[1] MCCORMICK JR, SAMA AJ, SCHILLER NC, et al. Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: A Guide to Diagnosis and Management. J Am Board Fam Med. 2020;33(2):303-313.
[2] 刘正蓬,王雅辉,张义龙,等.3D打印椎间融合器置入治疗脊髓型颈椎病:颈椎曲度及椎间高度恢复的半年随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(6):849-853.
[3] KHAN AF, HAYNES G, MOHAMMADI E, et al. Utility of MRI in Quantifying Tissue Injury in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. J Clin Med. 2023;12(9):3337.
[4] BONOSI L, MUSSO S, CUSIMANO LM, et al. The role of neuronal plasticity in cervical spondylotic myelopathy surgery: functional assessment and prognostic implication. Neurosurg Rev. 2023;46(1):149.
[5] TOCI GR, CANSECO JA, KARAMIAN BA, et al. The impact of preoperative neurological symptom severity on postoperative outcomes in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2022;13(1): 94-100.
[6] 邱丽英,王利仁.基于“阳化气,阴成形”及“温养督脉”理论探讨脊髓型颈椎病治法[J].陕西中医,2024,45(7):951-954.
[7] 睦顺姬,叶秀兰,姚敏,等.中医药治疗脊髓型颈椎病的机理研究概况[J].世界中医药,2017,12(1):222-224+228.
[8] BOOGAARTS HD, BARTELS RH. Prevalence of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2015;24 Suppl 2:139-141.
[9] 刘志伟,银河,陈忻,等.益肾养髓方治疗轻中度脊髓型颈椎病的疗效研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2022,30(8):36-40+45.
[10] 莫文,袁文.脊髓型颈椎病中西医结合诊疗指南(2023)[J].中国骨伤,2024,37(1):103-110.
[11] 卞正航,许金海,叶洁,等.中药治疗脊髓型颈椎病作用机制的研究进展[J].中医正骨,2023,35(12):36-41.
[12] 陈强,逯艳婷,王洪海.《伤寒论》葛根汤古今应用探析[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2024,26(10):165-169.
[13] 阴继爱,戴岳,安树庞.葛根汤的药理和临床研究概况[J].中华中医药学刊,2007(6):1275-1278.
[14] 王献宇.葛根汤加味防治脊髓型颈椎病颈椎前路术后发生轴性症状的疗效观察[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2018.
[15] 马梦全.补阳还五汤、身痛逐瘀汤、葛根汤复方加减治疗脊髓型颈椎病临床运用效果分析[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2017, 17(67):145.
