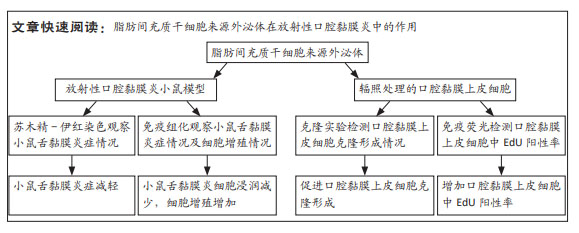
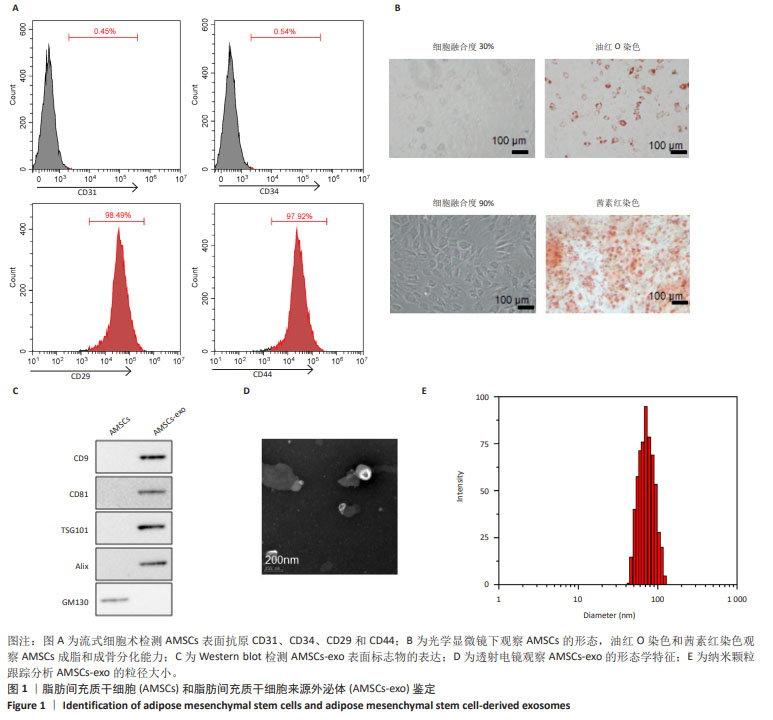
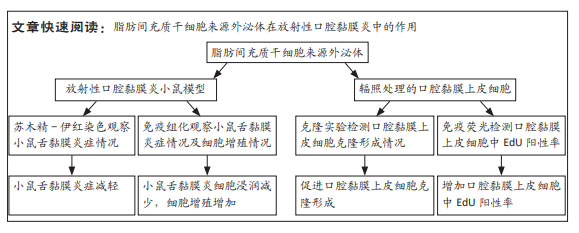
|
[1] LY KL, LUO X, RAUB CB. Oral mucositts on a chip: modeling inductton
by chemo- and radiatton treatments and recovery. Biofabricatton.
2022;15(1):10.1088/1758-5090/ac933b.
[2] MARIA OM, ELIOPOULOS N, MUANZA T. Radiatton-Induced Oral
Mucositts. Front Oncol. 2017;7:89.
[3] RAO D, BEHZADI F, LE RT, et al. Radiatton Induced Mucositts: What
the Radiologist Needs to Know. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2021;50(6):
899-904.
[4] SUBEDI P, HUBER K, STERR C, et al. Towards unravelling biological
mechanisms behind radiatton-induced oral mucositts via mass
spectrometry-based proteomics. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1180642.
[5] NIKITAKI Z, MAVRAGANI IV, LASKARATOU DA, et al. Systemic
mechanisms and effects of ionizing radiatton: A new ‘old’ paradigm of
how the bystanders and distant can become the players. Semin Cancer
Biol. 2016;37-38:77-95.
[6] GKANTAIFI A, VARDAS E, ALONGI F, et al. Radiatton-Induced Oral
Mucositts in Head and Neck Cancer Pattents. Five Years Literature
Review. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2021;16(2):151-165.
[7] KIM HJ, KANG SU, LEE YS, et al. Protecttve Effects of N-Acetylcysteine
against Radiatton-Induced Oral Mucositts In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancer
Res Treat. 2020;52(4):1019-1030.
[8] LEE CT, GALLOWAY TJ. Pathogenesis and Amelioratton of RadiattonInduced
Oral Mucositts. Curr Treat Opttons Oncol. 2022;23(3):
311-324.
[9] PULITO C, CRISTAUDO A, PORTA C, et al. Oral mucositts: the hidden side
of cancer therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):210.
[10] DAVY C, HEATHCOTE S. A systemattc review of interventtons to mittgate
radiotherapy-induced oral mucositts in head and neck cancer pattents.
Support Care Cancer. 2021;29(4):2187-2202.
