中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (33): 5370-5374.doi: 10.12307/2024.659
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
依据MRI影像组学数据构建颈椎失稳诊断分类模型的可行性
路广琦,崔 莹,李 靖,俞张镜泽,朱立国,于 杰,庄明辉
- 中国中医科学院望京医院,北京市 100102
Feasibility of constructing a diagnostic classification model for cervical instability by magnetic resonance imaging radiomics
Lu Guangqi, Cui Ying, Li Jing, Yu Zhangjingze, Zhu Liguo, Yu Jie, Zhuang Minghui
- Wangjing Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China
摘要:
文题释义:
影像组学:由荷兰学者LAMBIN等于2012年首次提出,即应用大量的自动化数据特征化算法从CT、PET或MRI等传统医学影像图像中将感兴趣区域的影像转换为可发掘的数据信息,并对之进行高通量定量分析,建立具有诊断、预后或预测价值的模型,为个性化诊疗提供有价值的信息。目前影像组学已广泛应用于肿瘤研究领域,在骨科研究领域尚处于起步阶段。颈椎失稳:是由于多种原因造成颈椎的结构功能退化,导致患者在生理状态下椎体节段过度或异常活动,并由此引发颈肩痛、头痛头晕等一系列的临床症状。
背景:既往颈椎失稳相关研究在传统影像学检查下对其病变发展过程中的动静力交互作用关系和病理特征变化阐释不明,近年来逐渐兴起的MRI影像组学可为颈椎失稳的深入研究提供新的途径。
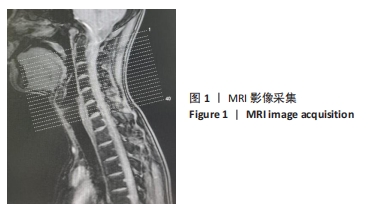
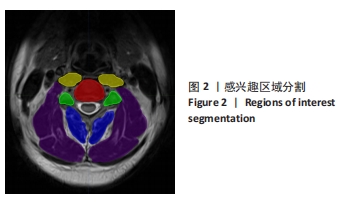
目的:探讨MRI影像组学在颈椎失稳研究中的应用价值。方法:通过招募广告和中国中医科学院望京医院脊柱二科门诊,纳入18-45岁青年颈椎失稳受试者和非失稳受试者进行颈椎MRI采集,在椎间盘所在的横断面图层,对椎间盘区、关节突区、椎前肌区、颈后肌群深层区及颈后肌群浅层区等5个特定感兴趣区域进行手动分割,以提取并筛选影像组学特征,最终进行颈椎失稳诊断分类模型的构建,并使用曲线下面积评价模型的效能。
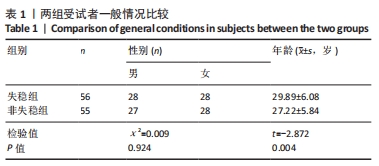
结果与结论:①共纳入56例颈椎失稳受试者和55例非失稳受试者,每个感兴趣区域提取影像组学特征各1 688个;经过筛选最终获得300组具有特异性的影像组学特征组合,每个感兴趣区域各60组;②初步建立了5个感兴趣区域的颈椎失稳诊断分类模型,其中关节突区的支持向量机模型和颈后肌群深层区的支持向量机模型对于失稳和非失稳的分类具有一定的准确性,十折交叉验证平均曲线下面积分别为0.719 7和0.703 3;③椎间盘区的Logistic模型、椎前肌区的LightGBM模型及颈后肌群浅层区的Logistic模型对于失稳和非失稳的分类准确性一般,十折交叉验证平均曲线下面积分别为0.650 4,0.620 7和0.644 2;④证明了MRI影像组学在颈椎失稳研究中应用的可行性,进一步深化了对颈椎失稳发病机制的认识,同时也为颈椎失稳的精准诊断提供了客观依据来源。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4774-9783 (路广琦)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: