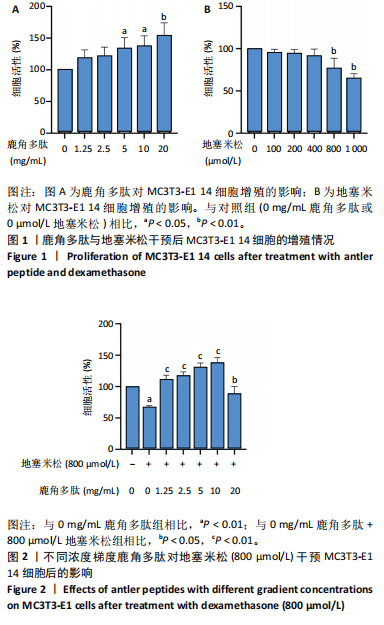
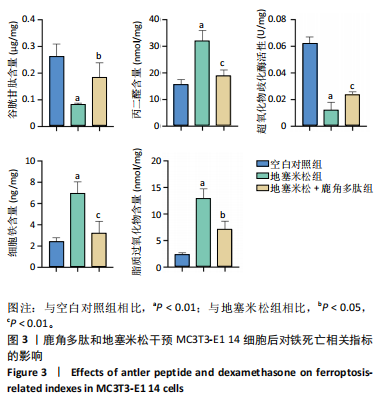
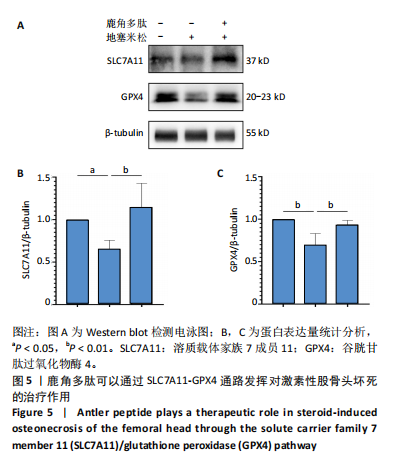
[1] GUERADO E, CASO E. The physiopathology of avascular necrosis of the femoral head: an update. Injury. 2016;47 Suppl 6:S16-S26.
[2] HUANG C, QING L, XIAO Y, et al. Insight into Steroid-Induced ONFH: The Molecular Mechanism and Function of Epigenetic Modification in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biomolecules. 2023;14(1):4.
[3] TAN B, LI W, ZENG P, et al. Epidemiological Study Based on China Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Database. Orthop Surg. 2021; 13(1):153-160.
[4] SATO R, ANDO W, FUKUSHIMA W, et al. Epidemiological study of osteonecrosis of the femoral head using the national registry of designated intractable diseases in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2022; 32(4):808-814.
[5] LI H, ZHANG Y, HAO Y, et al. Proanthocyanidins Inhibit Osteoblast Apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/Bcl-xL Pathway in the Treatment of Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Rats. Nutrients. 2023; 15(8):1936.
[6] NUGENT M, YOUNG SW, FRAMPTON CM, et al. The lifetime risk of revision following total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(3): 479-485.
[7] MONT MA, PIVEC R, BANERJEE S, et al. High-Dose Corticosteroid Use and Risk of Hip Osteonecrosis: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Literature Review. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(9):1506-1512.e5.
[8] LIU C, WANG C, LIU Y, et al. Selenium nanoparticles/carboxymethyl chitosan/alginate antioxidant hydrogel for treating steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int J Pharm. 2024;653:123929.
[9] LI W, LI W, ZHANG W, et al. Exogenous melatonin ameliorates steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by modulating ferroptosis through GDF15-mediated signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):171.
[10] LIN RLC, SUNG PH, WU CT, et al. Decreased Ankyrin Expression Is Associated with Repressed eNOS Signaling, Cell Proliferation, and Osteogenic Differentiation in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(Suppl 2):2-12.
[11] DUAN P, WANG H, YI X, et al. C/EBPα regulates the fate of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head by targeting the PPARγ signalling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):342.
[12] ZHOU DA, ZHENG HX, WANG CW, et al. Influence of glucocorticoids on the osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:239.
[13] MAZUR CM, CASTRO ANDRADE CD, TOKAVANICH N, et al. Partial prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteocyte deterioration in young male mice with osteocrin gene therapy. iScience. 2022;25(9):105019.
[14] SUN F, ZHOU JL, LIU ZL, et al. Dexamethasone induces ferroptosis via P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;602:149-155.
[15] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125.
[16] KUANG F, LIU J, TANG D, et al. Oxidative Damage and Antioxidant Defense in Ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:586578.
[17] LI FJ, LONG HZ, ZHOU ZW, et al. System Xc-/GSH/GPX4 axis: An important antioxidant system for the ferroptosis in drug-resistant solid tumor therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:910292.
[18] CHEN PY, STOKES AG, MCKITTRICK J. Comparison of the structure and mechanical properties of bovine femur bone and antler of the North American elk (Cervus elaphus canadensis). Acta Biomater. 2009; 5(2):693-706.
[19] LI C, ZHAO H, LIU Z, et al. Deer antler--a novel model for studying organ regeneration in mammals. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;56:111-122.
[20] Li X, Liu M, Bai X, et al. Molecular cloning, recombinant expression, and purification of osteocalcin in sika deer (Cervus nippon) antler. Pol J Vet Sci. 2019;22(1):143-150.
[21] 李娜,胡亚楠,王晓雪,等.鹿角胶化学成分、药理作用及质量控制研究进展[J].中药材,2021,44(7):1777-1783.
[22] 魏珍珍,方晓艳,苗明三.胶类中药的特点及现代研究分析[J].中国现代应用药学,2019,36(14):1842-1849.
[23] 张郑瑶,尚禹东,牟凤辉,等.鹿茸多肽及其生长因子制备工艺的研究进展[J].特产研究,2011,33(3):69-73
[24] 郭鑫,陈美华,何旭,等.梅花鹿角多肽的制备工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(8):1911-1915.
[25] 夏广清,郭鑫,刘伟,等.鹿角多肽研究进展[J].通化师范学院学报,2021,42(8):79-82.
[26] 高志惠,孙铁锋,王平,等.星点设计-效应面法优化鹿角胶-脱蛋白骨制备工艺[J].中成药,2016,38(8):1838-1841
[27] 王平,张会敏,李刚.鹿角多肽对骨髓间充质干细胞的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(12):5644-5647.
[28] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典[S].一部.北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020:343-344.
[29] 王平,张会敏,李刚,等. 星点设计-效应面法优化鹿角多肽酶解工艺[J].山东科学,2018,31(6):1-10.
[30] FANG L, ZHANG G, WU Y, et al. SIRT6 Prevents Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:6360133.
[31] KIM H, LEE K, KO CY, et al. The role of nacreous factors in preventing osteoporotic bone loss through both osteoblast activation and osteoclast inactivation. Biomaterials. 2012;33(30):7489-7496.
[32] DENG S, DAI G, CHEN S, et al. Dexamethasone induces osteoblast apoptosis through ROS-PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:602-608.
[33] LIU X, CHEN C, HAN D, et al. SLC7A11/GPX4 Inactivation-Mediated Ferroptosis Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Triptolide-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:3192607.
[34] YUAN S, WEI C, LIU G, et al. Sorafenib attenuates liver fibrosis by triggering hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis via HIF-1α/SLC7A11 pathway. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(1):e13158.
[35] 梁学振, 骆帝, 李嘉程, 等. 激素性股骨头坏死中的 PTGS2 和 STAT3:潜在铁死亡相关诊断生物标志物 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(36):5898-5904.
[36] LI W, LI W, ZHANG W, et al. Exogenous melatonin ameliorates steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by modulating ferroptosis through GDF15-mediated signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):171.
[37] YE Y, CHEN A, LI L, et al. Repression of the antiporter SLC7A11/glutathione/glutathione peroxidase 4 axis drives ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells to facilitate vascular calcification. Kidney Int. 2022;102(6):1259-1275.
[38] CHEN H, LIN X, YI X, et al. SIRT1-mediated p53 deacetylation inhibits ferroptosis and alleviates heat stress-induced lung epithelial cells injury. Int J Hyperthermia. 2022;39(1):977-986.
[39] LI Y, YAN J, ZHAO Q, et al. ATF3 promotes ferroptosis in sorafenib-induced cardiotoxicity by suppressing Slc7a11 expression. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:904314. |