTOS VKJD, MATZ LB, et al. Does partial medial knee arthroplaties have better results than total ones? Acta Ortop Bras. 2023;31(spe2):e262186.
[8] KERENS B, LEENDERS AM, SCHOTANUS MGM, et al. Patient-specific instrumentation in Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty is reliable and accurate except for the tibial rotation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(6):1823-1830.
[9] ALETO TJ, BEREND ME, RITTER MA, et al. Early failure of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty leading to revision. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(2):159-163.
[10] KOH YG, PARK KM, KANG K, et al. Finite element analysis of the influence of the posterior tibial slope on mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2021;29:116-125.
[11] ALRUWAILI SH, PARK KK, YANG IH, et al. Difference between medial and lateral tibia plateau in the coronal plane: importance of preoperative evaluation for medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorder. 2022;23(1):342.
[12] MARULLO M, RUSSO A, SPREAFICO A, et al. Mild valgus alignment after lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty led to lower functional results and survivorship at mean 8-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38(1):37-42.
[13] DOUIRI A, BOUGUENNEC N, BISET A, et al. Functional scores and prosthetic implant placement are different for navigated medial UKA left in varus alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(9):3919-3926.
[14] FAROOQ H, DECKARD ER, CARLSON J, et al. Coronal and sagittal component position in contemporary total knee arthroplasty: Targeting native alignment optimizes clinical outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S245-S251.
[15] MALYAVKO A, COHEN JS, FULLER SI, et al. Reduced early revision surgery and medical complications in computer-assisted knee arthroplasty compared with non-computer-assisted arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023; 31(2): 87-96.
[16] ZHANG J, NDOU WS, NG N, et al. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with improved accuracy and patient reported outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(8):2677-2695.
[17] ZHOU X, SUN C, XU R, et al. The effect of tibial component rotational alignment on clinical outcomes of mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023; 18(1):217.
[18] LIOW MHL, TSAI TY, DIMITRIOU D, et al. Does 3-dimensional in vivo component rotation affect clinical outcomes in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(10):2167-2172.
[19] JANG KM, LIM HC, HAN SB, et al. Does new instrumentation improve radiologic alignment of the Oxford® medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty? Knee. 2017;24(3):641-650.
[20] HERNIGOU P, DESCHAMPS G. Posterior slope of the tibial implant and the outcome of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(3):506-511.
[21] 田文明,王光达. CT在膝关节Oxford单髁置换术后假体位置评价中的应用[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘(连续型电子期刊),2018, 18(A2):31-33.
[22] 李相伟,丁晶. Oxford单髁置换术的术后影像学评价及分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013,7(1):48-51.
[23] CASPER DS, FLEISCHMAN AN, PAPAS PV, et al. Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Provides Significantly Greater Improvement in Function than Total Knee Arthroplasty Despite Equivalent Satisfaction for Isolated Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty.2019; 34(8):1611-1616.
[24] 张江涛,尚延春,李启义,等.全膝关节置换术与单髁置换术治疗内侧间室膝骨关节炎疗效对比的meta分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(10):830-835+858
[25] LEE SY, CHAY S, LIM HC, et al. Tibial component rotation during the unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: is the anterior superior iliac spine an appropriate landmark? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(12):3723-3732
[26] TSAI TY, DIMITRIOU D, HOSSEINI A, et al. Assessment of accuracy and precision of 3D reconstruction of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in upright position using biplanar radiography. Med Eng Phys. 2016; 38(7): 633-638.
[27] SERVIEN E, FARY C, LUSTIG S, et al. Tibial component rotation assessment using CT scan in medial and lateral unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97(3):272-275.
[28] IRIBERRI I, ARAGÓN JF. Alignment of the tibial component of the unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, assessed in the axial view by CT scan: does it influence the outcome? Knee. 2014;21(6):1269-1274.
[29] NG JP, FAN JCH, CHAU WW, et al. Does component axial rotational alignment affect clinical outcomes in Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty? Knee. 2020;27(6):1953-1962.
[30] IWAKI H, PINSKEROVA V, FREEMAN MA, et al. Tibiofemoral movement 1: the shapes and relative movements of the femur and tibia in the unloaded cadaver knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(8):1189-1195.
[31] HERNÁNDEZ-HERMOSO JA, NESCOLARDE L, YAÑEZ-SILLER F, et al. Combined femoral and tibial component total knee arthroplasty device rotation measurement is reliable and predicts clinical outcome. J Orthop Traumatol. 2023;24(1):40.
[32] RAJGOPAL A, SUDARSHANP, KUMAR S, et al. Failure modes in malrotated total knee replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023; 143(5):2713-2720.
[33] NICOLL D, ROWLEY DI. Internal rotational error of the tibial component is a major cause of pain after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92(9):1238-1244.
[34] BÉDARD M, VINCE KG, REDFERN J, et al. Internal rotation of the tibial component is frequent in stiff total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(8):2346-2355.
[35] KAMENAGA T, HIRANAKA T, TAKAYAMA K, et al. Adequate positioning of the tibial component is key to avoiding bearing impingement in oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(11): 2606-2613.
[36] ESCUDIER IC, JACQUET C, FLECHER X, et al. Better Implant Positioning and Clinical Outcomes With a Morphometric Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty. Results of a Retrospective,Matched-Controlled Study. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(12):2903-2908
[37] KAMENAGA T, HIRANAKA T, HIDA Y, et al. Rotational position of the tibial component can decrease bony coverage of the tibial component in Oxford mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2019;26(2):459-465.
[38] CHAU R, GULATI A, PANDIT H, et al. Tibial component overhang following unicompartmental knee replacement--does it matter? Knee. 2009;16(5): 310-313.
[39] GUDENA R, PILAMBARAEI MA, WERLE J, et al. A safe overhang limit for unicompartmental knee arthroplasties based on medial collateral ligament strains: an in vitro study. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(2):227-233.
[40] XU K, CHEN Q, YAN Q, et al. Comparison of computer-assisted navigated technology and conventional technology in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):123.
[41] AHMED AG, TIAN Y, HASAN M, et al. Revisiting short-term outcomes of conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty: A population-based study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022; 6(6):e22 68000.
[42] MALHOTRA R, GUPTA S, GUPTA V, et al. Navigated unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: A different perspective.Clin Orthop Surg. 2021;13(4):491-498
|