中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (31): 6753-6764.doi: 10.12307/2025.671
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
工程化外泌体靶向递送药物的抗肿瘤效应
代月优1,郭丹丹1,2,王茜茜1,2,王白燕1,2,冯书营1,2
- 1河南中医药大学医学院,河南省郑州市 450046;2河南省中医药特医食品工程研究中心,河南省郑州市 450046
-
收稿日期:2024-07-11接受日期:2024-08-13出版日期:2025-11-08发布日期:2025-02-26 -
通讯作者:冯书营,医学博士,博士生导师,河南中医药大学医学院,河南省郑州市 450046;河南省中医药特医食品工程研究中心,河南省郑州市 450046 -
作者简介:代月优,女,1997年生,汉族,河南省开封市人,河南中医药大学医学院在读硕士,主要从事中医药抗肿瘤研究。 并列第一作者:郭丹丹。河南中医药大学医学院,河南省郑州市 450046;河南省中医药特医食品工程研究中心,河南省郑州市 450046 -
基金资助:中国博士后科学基金(2023M731023),项目负责人:郭丹丹;河南省科技攻关项目(242102311212),项目负责人:郭丹丹;河南省高等学校重点科研项目(24A310005),项目负责人:郭丹丹;研究生科研创新能力提升计划项目(2023KYCX083),项目负责人:代月优;河南省科技研发计划联合基金(优势学科培育类)(23231420070),项目负责人:冯书营
Anti-tumor effects of engineered exosomes for targeted drug delivery
Dai Yueyou1, Guo Dandan1, 2, Wang Qianqian1, 2, Wang Baiyan1, 2, Feng Shuying1, 2
- 1School of Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Engineering Research Center of Special Medical Food of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-11Accepted:2024-08-13Online:2025-11-08Published:2025-02-26 -
Contact:Feng Shuying, MD, Doctoral supervisor, School of Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Henan Engineering Research Center of Special Medical Food of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
About author:Dai Yueyou, Master candidate, School of Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China Guo Dandan, School of Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Henan Engineering Research Center of Special Medical Food of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China Dai Yueyou and Guo Dandan contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2023M731023 (to GDD); Henan Provincial Science and Technology Project, No. 242102311212 (to GDD); Henan Provincial Key Scientific Research Project, No. 24A310005 (to GDD); Graduate Research and Innovation Capacity Improvement Program, No. 2023KYCX083 (to DYY); Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research and Development Program Joint Fund (Advantage Discipline Cultivation Category), No. 23231420070 (to FSY)
摘要:
文题释义:
外泌体:由细胞分泌的微小囊泡,内含丰富的蛋白质、脂质和核酸,直径为40-160 nm,能够轻松穿越生物屏障。作为纳米级药物递送载体,外泌体不仅具有高度的生物相容性和低免疫原性,还能实现药物的在治疗过程中的精准靶向和缓释,从而显著提高药物的疗效并降低不良反应。因此,外泌体在药物递送领域展现出巨大的应用潜力。工程化外泌体:是天然外泌体经过生物工程技术精细改造后的产物。这些改造后的外泌体不仅保留了原有的特性,还具备了更高的载药效率、更精准的靶向性和更强的抵抗机体清除能力。通过调整其膜负载物或内容物,工程化外泌体能够针对特定疾病或治疗需求进行定制,为药物递送和疾病治疗提供了新的高效途径。
摘要
背景:当前治疗肿瘤的药物主要以化学药为主,但存在着耐药和不良反应等问题。外泌体药物递送系统不仅避免了人工合成纳米颗粒药物的毒性,而且增加了药物的生物利用度和生物相容性。通过生物、物理和化学方法对外泌体进行修饰进而打造成一种新型的纳米载药平台。
目的:对外泌体药物递送系统的构建策略和在肿瘤疾病中的应用现状以及当前所面临的各种挑战进行了综述。
方法:以“Exosomal,tumor,microvesicle,extracellular vesicles ,engineered,therapeutics,characterization,isolation ,drug delivery,targeting,modification strategies, physics,chemistry, biology”为英文检索词和“外泌体,药物递送,肿瘤”为中文检索词检索PubMed及中国知网数据库,最终纳入了132篇文献进行深入地归纳和探讨。
结果与结论:①外泌体提取的技术手段,包括超速离心法、过滤法和试剂盒提取等,这些方法虽然能够高效地分离出外泌体,但是过程繁琐并且耗时较长,无法实现外泌体的大规模提取。②工程化外泌体主要分为4类:基因编辑工程化,通过基因改造提升功能;内源性工程化,利用炎症因子等预处理增强药物递送;外源性工程化,直接在外泌体中封装药物;混合型工程化,结合外泌体与脂质纳米颗粒形成新颗粒。目前部分工程化外泌体已进入癌症治疗的临床试验阶段,但多处于早期阶段。相比较而言,基因工程化外泌体因高靶向性和定制化潜力,被视为未来药物递送的重要方向。③实现工程化外泌体的临床转化还有诸多限制,在技术方面,大规模生产、纯化及载药效率等技术难题亟待解决;在生产方面,高昂成本及批次稳定性问题影响普及;在安全性方面,免疫原性及潜在毒性需全面评估;此外,监管政策的不完善及审批流程的复杂性也构成其临床转化的障碍。④未来需通过技术创新、成本控制、安全性提升及政策完善等多方面努力,推动工程化外泌体的临床转化进程。
中图分类号:
引用本文
代月优, 郭丹丹, 王茜茜, 王白燕, 冯书营. 工程化外泌体靶向递送药物的抗肿瘤效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(31): 6753-6764.