[11] WANG H, ZHANG K, RUAN Z, et al. Correctton to: Probucol enhances
the therapeuttc efffciency of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment
of erecttle dysfunctton in diabettc rats by prolonging their survival ttme
via Nrf2 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):47.
[12] SHIN JY, LEE PH. Mesenchymal stem cells modulate misfolded
α-synuclein in parkinsonian disorders: A multttarget disease-modifying
strategy. Stem Cell Res. 2020;47:101908.
[13] WANG Y, FANG J, LIU B, et al. Reciprocal regulatton of mesenchymal
stem cells and immune responses. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(11):
1515-1530.
[14] ANDRZEJEWSKA A, DABROWSKA S, LUKOMSKA B, et al. Mesenchymal
Stem Cells for Neurological Disorders. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(7):
2002944.
[15] XU L, JI H, JIANG Y, et al. Exosomes Derived From CircAkap7-Modiffed
Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Against Cerebral
Ischemic Injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:569977.
[16] HAN Y, YANG J, FANG J, et al. The secretton proffle of mesenchymal
stem cells and potenttal applicattons in treattng human diseases. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):92.
[17] OGAY V, SEKENOVA A, LI Y, et al. The Therapeuttc Potenttal of
Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Atherosclerosis. Curr
Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(7):897-913.
[18] VAN BALKOM BWM, GREMMELS H, GIEBEL B, et al. Proteomic
Signature of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Small Extracellular
Vesicles. Proteomics. 2019;19(1-2):e1800163.
[19] SHANG Y, WANG Q, LI J, et al. Zirconia Nanoparttcles Induce HeLa Cell
Death Through Mitochondrial Apoptosis and Autophagy Pathways
Mediated by ROS. Front Chem. 2021;9:522708.
[20] DING X, NIE Z, SHE Z, et al. The Regulatton of ROS- and BECN1-
Mediated Autophagy by Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase in
Glioblastoma. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6636510.
[21] KMA L, BARUAH TJ. The interplay of ROS and the PI3K/Akt pathway
in autophagy regulation. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2022;69(1):
248-264.
[22] SANKAR V, XU Y. Oral Complicattons from Oropharyngeal Cancer
Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(18):4548.
[23] ELTING LS, COOKSLEY CD, CHAMBERS MS, et al. Risk, outcomes, and
costs of radiatton-induced oral mucositts among pattents with headand-neck
malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68(4):
1110-1120.
[24] LIU S, ZHAO Q, ZHENG Z, et al. Status of Treatment and Prophylaxis
for Radiatton-Induced Oral Mucositts in Pattents With Head and Neck
Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:642575.
[25] SONIS ST. Precision medicine for risk predictton of oral complicattons
of cancer therapy-The example of oral mucositts in pattents receiving
radiatton therapy for cancers of the head and neck. Front Oral Health.
2022;3:917860.
[26] CHEN G, WANG M, RUAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived
exosomal miR-143-3p suppresses myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury by regulattng autophagy. Life Sci. 2021;280:119742.
[27] TELI P, KALE V, VAIDYA A. Extracellular vesicles isolated from
mesenchymal stromal cells primed with neurotrophic factors and
signaling modiffers as potenttal therapeuttcs for neurodegenerattve
diseases. Curr Res Transl Med. 2021;69(2):103286.
[28] LU X, BAO H, CUI L, et al. hUMSC transplantatton restores ovarian
functton in POI rats by inhibittng autophagy of theca-intersttttal cells
via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;
11(1):268.
[29] LI T, GU J, YANG O, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived
Exosomal miRNA-29c Decreases Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
Through Inhibitton of Excessive Autophagy via the PTEN/Akt/mTOR
Signaling Pathway. Circ J. 2020;84(8):1304-1311.
[30] MA CY, ZHAI Y, LI CT, et al. Translattng mesenchymal stem cell and their
exosome research into GMP compliant advanced therapy products:
Promises, problems and prospects. Med Res Rev. 2023. doi: 10.1002/
med.22002.
[31] ZHOU C, ZHANG B, YANG Y, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging
therapeuttc opportunittes for wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther.
2023;14(1):107.
[32] ZOU J, YANG W, CUI W, et al. Therapeuttc potenttal and mechanisms
of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as bioacttve materials in
tendon-bone healing. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):14.
[33] WANG L, HU L, ZHOU X, et al. Author Correctton: Exosomes secreted by
human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote scarless cutaneous
repair by regulattng extracellular matrix remodelling. Sci Rep. 2021;
11(1):3245.
[34] XU T, LIN Y, YU X, et al. Comparattve Effects of Exosomes and Ectosomes
Isolated From Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Achilles
Tendinopathy in a Rat Model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(10):
2740-2752.
[35] WANG X, JIAO Y, PAN Y, et al. Fetal Dermal Mesenchymal Stem CellDerived
Exosomes Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Acttvattng
Notch Signaling. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:2402916.
[36] VU NB, NGUYEN HT, PALUMBO R, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes for
wound healing: current status and promising directtons. Minerva Med.
2021;112(3):384-400.
|