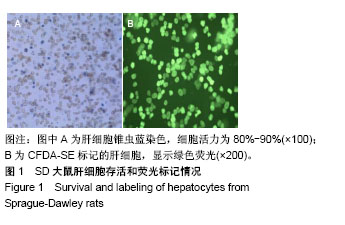
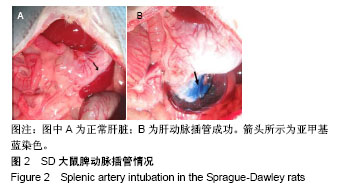
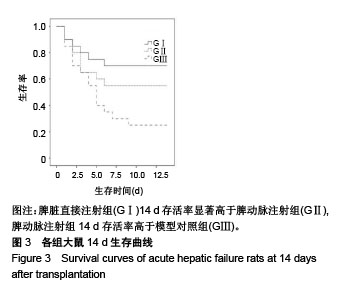
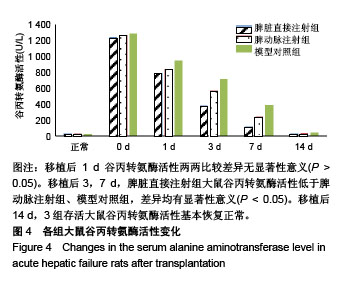
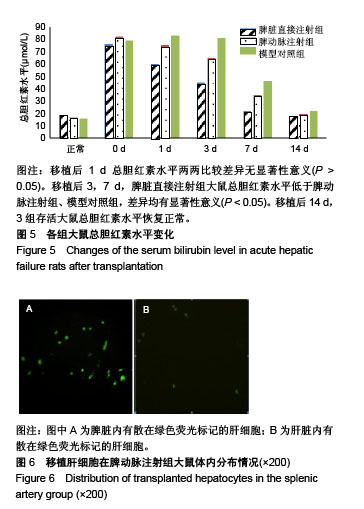
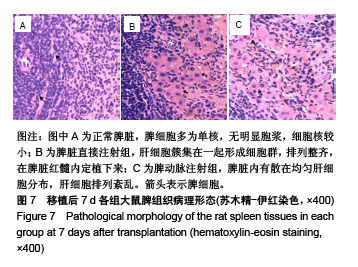
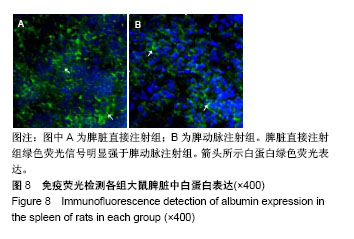
| [1] Newland CD. Acute Liver Failure. Pediatr Ann. 2016;45(12): e433-e438.[2] Sarin SK, Choudhury A. Acute-on-chronic Liver Failure. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2016;18(12):61.[3] Dhawan A.Clinical human hepatocyte transplantation: Current status and challenges. Liver Transpl. 2015;21 Suppl 1:S39-44.[4] Patel P, Okoronkwo N, Pyrsopoulos NT. Future Approaches and Therapeutic Modalities for Acute Liver Failure. Clin Liver Dis. 2018;22(2):419-427.[5] Thawley V. Acute Liver Injury and Failure. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2017;47(3):617-630.[6] Soltys KA, Setoyama K, Tafaleng EN, et al. Host conditioning and rejection monitoring in hepatocyte transplantation in humans. J Hepatol. 2017;66(5):987-1000.[7] Iansante V, Mitry RR, Filippi C, et al. Human hepatocyte transplantation for liver disease: current status and future perspectives. Pediatr Res. 2018;83(1-2):232-240.[8] Khan Z, Strom SC. Hepatocyte Transplantation in Special Populations: Clinical Use in Children. Methods Mol Biol. 2017; 1506:3-16.[9] Zern MA. Cell transplantation to replace whole liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(3):767-769.[10] Kobayashi E, Enosawa S, Nagashima H. Experimental Hepatocyte Transplantation in Pigs. Methods Mol Biol. 2017; 1506:149-160.[11] Pietrosi G, Vizzini GB, Gruttadauria S, et al. Clinical applications of hepatocyte transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(17): 2074-2077.[12] Nagata H, Ito M, Shirota C, et al. Route of hepatocyte delivery affects hepatocyte engraftment in the spleen. Transplantation. 2003;76(4):732-734.[13] Iwase H, Liu H, Schmelzer E, et al. Transplantation of hepatocytes from genetically engineered pigs into baboons. Xenotransplantation. 2017;24(2): 1-22.[14] Soltys KA, Setoyama K, Tafaleng EN, et al. Host conditioning and rejection monitoring in hepatocyte transplantation in humans. J Hepatol. 2017;66(5):987-1000.[15] Seglen PO. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29-83.[16] 冯渊,李德卫,杨晓波,等.原发肝细胞的分离和移植[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(18):3314-3317.[17] 冯渊,李德卫,杨均均,等.经大鼠脾动脉行肝细胞移植建立动物模型[J].复旦学报(医学版),2012,39(6):653-657.[18] Puppi J, Strom SC, Hughes RD, et al. Improving the techniques for human hepatocyte transplantation: report from a consensus meeting in London. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(1):1-10.