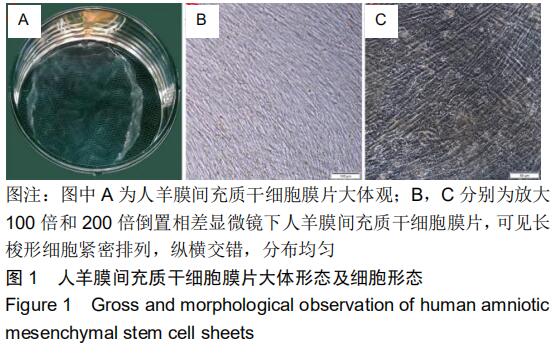
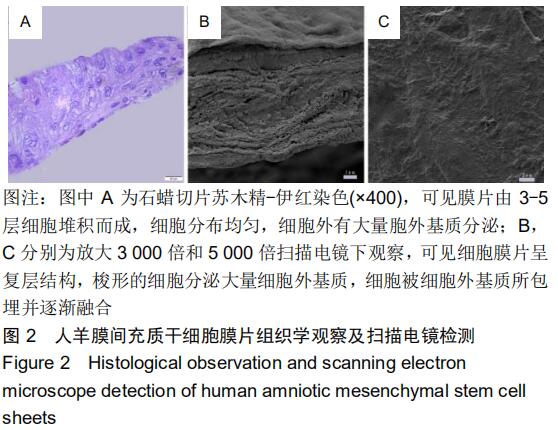
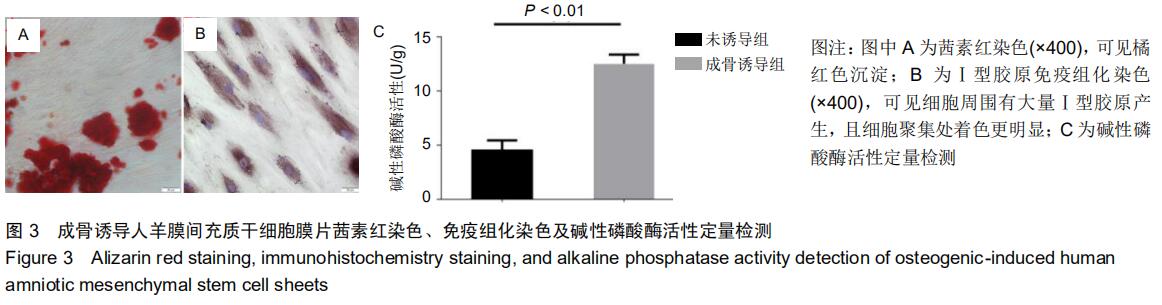
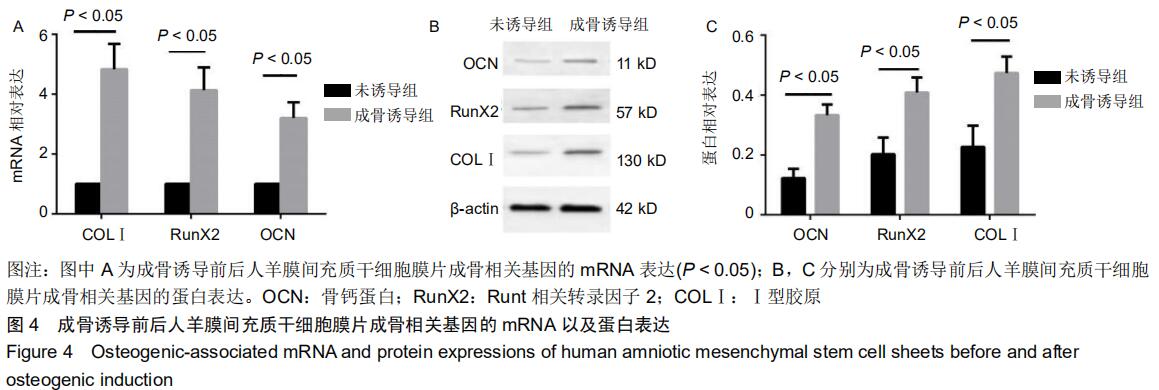
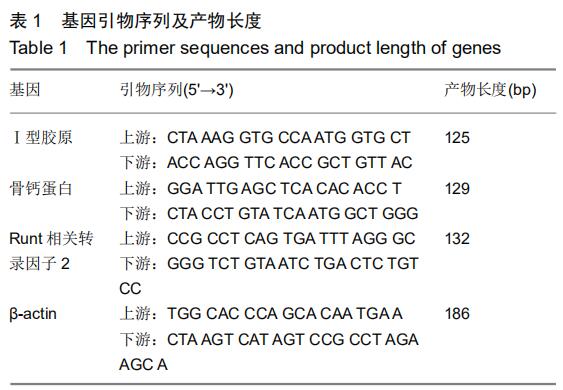
|
[1] 杜辉,付勤.同种异体骨移植与自体骨移植修复四肢粉碎性骨折:骨性愈合及骨活性比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(8):1206-1210.
[2] HERNIGOU P. Bone transplantation and tissue engineering. Part II: bone graft and osteogenesis in the seventeenth, eighteenth and nineteenth centuries (Duhamel, Haller, Ollier and MacEwen). Int Orthop. 2015;39(1):193-204.
