[1] GBD 2019 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2022; 400(10369):2221-2248.
[2] KUMAR S, SHARMA M, FRÖMLING T, et al. Antibacterial ferroelectric materials: advancements and future directions. J Ind Eng Chem. 2021; 97:95-110.
[3] MEHTA AC, MUSCARELLA LF. Bronchoscope-related “superbug” infections. Chest. 2020;157(2):454-469.
[4] MCCULLOCH TR, WELLS TJ, SOUZA-FONSECA-GUIMARAES F. Towards efficient immunotherapy for bacterial infection. Trends Microbiol. 2022;30(2):158-169.
[5] LARSSON DGJ, FLACH CF. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022;20(5):257-269.
[6] HUEMER M, MAIRPADY SHAMBAT S, BRUGGER SD, et al. Antibiotic resistance and persistence-Implications for human health and treatment perspectives. EMBO Rep. 2020;21(12):e51034.
[7] KAPAT K, SHUBHRA QTH, ZHOU M, et al. Piezoelectric nano-biomaterials for biomedicine and tissue regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2020. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201909045.
[8] 孙奇薇,薛国梁,周学凡,等.压电催化降解有机污染物的研究进展[J].中国有色金属学报,2021,31(8):1997-2013.
[9] YANG B, CHEN Y, SHI J. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-based nanomedicine. Chem Rev. 2019;119(8):4881-4985.
[10] QIAN W, YANG W, ZHANG Y, et al. Piezoelectric materials for controlling electro-chemical processes. Nanomicro Lett. 2020;12(1):149.
[11] HONG KS, XU HF, KONISHI H, et al. Direct water splitting through vibrating piezoelectric microfibers in water. J Phys Chem Lett. 2010; 1(6):997-1002.
[12] HONG KS, XU HF, KONISHI H, et al. Piezoelectrochemical effect: a new mechanism for azo dye decolorization in aqueous solution through vibrating piezoelectric microfibers. J Phys Chem Lett. 2012; 116(24):13045-13051.
[13] 战立慧,宁雪儿,郝平玉,等.压电催化技术在能源与环境领域中的研究进展[J].中国科学:化学,2023,53(8):1336-1354.
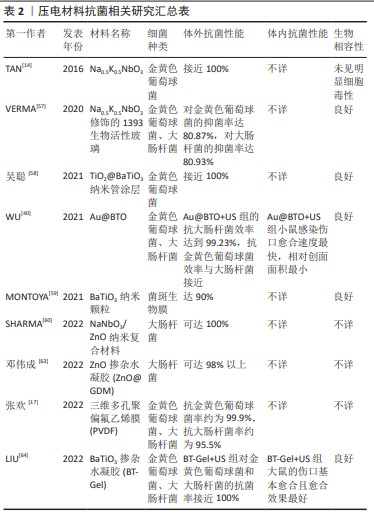
[14] TAN G, WANG S, ZHU Y, et al. Surface-selective preferential production of reactive oxygen species on piezoelectric ceramics for bacterial killing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(37):24306-24309.
[15] FENG JX, FU Y, LIU XS, et al. Significant improvement and mechanism of ultrasonic inactivation to escherichia coli with piezoelectric effect of hydrothermally synthesized t-BaTiO3. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2018;6(5):6032-6041.
[16] WU MQ, ZHANG ZY, LIU ZR, et al. Piezoelectric nanocomposites for sonodynamic bacterial elimination and wound healing. Nano Today. 2021;37:101104.
[17] 张欢.三维多孔压电聚偏氟乙烯膜的制备及其抗菌研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2022.
[18] GAZVODA L, PERIŠIĆ NANUT M, SPREITZER M, et al. Antimicrobial activity of piezoelectric polymer: piezoelectricity as the reason for damaging bacterial membrane. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(17):4933-4948.
[19] WANG W, LI J, LIU H, et al. Advancing versatile ferroelectric materials toward biomedical applications. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;3;8(1):2003074.
[20] MANDAL D, BANERJEE S. Surface acoustic wave (SAW) sensors: physics, materials, and applications. Sensors (Basel). 2022;22(3):820.
[21] KHARE D, BASU B, DUBEY AK. Electrical stimulation and piezoelectric biomaterials for bone tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120280.
[22] WANG K, HAN C, LI J, et al. The mechanism of piezocatalysis: energy band theory or screening charge effect? Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022;1;61(6):e202110429.
[23] WU JM, CHANG WE, CHANG YT, et al. Piezo-catalytic effect on the enhancement of the ultra-high degradation activity in the dark by single- and few-layers MoS2 nanoflowers. Adv Mater. 2016;28(19):3718-3725.
[24] WU MH, LEE J T, CHUNG YJ, et al. Ultrahigh efficient degradation activity of single- and few-layered MoSe2 nanoflowers in dark by piezo-catalyst effect. Nano Energy. 2017;40:369-375.
[25] WU J, QIN N, BAO DH. Effective enhancement of piezocatalytic activity of BaTiO3 nanowires under ultrasonic vibration. Nano Energy. 2018;45:44−51.
[26] NIE Q, XIE YF, MA JM, et al. High piezo-catalytic activity of ZnO/Al2O3 nanosheets utilizing ultrasonic energy for wastewater treatment. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020;242:118532.
[27] ZHANG A, LIU ZY, XIE B, et al. Vibration catalysis of eco-friendly Na0.5K0.5NbO3-based piezoelectric: an efficient phase boundary catalyst. Appl Catal B. 2020;279:119353.
[28] ZHANG A, LIU ZY, GENG XH, et al. Ultrasonic vibration driven piezocatalytic activity of lead-free K0.5Na0.5NbO3 materials. Ceramics Int. 2019;45(17):22486-22492.
[29] D’AUTRÉAUX B, TOLEDANO MB. ROS as signalling molecules: mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:813-824.
[30] MITTLER R. ROS are good. Trends Plant Sci. 2017;22(1):11-19.
[31] NATHAN C, CUNNINGHAM-BUSSEL A. Beyond oxidative stress: an immunologist’s guide to reactive oxygen species. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(5):349-61.
[32] CHEUNG EC, VOUSDEN KH. The role of ROS in tumour development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(5):280-297.
[33] HERB M, SCHRAMM M. Functions of ROS in macrophages and antimicrobial immunity. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(2):313.
[34] 卢璐,张坤.可调控活性氧的纳米声敏剂在声动力疗法的应用进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2022,42(4):995-1001.
[35] EZRATY B, GENNARIS A, BARRAS F, et al. Oxidative stress, protein damage and repair in bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017;15(7):385-396.
[36] SON S, KIM JH, WANG X, et al. Multifunctional sonosensitizers in sonodynamic cancer therapy. Chem Soc Rev. 2020;49(11):3244-3261.
[37] WANG G, WU W, ZHU JJ, et al. The promise of low-intensity ultrasound: a review on sonosensitizers and sonocatalysts by ultrasonic activation for bacterial killing. Ultrason Sonochem. 2021;79:105781.
[38] CARNEIRO BA, EL-DEIRY WS. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17(7):395-417.
[39] 王晓东,程文.声动力疗法介导肿瘤细胞死亡模式的研究进展[J].医学影像学杂志,2023,33(6):1108-1111.
[40] WU CF, LI YX, ZHONG S, et al. ROS is essential for initiation of energy deprivation-induced autophagy. J Genet Genomics. 2021;48(6):512-515.
[41] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282.
[42] YANG Y, HUANG J, LIU M, et al. Emerging sonodynamic therapy-based nanomedicines for cancer immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023; 10(2):e2204365.
[43] 蒋恩琰,王丹,张照霞,等.声动力疗法的机制研究进展[J].临床超声医学杂志,2023,25(8):677-680.
[44] ABDULLAH Z, KNOLLE PA. Scaling of immune responses against intracellular bacterial infection. EMBO J. 2014;33(20):2283-2294.
[45] NATHAN C. Nonresolving inflammation redux. Immunity. 2022;55(4): 592-605.
[46] HARDY KS, TESSMER MH, FRANK DW, et al. Perspectives on the pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system effector ExoU and its subversion of the host innate immune response to infection. Toxins (Basel). 2021;13(12):880.
[47] WILDE S, JOHNSON AF, LAROCK CN. Playing with fire: proinflammatory virulence mechanisms of group a streptococcus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:704099.
[48] COHEN J, VINCENT JL, ADHIKARI NK, et al. Sepsis: a roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15(5):581-614.
[49] KELLER N, ANDREONI F, REIBER C, et al. Human streptococcal necrotizing fasciitis histopathology mirrored in a murine model. Am J Pathol. 2018;188(7):1517-1523.
[50] FLEMMING HC, WINGENDER J, SZEWZYK U, et al. Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016;14(9):563-575.
[51] KARYGIANNI L, REN Z, KOO H. et al. Biofilm matrixome: extracellular components in structured microbial communities. Trends Microbiol. 2020;28(8):668-681.
[52] KOO H, YAMADA KM. Dynamic cell-matrix interactions modulate microbial biofilm and tissue 3D microenvironments. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2016;42:102-112.
[53] DRAGOŠ A, KOVÁCS ÁT. The peculiar functions of the bacterial extracellular matrix. Trends Microbiol. 2017;25(4):257-266.
[54] KOO H, ALLAN RN, HOWLIN RP, et al. Targeting microbial biofilms: current and prospective therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017;15(12):740-755.
[55] HUGHES G, WEBBER MA. Novel approaches to the treatment of bacterial biofilm infections. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(14):2237-2246.
[56] SHARMA D, MISBA L, KHAN AU. Antibiotics versus biofilm: an emerging battleground in microbial communities. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2019;8:76.
[57] VERMA AS, KUMAR D, DUBEY AK. Antibacterial and cellular response of piezoelectric Na0.5K0.5NbO3 modified 1393 bioactive glass. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;116:111138.
[58] 吴聪.钛表面生物压电涂层的构建及其骨修复促进机制研究[D].西安:西安理工大学,2021.
[59] MONTOYA C, JAIN A, LONDOÑO JJ, et al. Multifunctional dental composite with piezoelectric nanofillers for combined antibacterial and mineralization effects. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(37): 43868-43879.
[60] SHARMA A, BHARDWAJ U, JAIN D, et al. NaNbO3/ZnO piezocatalyst for non-destructive tooth cleaning and antibacterial activity. iScience. 2022;25(9):104915.
[61] LAURENTI M, CAUDA V. ZnO Nanostructures for tissue engineering applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017;7(11):374.
[62] KHADER A, ARINZEH TL. Biodegradable zinc oxide composite scaffolds promote osteochondral differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020;117(1):194-209.
[63] 邓伟成,谭帼馨,田雨,等.氧化锌掺杂压电水凝胶的制备及其抗菌机理[J].中国表面工程,2022,35(3):254-261.
[64] LIU D, LI L, SHI BL, et al. Ultrasound-triggered piezocatalytic composite hydrogels for promoting bacterial-infected wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2022;24:96-111.
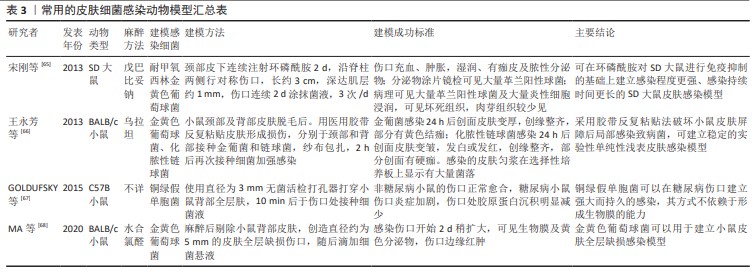
[65] 宋刚,王新,柳江枫,等.环磷酰胺免疫抑制大鼠的皮肤感染模型建立[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2013,33(6):458-461.
[66] 王永芳,李新宇,宋莎莎,等.单纯性浅表皮肤感染小鼠模型的建立及有效性验证[J].中国药科大学学报,2013,44(6):573-576.
[67] GOLDUFSKY J, WOOD SJ, JAYARAMAN V, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses T3SS to inhibit diabetic wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2015;23(4):557-564.
[68] MA M, ZHONG Y, JIANG X. Thermosensitive and pH-responsive tannin-containing hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel with long-lasting antibacterial activity for wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;15;236:116096.
|