[19] Hansel MC, Gramignoli R, Skvorak KJ, et al. The history and use of human hepatocytes for the treatment of liver diseases: the first 100 patients. Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2014;62: 14.12.1-14.12.23.[20] Kluge M, Reutzel-Selke A, Napierala H, et al. Human Hepatocyte Isolation: Does Portal Vein Embolization Affect the Outcome. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(1):38-48.[21] Moris D, Vernadakis S, Papalampros A, et al. Mechanistic insights of rapid liver regeneration after associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for stage hepatectomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(33):7613-7624.[22] Dagher I, Boudechiche L, Branger J, et al. Efficient hepatocyte engraftment in a nonhuman primate model after partial portal vein embolization. Transplantation. 2006;82(8):1067-1073.[23] Timm F, Vollmar B. Heterogeneity of the intrahepatic portal venous blood flow: impact on hepatocyte transplantation. Microvasc Res. 2013;86:34-41.[24] Strom SC, Chowdhury JR, Fox IJ. Hepatocyte transplantation for the treatment of human disease. Semin Liver Dis. 1999;19(1): 39-48.[25] Dhawan A, Puppi J, Hughes RD, et al. Human hepatocyte transplantation: current experience and future challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(5):288-298.[26] Ho CM, Chen YH, Chien CS, et al. Transplantation speed offers early hepatocyte engraftment in acute liver injured rats: A translational study with clinical implications. Liver Transpl. 2015; 21(5):652-661.[27] Bilir BM, Guinette D, Karrer F, et al. Hepatocyte transplantation in acute liver failure. Liver Transpl. 2000;6(1):32-40.[28] Wang F, Zhou L, Ma X, et al. Monitoring of intrasplenic hepatocyte transplantation for acute-on-chronic liver failure: a prospective five-year follow-up study. Transplant Proc. 2014;46(1):192-198.[29] Nordlinger B, Bouma ME, Wang SR, et al. High-yield preparation of porcine hepatocytes for long survival after transplantation in the spleen. Eur Surg Res. 1985;17(6):377-382.[30] Fox IJ, Roy-Chowdhury J. Hepatocyte transplantation. J Hepatol. 2004;40(6):878-886.[31] Gäbelein G, Nüssler AK, Morgott F, et al. Intrasplenic or subperitoneal hepatocyte transplantation to increase survival after surgically induced hepatic failure. Eur Surg Res. 2008;41(3): 253-259.[32] Koblihová E, Lukšan O, Mrázová I, et al. Hepatocyte transplantation attenuates the course of acute liver failure induced by thioacetamide in Lewis rats. Physiol Res. 2015;64(5):689-700.[33] 李宏涛,陈国民. D-氨基半乳糖研究的回顾和展望[J] .肝脏, 2004, 9(3):209-210.[34] 冯渊,李德卫,杨晓波,等.经颈动脉途径肝动脉插管及脾内注射肝细胞移植治疗急性肝衰大鼠的疗效比较[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2012, 37(1):84-88. |
.jpg)
.jpg)