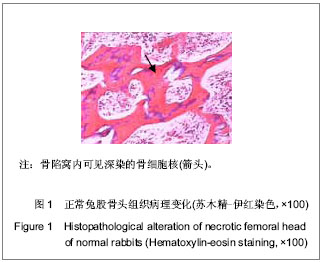
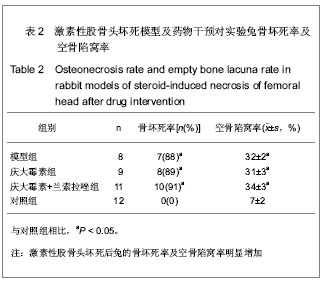
| [1] Hu MF, Zhou XC, Shan LT, et al. Research progress on proteomics in femur head necrosis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(3):264-266. [2] Hu HZ, Li TZ, Tong PJ, et al. Forecasting and prevention of collapse in femur head necrosis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010; 23(11):879-881. [3] Schneider W, Breitenseher M, Engel A, et al. The value of core decompression in treatment of femur head necrosis. Orthopade. 2000;29(5):420-429. [4] Kramer J, Breitenseher M, Imhof H, et al. Diagnostic imaging in femur head necrosis. Orthopade. 2000;29(5):380-388. [5] Vogel HJ, Schwetlick G. Femur head necrosis in the adult. Diagnosis, therapy, legal aspects for insurance medicine. Versicherungsmedizin. 1997;49(3):82-85. [6] Wang Y, Zhu ZX. Early diagnosis and treatment of ischemic femur head necrosis in adult. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1994; 74(10):642-644. [7] Hofmann S, Kramer J, Leder K, et al. The non-traumatic femur head necrosis in the adult. I: pathophysiology, clinical picture and therapeutic options. Radiologe. 1994;34(1): 1-10. [8] Montskó P. Treatment of idiopathic femur head necrosis by implantation of a preserved bone graft. Critical evaluation of the method. Magy Traumatol Orthop Helyreallito Seb. 1992; 35(1):31-36. [9] Hungerford DS. Role of core decompression as treatment method for ischemic femur head necrosis. Orthopade. 1990; 19(4):219-223.[10] 王建忠,武永刚,王坤正.激素性股骨头坏死患者骨组织MMP-2、MMP-9、TIMP-1、TIMP-2蛋白的表达[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012,6(1):59-62. [11] Ahmed N, Dreier R, Göpferich A, et al. Soluble signalling factors derived from differentiated cartilage tissue affect chondrogenic differentiation of rat adult marrow stromal cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007;20(5):665-678. [12] Chen TH, Chen L, Hsieh MS, et al. Evidence for a protective role for adiponectin in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1762(8):711-718.[13] 朱和玉.激素性骨坏死动物模型研究进展[J].医学综述,2012, 18(1): 118-121. [14] Maillefert JF, Tavernier C, Toubeau M, et al. Non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(3):473-474. [15] Iwakiri K, Oda Y, Kaneshiro Y, et al. Effect of simvastatin on steroid-induced osteonecrosis evidenced by the serum lipid level and hepatic cytochrome P4503A in a rabbit model. J Orthop Sci. 2008;13(5):463-468. [16] Takao M, Sugano N, Nishii T, et al. Different magnetic resonance imaging features in two types of nontraumatic rabbit osteonecrosis models. Magn Reson Imaging. 2009; 27(2): 233-239. [17] Nishida K, Yamamoto T, Motomura G, et al. Pitavastatin may reduce risk of steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits: a preliminary histological study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466(5):1054-1058. [18] Wang L, Wang N, Li M, et al. To investigate the role of the nervous system of bone in steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(12):2057-2066. [19] Sugano N, Kubo T, Takaoka K, et al. Diagnostic criteria for non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A multicentre study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(4):590-595.[20] Liu Z, Zhang G, Man CW, et al. Establishment of a steroid-induced osteonecrosis animal model in bipedal emus. Bone. 2010;47(6):S447.[21] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[22] 田力,梁晓鹏,田晓晔,等.地塞米松联合脂多糖诱导股骨头坏死模型的构建[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(35): 6571-6574.[23] Miyanishi K, Yamamoto T, Irisa T, et al. A high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as a potential risk factor for corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001;40(2): 196-201. [24] Temelkova-Kurktschiev T, Hanefeld M. The lipid triad in type 2 diabetes - prevalence and relevance of hypertriglyceridaemia/low high-density lipoprotein syndrome in type 2 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2004;112(2): 75-79. [25] Maki KC, Galant R, Davidson MH. Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol: the forgotten therapeutic target. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(9A):59K-64K; discussion 34K-35K. [26] Evans M, Roberts A, Davies S, et al. Medical lipid-regulating therapy: current evidence, ongoing trials and future developments. Drugs. 2004;64(11):1181-1196. [27] Miller NE. Raising high density lipoprotein cholesterol. The biochemical pharmacology of reverse cholesterol transport. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;40(3):403-410.[28] Yamamoto T, Hirano K, Tsutsui H, et al. Corticosteroid enhances the experimental induction of osteonecrosis in rabbits with Shwartzman reaction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;(316):235-243. [29] Warner JJ, Philip JH, Brodsky GL, et al. Studies of nontraumatic osteonecrosis. Manometric and histologic studies of the femoral head after chronic steroid treatment: an experimental study in rabbits. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; (225):128-140. [30] Boss JH, Misselevich I. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head of laboratory animals: the lessons learned from a comparative study of osteonecrosis in man and experimental animals. Vet Pathol. 2003;40(4):345-354. [31] Cruess RL. Osteonecrosis of bone. Current concepts as to etiology and pathogenesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(208): 30-39. [32] Piesold JU, Al-Nawas B, Grötz KA. Osteonecrosis of the jaws by long term therapy with bisphosphonates. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir. 2006;10(5):287-300. [33] Gorskaia EM. Current concepts of the mechanism of the local Shwartzman phenomenon. Patol Fiziol Eksp Ter. 1981;(5): 79-83. [34] Powell C, Chang C, Gershwin ME. Current concepts on the pathogenesis and natural history of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011;41(1): 102-113. [35] Kerachian MA, Séguin C, Harvey EJ. Glucocorticoids in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a new understanding of the mechanisms of action. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2009; 114(3-5):121-128. [36] Yamamoto T, Miyanishi K, Motomura G, et al. Animal models for steroid-induced osteonecrosis. Clin Calcium. 2007; 17(6): 879-886.[37] Qin L, Zhang G, Sheng H, et al. Multiple bioimaging modalities in evaluation of an experimental osteonecrosis induced by a combination of lipopolysaccharide and methylprednisolone. Bone. 2006;39(4):863-871. [38] Tanahashi N. Thrombolysis by intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA)--current status and future direction. Brain Nerve. 2009;61(1):41-52. [39] Saini A, Saifuddin A. MRI of osteonecrosis. Clin Radiol. 2004;59(12):1079-1093. [40] Ditzian-Kadanoff R, Ellman MH. How safe is it? High dose intravenous methylprednisolone. IMJ Ill Med J. 1987; 172(6): 432-434.[41] Okazaki S, Nishitani Y, Nagoya S, et al. Femoral head osteonecrosis can be caused by disruption of the systemic immune response via the toll-like receptor 4 signalling pathway. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(3):227-232.[42] Fujioka M, Arai Y, Kuribayashi M, et al. Genetic analysis for prevention of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Calcium. 2007;17(6):894-900. [43] Kubo T, Fujioka M, Ishida M. Clinical condition of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Calcium. 2007;17(6):856-862. [44] Zeng P, Wei BF, He W, et al. Advances in researches on genetic predisposition to steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010;23(2):156-159. [45] Matsumoto T, Kitamura K, Ichiseki T, et al. Oxidative stress on idiopathic osteonecrosis. Clin Calcium. 2007;17(6):887-891. [46] Lüring C, Beckmann J, Pennekamp PH, et al. Conservative treatment of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. Are there evidence-based therapy concepts? Orthopade. 2007;36(5): 441-442, 444-445. [47] Fukushima W, Ohfuji S, Hirota Y. Epidemiology of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan. Clin Calcium. 2007;17(6):843-848. [48] Hadjigeorgiou G, Dardiotis E, Dardioti M, et al. Genetic association studies in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: mini review of the literature. Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37(1):1-7. [49] Jones KB, Seshadri T, Krantz R, et al. Cell-based therapies for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(10):1081-1087.[50] 李亚春,李颖川,周明,等.脂多糖对大鼠肺微血管内皮细胞ACE和ACE2表达的影响及血管紧张素转换酶抑制剂的干预作用[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2012,32(4):452-457. [51] Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Matumoto S, et al. Effects of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor on the inflammatory response in in vivo and in vitro models. Crit Care Med. 2009; 37(2):626-633. [52] Marshall RP, Webb S, Bellingan GJ, et al. Angiotensin converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism is associated with susceptibility and outcome in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(5):646-650.[53] 鲁春晓.糖皮质激素类药物的临床合理应用[J]. 临床合理用药杂志,2012,5(7):90-91.[54] 陈冠儒,王萧枫,王利明,等.兔激素性股骨头坏死造模中的致死因素与干预分析[J].浙江中西医结合杂志2012,22(5):342-344.[55] 周玉兰,王鲜忠.有效防治家兔腹泻,提高养兔业的经济效益[J].中国动物保健,2008,117(2):28-32.[56] 范淑敏.兰索拉唑联合立止血治疗上消化道出血79例疗效观察[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(19):167-168.[57] 康军,邓小艳. 兰索拉唑治疗上消化道出血48例疗效观察[J]. 临床合理用药杂志,2010,3(17):41-42. |