中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (22): 3470-3475.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.22.005
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
关节软骨细胞外基质/人脐带Wharton胶复合多孔支架的制备及评估
肖统光1,2,郝春香3,荆晓光2,刘雪剑2,郭岗岗2,杨建华2,郭全义1
- 1解放军总医院骨科研究所,北京市 100853;2佳木斯大学,黑龙江省佳木斯市 154007;3解放军总医院,北京市 100853
Preparation and evaluation of an articular cartilage extracellular matrix/human umbilical cord Wharton gel composite scaffold
Xiao Tong-guang1, 2, Hao Chun-xiang3, Jing Xiao-guang2, Liu Xue-jian2, Guo Gang-gang2, Yang Jian-hua2, Guo Quan-yi1
- 1Institute of Orthopaedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; 2Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China; 3Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
细胞外基质:是由动物细胞合成并分泌到胞外、分布在细胞表面或细胞之间的大分子,主要是一些多糖和蛋白,或蛋白聚糖,这些物质构成复杂的网架结构,支持并连接组织结构、调节组织的发生和细胞的生理活动。细胞外基质是动物组织的一部分,不属于任何细胞,它决定结缔组织的特性,对于一些动物组织的细胞具有重要作用。
脐带Wharton胶:脐带包括2条动脉和1条静脉,在动脉和静脉之间有特殊的胚胎黏液状结缔组织,这种特殊的黏液状组织被称为脐带Wharton胶,富含透明质酸、糖胺多糖及胶原等、成分与天然软骨细胞外基质类似。
背景:软骨组织工程主要包括种子细胞、支架材料、细胞因子及生物反应器等,其中支架材料是构建组织工程软骨的关键环节。
目的:制备关节软骨细胞外基质/人脐带Wharton胶复合多孔支架,评估其理化特性及细胞相容性。
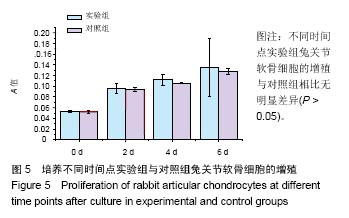
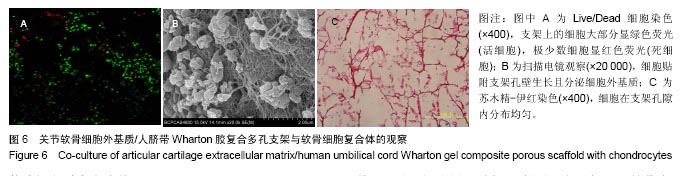
方法:采用物理法分别制备猪关节软骨细胞外基质及人脐带Wharton胶,然后以冻融干燥法制备关节软骨细胞外基质/人脐带Wharton胶复合多孔支架,检测支架的孔隙率、吸水率、组织成分及纵向压缩弹性模量,并进行组织学染色。将关节软骨细胞外基质/人脐带Wharton胶复合多孔支架与兔软骨细胞共培养7 d,进行扫描电镜观察、活-死细胞染色及苏木精-伊红染色;分别采用关节软骨细胞外基质/人脐带Wharton胶复合多孔支架浸提液与细胞培养液培养兔软骨细胞6 d,MTT法检测细胞增殖。
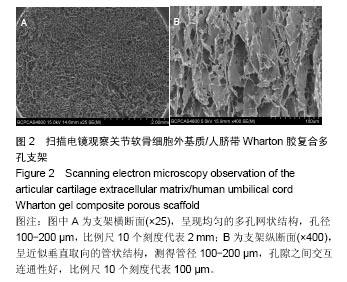
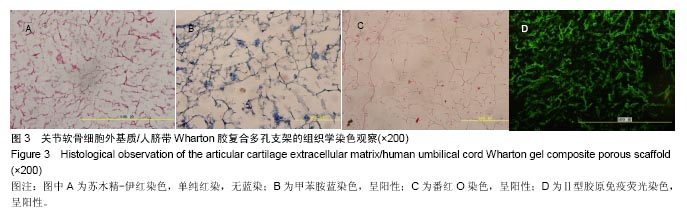
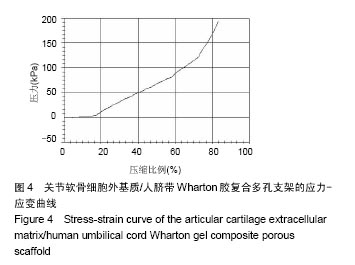
结果与结论:①关节软骨细胞外基质/人脐带Wharton胶复合多孔支架横断面为均匀的多孔网状结构,孔壁上密布软骨纤维,纵断面为垂直管状结构,支架苏木精-伊红红染、番红O及甲苯胺蓝染色均呈阳性,含有胶原和糖胺多糖成分,支架的吸水率、孔隙率和纵向压缩弹性模量分别为(17.418 8±0.909 0)%、(81.495 1±6.621 0)%和(2.833 3±0.456 4) kPa;②共培养7 d,兔软骨细胞在支架上黏附和增殖,并均匀长入支架孔隙内;③关节软骨细胞外基质/人脐带Wharton胶复合多孔支架浸提液对软骨细胞无毒性;④结果表明,关节软骨细胞外基质/人脐带Wharton胶复合多孔支架的理化性能及生化成分与天然软骨相似,具有良好的细胞相容性。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)