中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (48): 8455-8460.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.48.025
• 骨与关节临床实践 clinical practice of the bone and joint • 上一篇
不同病因致股骨头缺血性坏死的影像对比
张德洲,易雪冰,钟 鉴
- 四川省骨科医院放射科,四川省成都市 610041
Imaging comparison for avascular necrosis of the femoral head induced by different etiologies
Zhang De-zhou, Yi Xue-bing, Zhong Jian
- Department of Radiology, Sichuan Orthopaedic Hospital, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
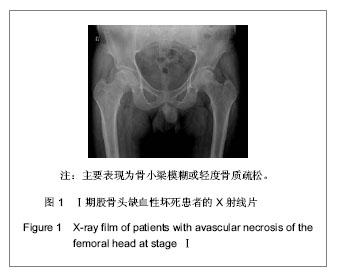
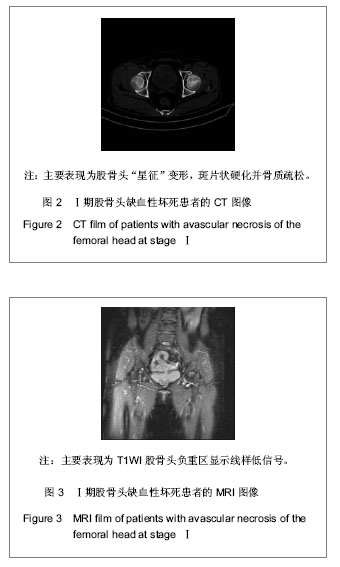
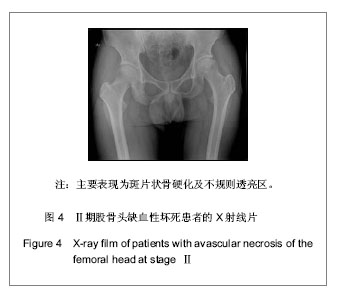
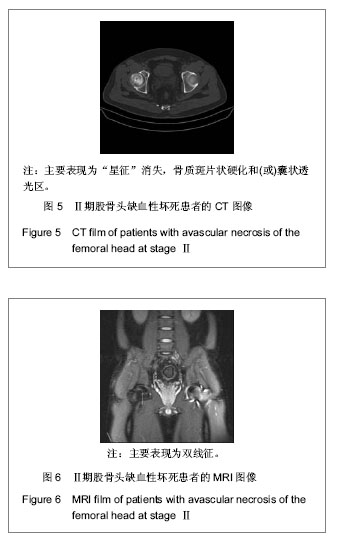
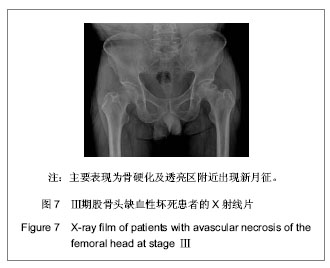
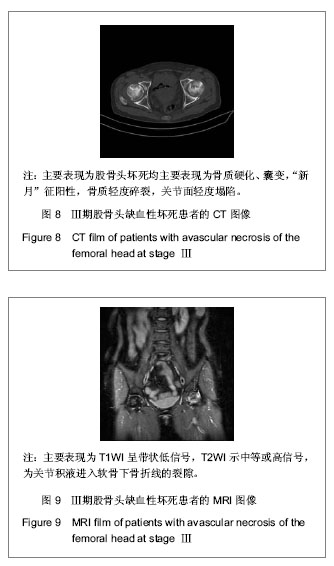
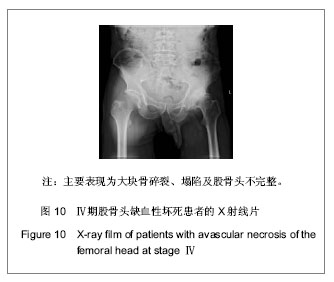
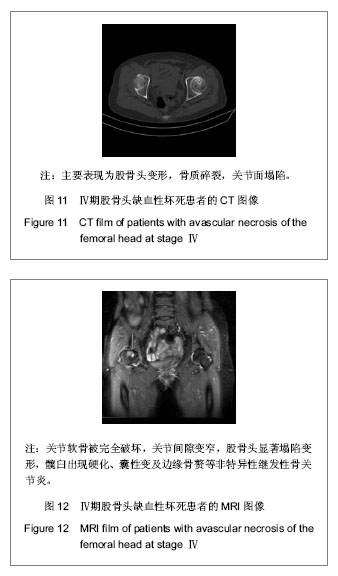
背景:股骨头缺血性坏死的临床诊断主要依靠影像学检查,对不同病因所致股骨头缺血性坏死的影像学对比研究目前报道甚少。 目的:对不同病因股骨头缺血性坏死的影像学表现进行比较研究,观察不同病因股骨头缺血性坏死的影像学表现有无差别。 方法:收集经临床及影像学检查证实的股骨头缺血性坏死54例共计60个髋关节影像资料,根据病因将其分为特发性、酒精性、激素性、股骨颈骨折性4类,将这4类股骨头缺血坏死的X射线、CT、MRI表现进行对比分析。 结果与结论:60个股骨头缺血性坏死髋关节中特发性12个、酒精性21个、激素性15个、股骨颈骨折性12个。X射线、CT主要表现依次为:股骨头“星征”变形或 “星征”消失;“新月”征阳性,骨质轻度碎裂,关节面轻度塌陷;股骨头变形,骨质碎裂,关节面塌陷,髋关节退性行改变,并以CT更可靠。股骨头缺血性坏死分期MRI均表现为:Ⅰ期T1WI股骨头负重区显示线样低信号、T2WI 加权呈高信号为主要改变;Ⅱ期T1WI为新月形边界清楚的不均匀信号,T2WI加权呈中等稍高信号,周围不均匀稍低信号环绕,呈典型的双线征;Ⅲ期股骨头变形,软骨下骨折、塌陷、新月体形成。T1WI呈带状低信号, T2WI示中等或高信号;Ⅳ、Ⅴ期关节软骨被完全破坏,关节间隙变窄,股骨头显著塌陷变形,髋臼出现硬化、囊性变及边缘骨赘等非特异性继发性骨关节炎。提示不同病因相同分期股骨头缺血性坏死的X射线、CT、MRI表现特点及规律是相同的。
中图分类号: