[1] ČOBEC J, KOZINC Ž. Conservative Treatments for Patellar Tendinopathy: A Review of Recent High-Quality Evidence. BioMed. 2022;2(4):359-375.
[2] MUAIDI QI. Rehabilitation of patellar tendinopathy. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(4):535-540.
[3] COOK J, KHAN K, HARCOURT P, et al. A cross sectional study of 100 athletes with jumper’s knee managed conservatively and surgically. Br J Sports Med. 1997;31(4):332-336.
[4] BURTON I. Interventions for prevention and in-season management of patellar tendinopathy in athletes: A scoping review. Phys Ther Sport. 2022;55:80-89.
[5] CHALLOUMAS D, PEDRET C, BIDDLE M, et al. Management of patellar tendinopathy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised studies. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2021;7(4):e001110.
[6] MARIGI EM, BUCKLEY P, RAZI F, et al. Patellar tendinopathy: critical analysis review of current nonoperative treatments. JBJS Rev. 2022;10(3). doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.21.00168.
[7] SILBERNAGEL KG,HANLON S,SPRAGUE A.Current clinical concepts: conservative management of Achilles tendinopathy. J Athl Train. 2020;55(5):438-447.
[8] BREDA SJ, OEI EH, ZWERVER J, et al. Effectiveness of progressive tendon-loading exercise therapy in patients with patellar tendinopathy: a randomised clinical trial. Br J Sports Med. 2021;55(9):501-509.
[9] GAIDA JE, COOK J.Treatment options for patellar tendinopathy: critical review. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2011;10(5):255-570.
[10] RITTWEGER J. Vibration as an exercise modality: how it may work, and what its potential might be. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;108(5):877-904.
[11] 王明伟, 吴香芝, 李立. 从第65届美国运动医学年会看全身震动对健康促进研究的影响[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2018,41(8):77-83.
[12] CHANG WD, CHEN S, TSOU YA. Effects of whole-body vibration and balance training on female athletes with chronic ankle instability. J Clin Med. 2021;10(11):2380.
[13] LAI Z, LEE S, CHEN Y, et al. Comparison of whole-body vibration training and quadriceps strength training on physical function and neuromuscular function of individuals with knee osteoarthritis: A randomised clinical trial. J Exerc Sci Fit. 2021;19(3):150-157.
[14] PARK SH, SEO JH, LEE MM. Effect of neuromuscular stabilization exercise program using whole body vibration on patients with low back pain. Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science. 2021;10(3):278-288.
[15] 刘衡, 叶姝.不同频率振动训练对膝骨关节炎老年人下肢肌力和症状的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(8):947-954.
[16] RIEDER F, WIESINGER H-P, HERFERT J, et al. Whole body vibration for chronic patellar tendinopathy: A randomized equivalence trial. Front Physiol. 2022;13:1017931.
[17] YAñEZ-ÁLVAREZ A, BERMúDEZ-PULGARíN B, HERNáNDEZ-SÁNCHEZ S, et al. Effects of exercise combined with whole body vibration in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome: a randomised-controlled clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):582.
[18] 吴章祥. 全身振动训练联合髋膝肌强化训练对成人髌股疼痛综合征的疗效研究[D].广州:广州体育学院,2020.
[19] ALAM MM, KHAN AA, FAROOQ M.Effect of whole-body vibration on neuromuscular performance: A literature review. Work. 2018;59(4):571-583.
[20] Huang Y, Wang Z, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of weight bearing vibration stimulation on surface myoelectric activation of lower limb muscle groups//2022 2nd International Conference on Information Technology and Contemporary Sports (TCS).IEEE. 2022:48-51.
[21] RITZMANN R, GOLLHOFER A, KRAMER A. The influence of vibration type, frequency, body position and additional load on the neuromuscular activity during whole body vibration. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(1):1-11.
[22] AL MASUD A, SHEN CL, CHYU MC. On the Optimal Whole-Body Vibration Protocol for Muscle Strength. Biomechanics. 2022;2(4):547-561.
[23] 王国祥, 岳春林. 髌腱末端病运动员膝关节屈伸峰力矩和表面肌电图的变化特征[J].体育科学,2009,29(12):56-59.
[24] RIEDER F, WIESINGER HP, KöSTERS A, et al. Whole‐body vibration training induces hypertrophy of the human patellar tendon. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2016;26(8):902-910.
[25] 侯捷, 李文彦, 刘瑞瑞, 等. 运动员髌腱末端病危险因素及治疗方案的研究进展[J].体育科技文献通报,2021,29(11):10-3+6.
[26] BAHR R, FOSSAN B, LøKEN S, et al.Surgical treatment compared with eccentric training for patellar tendinopathy (Jumper’s Knee). A randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(8):1689-1698.
[27] FROHM A, SAARTOK T, HALVORSEN K, et al. Eccentric treatment for patellar tendinopathy: a prospective randomised short-term pilot study of two rehabilitation protocols. Br J Sports Med. 2007;41(7): e7.
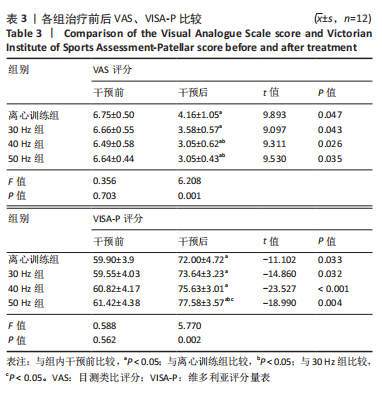
[28] VISENTINI PJ, KHAN KM, COOK JL, et al. The VISA score: an index of severity of symptoms in patients with jumper’s knee (patellar tendinosis). Victorian Institute of Sport Tendon Study Group. J Sci Med Sport. 1998;1(1):22-28.
[29] CHENG L, XU H, HE B, et al. Effect of the frequency of weight-free vibration training on the isokinetic strength of knee muscles in juvenile football players. Isokinet Exerc Sci. 2022;30(2):109-115.
[30] TORVINEN S, SIEVäNEN H, JäRVINEN TA, et al.Effect of 4-min vertical whole body vibration on muscle performance and body balance: a randomized cross-over study. Int J Sports Med. 2002;23(5):374-379.
[31] DI GIMINIANI R, MASEDU F, TIHANYI J, et al. The interaction between body position and vibration frequency on acute response to whole body vibration. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2013;23(1):245-251.
[32] ESCAMILLA RF, FLEISIG GS, ZHENG N, et al. Biomechanics of the knee during closed kinetic chain and open kinetic chain exercises. Med Sci Sports Exerc.1998;30(4):556-569.
[33] 王国祥, 严永军, 岳春林. 髌腱末端病运动员膝关节等速向心和离心运动时股四头肌表面肌电的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(46): 9105-9108.
[34] COUPPé C, KONGSGAARD M, AAGAARD P, et al.Differences in tendon properties in elite badminton players with or without patellar tendinopathy. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013; 23(2):e89-e95.
[35] OBARA K, CHIBA R, TAKAHASHI M, et al. Knee dynamics during take-off and landing in spike jumps performed by volleyball players with patellar tendinopathy. J Phys Ther Sci. 2022;34(2):103-109.
[36] VAN DER WORP H, DE POEL HJ, DIERCKS RL, et al. Jumper’s knee or lander’s knee? A systematic review of the relation between jump biomechanics and patellar tendinopathy. Int J Sports Med. 2014;35(8):714-722.
[37] EDWARDS S, STEELE JR, MCGHEE DE, et al.Landing strategies of athletes with an asymptomatic patellar tendon abnormality. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010 Nov;42(11):2072-2080.
[38] PIETROSIMONE LS, BLACKBURN JT, WIKSTROM EA, et al. Landing Biomechanics, But Not Physical Activity, Differ in Young Male Athletes With and Without Patellar Tendinopathy.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2020;50(3):158-166.
[39] DEVITA P, SKELLY WA. Effect of landing stiffness on joint kinetics and energetics in the lower extremity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1992;24(1):108-115.
[40] MINGORANCE JA, MONTOYA P, MIRANDA JGV, et al.The Therapeutic Effects of Whole-Body Vibration in Patients With Fibromyalgia. A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front Neurol. 2021;12:658383
[41] ALEV A, MIHRIBAN A, BILGE E, et al. Effects of whole body vibration therapy in pain, function and depression of the patients with fibromyalgia. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2017;28:200-203.
|