[3] NIWA H, MASUI S, CHAMBERS I, et al. Phenotypic complementation establishes requirements for specific POU domain and generic transactivation function of Oct-3/4 in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(5):1526-1536.
[4] DING C, ZOU Q, WANG F, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells improve ovarian function in natural aging through secreting hepatocyte growth factor and epidermal growth factor. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):55.
[5] LV X, GUO Q, HAN F, et al. Electrospun Poly(l-lactide)/Poly(ethylene glycol) Scaffolds Seeded with Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Urethral Epithelium Repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(8). pii: E1262.
[6] LI Y, LIU Z, JIN Y, et al. Differentiation of Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Human Anterior Cruciate Ligament Fibroblast Cells by In Vitro Coculture. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017: 7360354.
[7] PAROLINI O, CARUSO M. Review: Preclinical studies on placenta-derived cells and amniotic membrane: an update. Placenta. 2011;32 Suppl 2:S186-195.
[8] GE X, WANG IN, TOMA I, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell-derived induced pluripotent stem cells may generate a universal source of cardiac cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(15):2798-2808.
[9] WU PH, CHUNG HY, WANG JH, et al. Amniotic membrane and adipose-derived stem cell co-culture system enhances bone regeneration in a rat periodontal defect model. J Formos Med Assoc. 2016;115(3):186-194.
[10] MIKI T. A Rational Strategy for the Use of Amniotic Epithelial Stem Cell Therapy for Liver Diseases. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(4): 405-409.
[11] SHU J, HE X, LI H, et al. The Beneficial Effect of Human Amnion Mesenchymal Cells in Inhibition of Inflammation and Induction of Neuronal Repair in EAE Mice. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:5083797.
[12] LIU Y, CAO DL, GUO LB, et al. Amniotic stem cell transplantation therapy for type 1 diabetes: a case report. J Int Med Res. 2013;41(4): 1370-1377.
[13] COHEN J, ZALESKI KL, NOURISSAT G, et al. Survival of porcine mesenchymal stem cells over the alginate recovered cellular method. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;96(1):93-99.
[14] SHI D, XU X, YE Y, et al. Photo-Cross-Linked Scaffold with Kartogenin-Encapsulated Nanoparticles for Cartilage Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2016;10(1):1292-1299.
[15] SETO Y, INABA R, OKUYAMA T, et al. Engineering of capillary-like structures in tissue constructs by electrochemical detachment of cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31(8):2209-2215.
[16] TANG CS, SCHMUTZ P, PETRONIS S, et al. Locally Addressable Electrochemical Patterning Technique (LAEPT) applied to poly(L-lysine)-graft-poly(ethylene glycol) adlayers on titanium and silicon oxide surfaces. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2005;91(3):285-295.
[17] ISHII M, SHIBATA R, NUMAGUCHI Y, et al. Enhanced angiogenesis by transplantation of mesenchymal stem cell sheet created by a novel magnetic tissue engineering method. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31(10):2210-2215.
[18] HONG Y, YU M, WENG W, et al. Light-induced cell detachment for cell sheet technology. Biomaterials. 2013;34(1):11-18.
[19] BYAMBAA B, KONNO T, ISHIHARA K. Detachment of cells adhered on the photoreactive phospholipid polymer surface by photoirradiation and their functionality. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;103:489-495.
[20] GUILLAUME-GENTIL O, SEMENOV OV, ZISCH AH, et al. pH-controlled recovery of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheets. Biomaterials. 2011;32(19):4376-4384.
[21] CHEN YH, CHUNG YC, WANG IJ, et al. Control of cell attachment on pH-responsive chitosan surface by precise adjustment of medium pH. Biomaterials. 2012;33(5):1336-1342.
[22] TAKAGI R, YAMATO M, KANAI N, et al. Cell sheet technology for regeneration of esophageal mucosa. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18(37):5145-5150.
[23] LORIES RJ, DERESE I, LUYTEN FP. Modulation of bone morphogenetic protein signaling inhibits the onset and progression of ankylosing enthesitis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(6):1571-1579.
[24] YING J, WANG P, ZHANG S, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta1 promotes articular cartilage repair through canonical Smad and Hippo pathways in bone mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2018;192:84-90.
[25] BEACHY PA, KARHADKAR SS, BERMAN DM. Tissue repair and stem cell renewal in carcinogenesis. Nature. 2004;432(7015):324-331.
[26] MATSUURA K, SHIMIZU T, OKANO T. Toward the development of bioengineered human three-dimensional vascularized cardiac tissue using cell sheet technology. Int Heart J. 2014;55(1):1-7.
[27] KOBAYASHI T, KAN K, NISHIDA K, et al. Corneal regeneration by transplantation of corneal epithelial cell sheets fabricated with automated cell culture system in rabbit model.Biomaterials. 2013; 34(36):9010-9017.
[28] ZHAO YH, ZHANG M, LIU NX, et al. The combined use of cell sheet fragments of periodontal ligament stem cells and platelet-rich fibrin granules for avulsed tooth reimplantation. Biomaterials. 2013;34(22): 5506-5520.
[29] LIN YC, GRAHOVAC T, OH SJ, et al. Evaluation of a multi-layer adipose-derived stem cell sheet in a full-thickness wound healing model. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(2):5243-5250.
[30] SATO M, YAMATO M, HAMAHASHI K, et al. Articular cartilage regeneration using cell sheet technology. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014; 297(1):36-43.
|