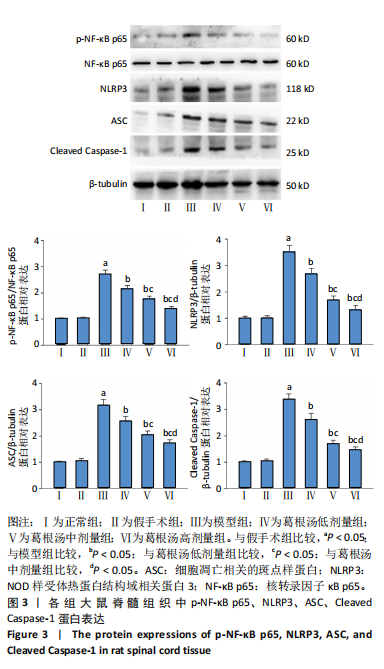
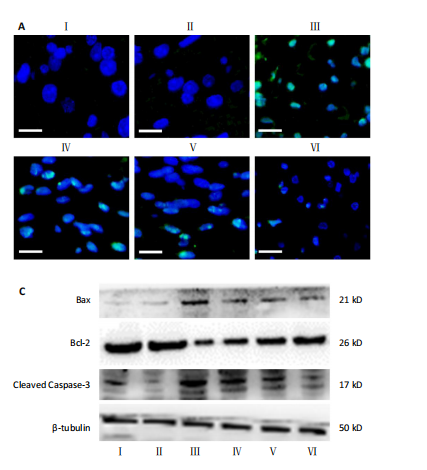
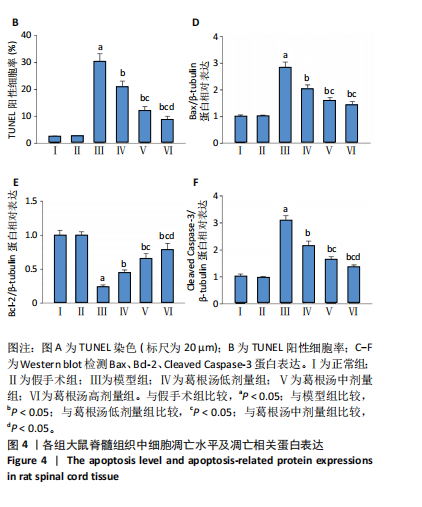
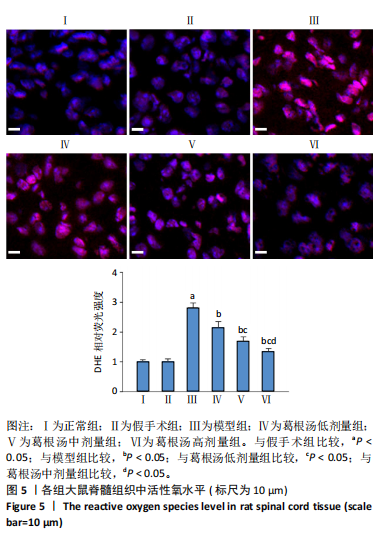
[16] 张典,银河,朱立国,等.益肾养髓方对脊髓型颈椎病大鼠脊髓中细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2024,32(1):1-6.
[17] KARADIMAS SK, GATZOUNIS G, FEHLINGS MG. Pathobiology of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2015;24 Suppl 2:132-138.
[18] KALSI-RYAN S, KARADIMAS SK, FEHLINGS MG. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: the clinical phenomenon and the current pathobiology of an increasingly prevalent and devastating disorder. Neuroscientist. 2013;19(4):409-421.
[19] 刘恩旭,段嘉豪,杨雷,等.杨少锋教授基于六经辨证治疗颈椎病的经验[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2023,43(11):2013-2017.
[20] 林少平,伦婷婷,王世雄,等.葛根汤联合高能量体外冲击波对神经根型颈椎病患者血清炎性因子的影响[J/OL].中华中医药学刊,1-11[2024-08-24].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1546.R.20240306.1737.002.html.
[21] 杨博文,朱立国,陈忻,等.益肾养髓方对脊髓型颈椎病大鼠脊髓炎症的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(5):1056-1059.
[22] 李淦.参芪麝蓉丸调控内质网应激抑制神经元凋亡治疗脊髓型颈椎病的机制研究[D].上海:上海中医药大学,2021.
[23] 邓文龙.动物中人体剂量换算遵循的原则[J].中药药理与临床, 2016,32(3):196-197.
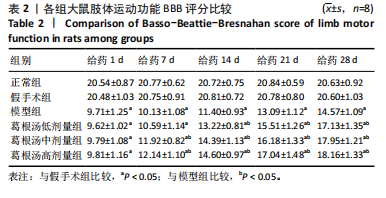
[24] BASSO DM, BEATTIE MS, BRESNAHAN JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1):1-21.
[25] IYER A, AZAD TD, THARIN S. Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(10):408-414.
[26] 李梁,赵晓玲,詹常森.治疗脊髓型颈椎病的中药组方及临床评价研究进展[J].中成药,2023,45(3):861-865.
[27] 卜献忠,钟远鸣,卜保献,等.脊髓伤方促进脊髓型颈椎病(气虚血瘀证)术后恢复的效果研究[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(12): 2951-2955.
[28] 王文雅,王会生,陈萌.基于津液理论探讨经方治疗颈椎病的科学内涵[J].环球中医药,2023,16(3):518-521.
[29] 黄代富,王庆龙,闵欢.葛根汤加减配合手法,颈部十字操治疗混合型颈椎病的临床研究[J].贵州中医药大学学报,2023,45(5):57-60.
[30] YAO M, LI G, PU PM, et al. Neuroinflammation and apoptosis after surgery for a rat model of double-level cervical cord compression. Neurochem Int. 2022;157:105340.
[31] YU WR, LIU T, KIEHL TR, et al. Human neuropathological and animal model evidence supporting a role for Fas-mediated apoptosis and inflammation in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 5):1277-1292.
[32] 劳泽辉,凌国伟,华国花.circRNAs调控NF-κB信号通路在脊髓型颈椎病中的作用及机制研究[J].中国医学工程,2022,30(12):24-28.
[33] PENG L, WEN L, SHI QF, et al. Scutellarin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(11):978.
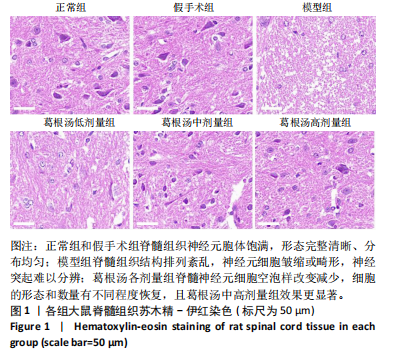
[34] O’SHEA TM, BURDA JE, SOFRONIEW MV. Cell biology of spinal cord injury and repair. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3259-3270.
[35] BRENNAN FH, LI Y, WANG C, et al. Microglia coordinate cellular interactions during spinal cord repair in mice. Nat Commun. 2022; 13(1):4096.
[36] 成志红,冯松,王霞,等.米诺环素对脊神经结扎大鼠脊髓内M1/M2型小胶质细胞极化的影响[J].陆军军医大学学报,2024, 46(15):1740-1750.
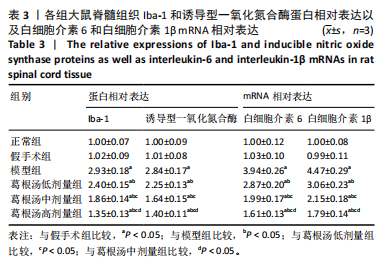
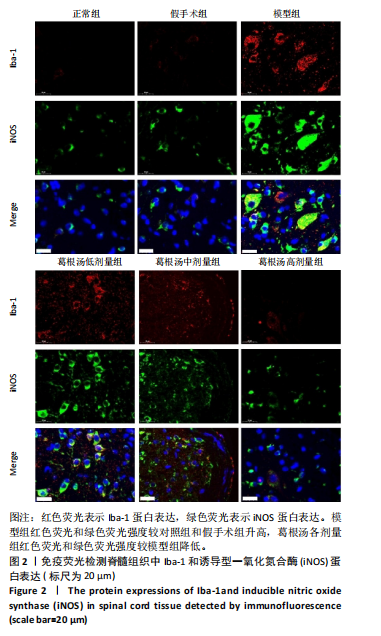
[37] 杨博文,朱立国,陈忻,等.益肾养髓方对脊髓型颈椎病大鼠小胶质细胞极化的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023,31(3):1-5.
[38] JIANG D, YANG X, GE M, et al. Zinc defends against Parthanatos and promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury through SIRT3-mediated anti-oxidative stress and mitophagy. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29(10):2857-2872.
[39] Schmidt J, Quintá HR. Mitochondrial dysfunction as a target in spinal cord injury: intimate correlation between pathological processes and therapeutic approaches. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(10):2161-2166.
[40] TILOKANI L, NAGASHIMA S, PAUPE V, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics: overview of molecular mechanisms. Essays Biochem. 2018;62(3): 341-360.
[41] 周文洋,廖烨晖,田明昊,等.NLRP3炎性小体在脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(13):2849-2860.
[42] PU PM, LI ZY, DAI YX, et al. Analysis of gene expression profiles and experimental validations of a rat chronic cervical cord compression model. Neurochem Int. 2023;168:105564. |