[1] CAREY RM, MORAN AE, WHELTON PK. Treatment of hypertension: A review. JAMA. 2022;328(18):1849-1861.
[2] WANG C, YUAN Y, ZHENG M, et al. Association of age of onset of hypertension with cardiovascular diseases and mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(23):2921-2930.
[3] YUSUF S, JOSEPH P, RANGARAJAN S, et al. Modifiable risk factors, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in 155 722 individuals from 21 high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries (PURE): A prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10226):795-808.
[4] LEWINGTON S, CLARKE R, QIZILBASH N, et al. Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: A meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360(9349):1903-1913.
[5] MALIK R, GEORGAKIS MK, VUJKOVIC M, et al. Relationship between blood pressure and incident cardiovascular disease: Linear and nonlinear Mendelian randomization analyses. Hypertension. 2021; 77(6):2004-2013.
[6] ARVANITIS M, QI G, BHATT DL, et al. Linear and nonlinear Mendelian randomization analyses of the association between diastolic blood pressure and cardiovascular events: The J-curve revisited. Circulation. 2021;143(9):895-906.
[7] MCEVOY JW, MCCARTHY CP, BRUNO RM, et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2024;45(38):3912-4018.
[8] ZHANG M, SHI Y, ZHOU B, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in China, 2004-18: Findings from six rounds of a national survey. BMJ. 2023;380:e071952.
[9] WANG Z, CHEN Z, ZHANG L, et al. China Hypertension Survey Investigators. Status of hypertension in China: Results from the China Hypertension Survey, 2012-2015. Circulation. 2018;137(22):2344-2356.
[10] KATSIMARDOU A, IMPRIALOS K, STAVROPOULOS K, et al. Hypertension in metabolic syndrome: Novel insights. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2020; 16(1):12-18.
[11] 中华医学会心血管病学分会高血压学组.肥胖相关性高血压管理的中国专家共识[J].中华心血管病杂志,2016,44(3):212-219.
[12] YAO Y, WANG B, GENG T, et al. The association between TyG and all-cause/non-cardiovascular mortality in general patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is modified by age: Results from the cohort study of NHANES 1999-2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024;23(1):43.
[13] LEE SH, PARK SY, CHOI CS. Insulin resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):15-37.
[14] DZIĘGIELEWSKA-GĘSIAK S, MUC-WIERZGOŃ M. Inflammation and oxidative stress in frailty and metabolic syndromes-two sides of the same coin. Metabolites. 2023;13(4):475.
[15] QUESADA O, CLAGGETT B, RODRIGUEZ F, et al. Associations of insulin resistance with systolic and diastolic blood pressure: A study from the HCHS/SOL. Hypertension. 2021;78(3):716-725.
[16] 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会.中国高血压防治指南(2024年修订版)[J].中华高血压杂志,2024,32(7):603-700.
[17] LEE EY, YANG HK, LEE J, et al. Triglyceride glucose index, a marker of insulin resistance, is associated with coronary artery stenosis in asymptomatic subjects with type 2 diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. 2016;15(1):155.
[18] ER LK, WU S, CHOU HH, et al. Triglyceride glucose-body mass index is a simple and clinically useful surrogate marker for insulin resistance in nondiabetic individuals. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0149731.
[19] WANG X, LIU J, CHENG Z, et al. Triglyceride glucose-body mass index and the risk of diabetes: A general population-based cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. 2021;20(1):99.
[20] YU XR, DU JL, JIANG M, et al. Correlation of TyG-BMI and TyG-WC with severity and short-term outcome in new-onset acute ischemic stroke. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne). 2024;15:1327903.
[21] FAN C, GUO M, CHANG S, et al. Elevated TyG-BMI index predicts incidence of chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Med. 2024;24(1):203.
[22] WANG R, DAI L, ZHONG Y, et al. Usefulness of the triglyceride glucose-body mass index in evaluating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Insights from a general population. Lipids Health Dis. 2021;20(1):77.
[23] ZHAO Y, HU Y, SMITH JP, et al. Cohort profile: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43(1): 61-68.
[24] HUO RR, ZHAI L, LIAO Q, et al. Changes in the triglyceride glucose-body mass index estimate the risk of stroke in middle-aged and older Chinese adults: A nationwide prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1):254.
[25] CHEN X, CRIMMINS E, HU PP, et al. Venous blood-based biomarkers in the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study: Rationale, design, and results from the 2015 wave. Am J Epidemiol. 2019;188(11):1871-1877.
[26] WILLIAMS B, MANCIA G, SPIERING W, et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(33):3021-3104.
[27] SHAO Y, HU H, LI Q, et al. Link between triglyceride-glucose-body mass index and future stroke risk in middle-aged and elderly Chinese: A nationwide prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024;23(1):81.
[28] VAN OORT S, BEULENS JWJ, VAN BALLEGOOIJEN AJ, et al. Association of cardiovascular risk factors and lifestyle behaviors with hypertension: A Mendelian randomization study. Hypertension. 2020;76(6):1971-1979.
[29] KUANG M, YANG R, HUANG X, et al. Assessing temporal differences in the predictive power of baseline TyG-related parameters for future diabetes: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):299.
[30] SELVARAJ S, STEG PG, ELBEZ Y, et al. REACH Registry Investigators. Pulse pressure and risk for cardiovascular events in patients with atherothrombosis: From the REACH registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016; 67(4):392-403.
[31] ZHANG Z, GU X, TANG Z, et al. Associations of blood pressure components with risk of cardiovascular events and all-cause death in a Chinese population: A prospective study. J Clin Hypertens(Greenwich). 2022;24(7):825-837.
[32] LIU D, QIN P, LIU L, et al. Association of pulse pressure with all-cause and cause-specific mortality. J Hum Hypertens. 2021;35(3):274-279.
[33] WANG Y, YANG W, JIANG X. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and hypertension: A meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:644035.
[34] ZHU B, WANG J, CHEN K, et al. A high triglyceride glucose index is more closely associated with hypertension than lipid or glycemic parameters in elderly individuals: A cross-sectional survey from the Reaction Study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020;19(1):112.
[35] SHAN S, LI S, LU K, et al. Associations of the triglyceride and glucose index with hypertension stages, phenotypes, and their progressions among middle-aged and older Chinese. Int J Public Health. 2023; 68:1605648.
[36] XIN F, HE S, ZHOU Y, et al. The triglyceride glucose index trajectory is associated with hypertension: A retrospective longitudinal cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1):347.
[37] YU L, YANG YX, GONG Z, et al. FcRn-dependent IgG accumulation in adipose tissue unmasks obesity pathophysiology. Cell Metab. 2025;37(3):656-672.
[38] JIA G, SOWERS JR, WHALEY-CONNELL AT. Obesity in Hypertension: The Role of the Expanding Waistline Over the Years and Insights Into the Future. Hypertension. 2024;81(4):687-690.
[39] HU L, LI J, TANG Z, et al. How does biological age acceleration mediate the associations of obesity with cardiovascular disease? Evidence from international multi-cohort studies. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025;24(1):209.
[40] ZHAO M, BOVET P, XI B. Weight status change from adolescence to young adulthood and the risk of hypertension and diabetes mellitus. Hypertension. 2020;76(2):583-588.
[41] CAI A, LIU L, ZHOU D, et al. Obesity and risk of incident left ventricular hypertrophy in community-dwelling populations with hypertension: An observational study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024;13(12):e033521.
[42] VALENZUELA PL, CARRERA-BASTOS P, CASTILLO-GARCÍA A, et al. Obesity and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023;20(7):475-494.
[43] RAIMI TH, DELE-OJO BF, DADA SA, et al. Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Related Parameters Predicted Metabolic Syndrome in Nigerians. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2021;19(2):76-82.
[44] ZHOU Z, LIU Q, ZHENG M, et al. Comparative study on the predictive value of TG/HDL-C, TyG and TyG-BMI indices for 5-year mortality in critically ill patients with chronic heart failure: a retrospective study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024;23(1):213.
[45] DANG K, WANG X, HU J, et al. The association between triglyceride-glucose index and its combination with obesity indicators and cardiovascular disease: NHANES 2003-2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024;23(1):8.
[46] PENG N, KUANG M, PENG Y, et al. Associations between TyG-BMI and normal-high blood pressure values and hypertension: cross-sectional evidence from a non-diabetic population. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023;10:1129112.
[47] WANG F, HAN L, HU D. Fasting insulin, insulin resistance and risk of hypertension in the general population: A meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2017;464:57-63.
[48] CHE B, ZHONG C, ZHANG R, et al. Triglyceride-glucose index and triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as potential cardiovascular disease risk factors: an analysis of UK biobank data. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1):34.
[49] LIU Y, ZHU B, ZHOU W, et al. Triglyceride-glucose index as a marker of adverse cardiovascular prognosis in patients with coronary heart disease and hypertension. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1):133.
[50] KOSAMI K, KUWABARA M, OKAYAMA A, et al. Body mass index and weight change as predictors of hypertension development: A sex-specific analysis. Nutrients. 2024;17(1):119.
[51] CHEN Y, YU W, LV J, et al. Early adulthood BMI and cardiovascular disease: a prospective cohort study from the China Kadoorie Biobank. Lancet Public Health. 2024;9(12):e1005-e1013.
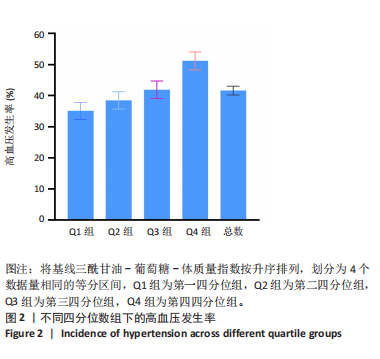
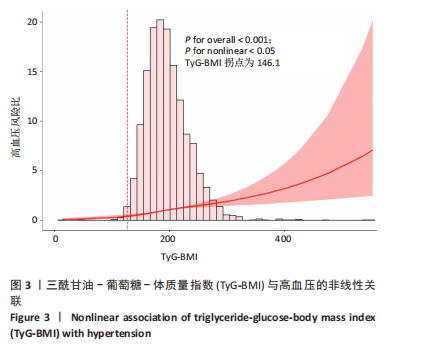
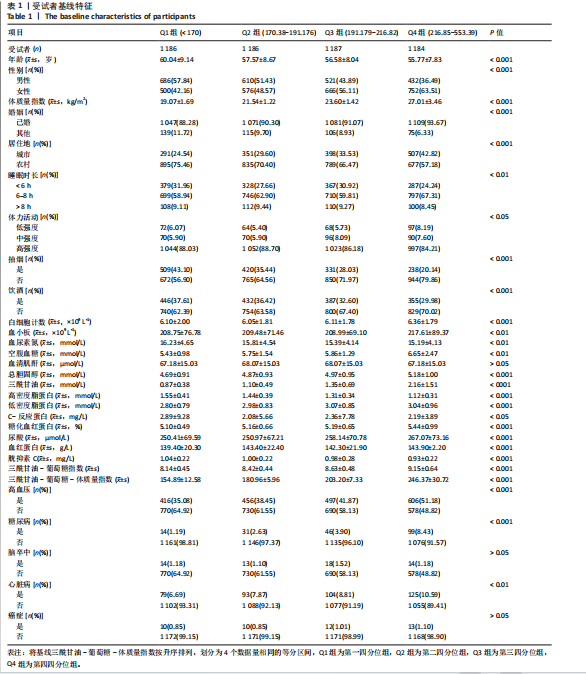
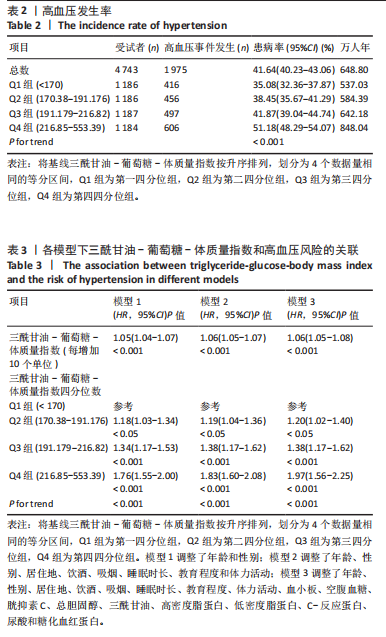
|