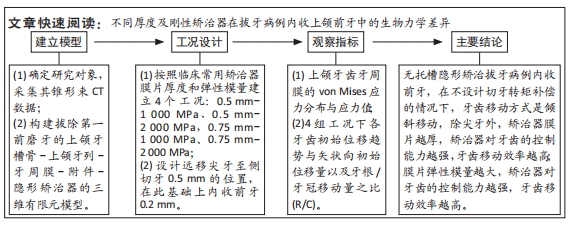
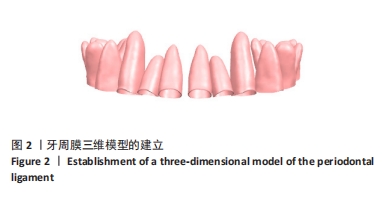
[1] WEIR T. Clear aligners in orthodontic treatment. Aust Dent J. 2017;62 Suppl 1:58-62.
[2] JENA AK, MOHAPATRA M, SHARAN J, et al. Temporary deterioration of oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) in nonextraction and extraction modalities of comprehensive orthodontic treatment in adolescents. Angle Orthod. 2020;90(4):578-586.
[3] 白玉兴.口腔正畸无托槽隐形矫治技术指南(2021版)解读[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2021,56(10):989-991.
[4] DAI FF, XU TM, SHU G. Comparison of achieved and predicted tooth movement of maxillary first molars and central incisors: First premolar extraction treatment with Invisalign. Angle Orthod. 2019;89(5):679-687.
[5] LIU JQ, ZHU GY, WANG YG, et al. Different biomechanical effects of clear aligners in closing maxillary and mandibular extraction spaces: Finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2023;163(6):811-824.e2.
[6] YASSIR YA, NABBAT SA, MCINTYRE GT, et al. Clinical effectiveness of clear aligner treatment compared to fixed appliance treatment: an overview of systematic reviews. Clin Oral Investig. 2022;26(3):2353-2370.
[7] REN L, LIU L, WU Z, et al. The predictability of orthodontic tooth movements through clear aligner among first-premolar extraction patients: a multivariate analysis. Prog Orthod. 2022; 23(1):52.
[8] WANG CY, SU MZ, CHANG HH, et al. Tension-compression viscoelastic behaviors of the periodontal ligament. J Formos Med Assoc. 2012; 111(9):471-481.
[9] AMMOURY MJ, MUSTAPHA S, DECHOW PC, et al. Two distalization methods compared in a novel patient-specific finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2019;156(3):326-336.
[10] ELKHOLY F, SCHMIDT S, AMIRKHANI M, et al. Mechanical Characterization of Thermoplastic Aligner Materials: Recommendations for Test Parameter Standardization. J Healthc Eng. 2019;2019:8074827.
[11] PALONE M, LONGO M, ARVEDA N, et al. Micro-computed tomography evaluation of general trends in aligner thickness and gap width after thermoforming procedures involving six commercial clear aligners: an in vitro study. Korean J Orthod. 2021;51(2):135-141.
[12] SEO JH, EGHAN-ACQUAH E, KIM MS, et al. Comparative analysis of stress in the periodontal ligament and Center of Rotation in the tooth after orthodontic treatment depending on clear aligner thickness--finite element analysis study. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(2):324.
[13] MA Y, LI S. The optimal orthodontic displacement of clear aligner for mild, moderate and severe periodontal conditions: an in vitro study in a periodontally compromised individual using the finite element model. BMC Oral Health. 2021;21(1):109.
[14] RAMALHO A, ANTUNES VP. Reciprocating wear test of dental composites against human teeth and glass. Wear. 2007;263(7-12): 1095-1104.
[15] LIANG W, RONG Q, LIN J, et al. Torque control of the maxillary incisors in lingual and labial orthodontics: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;135(3): 316-322.
[16] HONG K, KIM WH, EGHAN-ACQUAH E, et al. Efficient Design of a Clear Aligner Attachment to Induce Bodily Tooth Movement in Orthodontic Treatment Using Finite Element Analysis. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(17):4926.
[17] ELSHAZLY TM, BOURAUEL C, ALDESOKI M, et al. Computer-aided finite element model for biomechanical analysis of orthodontic aligners. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(1):115-124.
[18] 张国瑞,张坤武,陈文远锋,等.舌侧活动翼不同翼拉伸长度内收下前牙的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(2):247-251.
[19] FAN D, LIU H, YUAN CY, et al. Effectiveness of the attachment position in molar intrusion with clear aligners: a finite element study. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):474.
[20] 康芙嘉,余磊,张琦,等.隐形矫治器远移下颌第一磨牙的三维有限元研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2023,41(4):405-413.
[21] JIANG T, WU RY, WANG JK, et al. Clear aligners for maxillary anterior en masse retraction: a 3D finite element study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1): 10156.
[22] LIU JQ, ZHU GY, WANG YG, et al. Different biomechanical effects of clear aligners in bimaxillary space closure under two strong anchorages: finite element analysis. Prog Orthod. 2022;23(1):41.
[23] LYU X, CAO X, YAN J, et al. Biomechanical effects of clear aligners with different thicknesses and gingival-margin morphology for appliance design optimization. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2023;164(2): 239-252.
[24] WANG YG, ZHU GY, LIU JQ, et al. Dynamic biomechanical changes of clear aligners during extraction space closure: Finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2024;165(3):272-284.e3.
[25] 曹世陶,杨宜靓,徐宝华.无托槽隐形矫治器整体内收与分步内收下颌前牙的三维有限元对比分析 [J].中日友好医院学报,2022,36(4): 207-210.
[26] FENG X, JIANG Y, ZHU Y, et al. Comparison between the designed and achieved mesiodistal angulation of maxillary canines and posterior teeth and influencing factors: First premolar extraction treatment with clear aligners. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2022;162(2):e63-e70.
[27] CHENG Y, LIU X, CHEN X, et al. The three-dimensional displacement tendency of teeth depending on incisor torque compensation with clear aligners of different thicknesses in cases of extraction: a finite element study. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1): 499.
[28] REN L, LIU L, WU Z, et al. The predictability of orthodontic tooth movements through clear aligner among first-premolar extraction patients: a multivariate analysis. Prog Orthod. 2022;23(1): 52.
[29] 李晓梅,宋云鹏,徐宝华.牵引方向对无托槽隐形矫治器联合种植支抗内收上前牙的生物力学影响[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志,2022, 38(3):152-156.
[30] 苏涛,王星星,向彪,等.不同刚度的无托槽隐形矫治器扩大上颌牙弓的有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(5):454-458.
[31] ALHASYIMI AA, AYUB A, FARMASYANTI CA. Effectiveness of the Attachment Design and Thickness of Clear Aligners during Orthodontic Anterior Retraction: Finite Element Analysis. Eur J Dent. 2024;18(1):174-181.
[32] LIU DS, CHEN YT. Effect of thermoplastic appliance thickness on initial stress distribution in periodontal ligament. Adv Mech Eng. 2015;7(4): 168781401557836-168781401557836.
[33] GRANT J, FOLEY P, BANKHEAD B, et al. Forces and moments generated by 3D direct printed clear aligners of varying labial and lingual thicknesses during lingual movement of maxillary central incisor: an in vitro study. Prog Orthod. 2023;24(1):23.
[34] UPADHYAY M, ARQUB SA. Biomechanics of clear aligners: hidden truths & first principles. J World Fed Orthod. 2022;11(1):12-21.
[35] LIU L, SONG Q, ZHOU J, et al. The effects of aligner overtreatment on torque control and intrusion of incisors for anterior retraction with clear aligners: A finite-element study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2022;162(1):33-41.
[36] CATTANEO PM, CORNELIS MA. Orthodontic Tooth Movement Studied by Finite Element Analysis: an Update. What Can We Learn from These Simulations? Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021;19(2):175-181.
[37] KANG F, WU Y, CUI Y, et al. The displacement of teeth and stress distribution on periodontal ligament under different upper incisors proclination with clear aligner in cases of extraction: a finite element study. Prog Orthod. 2023;24(1):38.
[38] ZENO KG, AMMOURY MJ. The surge of finite element analysis in the study of orthodontic mechanics: are the findings applicable in practice? Semin Orthod. 2023;29(3):308-316. |