Dai Yueyou, Guo Dandan, Wang Qianqian, Wang Baiyan, Feng Shuying. Anti-tumor effects of engineered exosomes for targeted drug delivery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6753-6764.
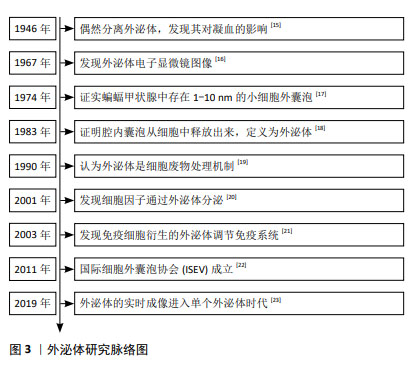
2.1.1 外泌体的研究历程 在1946年,Chargaff和West在研究贫血和血友病时发现了一种类似于血栓形成蛋白的凝血因子[15],这被认为是细胞外囊泡生物学领域的开端。大约20年后,Wolf[16]发表了这些粒子的电子显微镜图像。在1974年,Nunez和Gershon证实蝙蝠甲状腺中存在1-10 nm的小细胞外囊泡[17]。在1983年,两项研究证实了腔内囊泡从细胞中释放,并将其定义为外泌体,这被认为是该领域的起源[18]。除了外泌体的发现外,也出现了关于细胞外囊泡特征的研究。Johnstone等[19]在20世纪90年代将外泌体描述为“废物处理机制”。21世纪初,人们对外泌体的兴趣不断增加,导致该领域的研究呈指数级增长。例如,在2001年发现细胞因子通过外泌体分泌[20]。2年后,免疫细胞来源的外泌体被证明可调节免疫系统的功能[21]。在2011年,国际细胞外囊泡学会(International Society for Extracellular Vesicles,ISEV)成立[22],极大地推动了外泌体的创新和应用。在2019年,研究者使用新技术检测出单个外泌体,表明外泌体成像进入了体内单个外泌体时代[23],见图3。这些发现改变了真核细胞间信息传递及外泌体运作的传统认知。外泌体作为天然运输载体,参与心血管系统疾病、神经系统疾病和癌症等多种疾病进程,尤其在癌症中,通过调控靶基因与信号通路,影响肿瘤增殖、凋亡和血管生成等关键环节[24]。这一革命性发现,不仅拓宽了肿瘤机制研究的视野,更为肿瘤的早期诊断、精准治疗及预后评估提供了前所未有的新策略与途径。
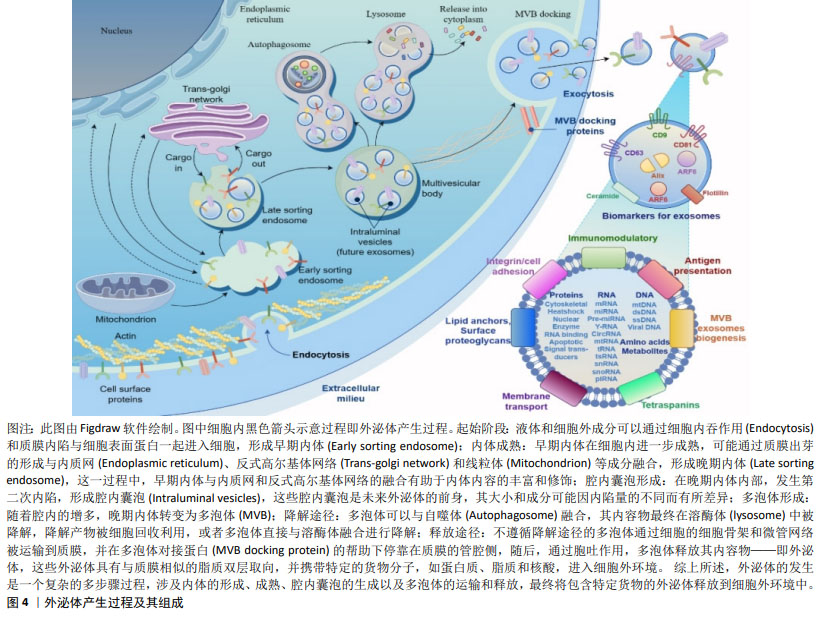
2.1.2 外泌体的形成 外泌体是细胞在生理和病理情况下释放的纳米级囊泡,直径范围为40-160 nm[25]。外泌体的形成包括4个过程:出芽、内陷、细胞内多囊泡体形成和分泌[20]。首先,细胞通过出芽的形式产生小囊泡,然后细胞膜内陷形成网格蛋白包被的囊泡,这些囊泡进入细胞质后形成早期内体,内部富含大量蛋白质、核酸和其他生物活性分子。这些早期内体经过特异性分选和封装,形成多个腔内囊泡,即晚期内体。随后,一部分晚期内体与溶酶体结合,其部分内容物和蛋白质被降解[26]。最后,其他晚期内体与细胞膜融合,将胞内囊泡以外泌体的形式释放到细胞外[27],见图4。
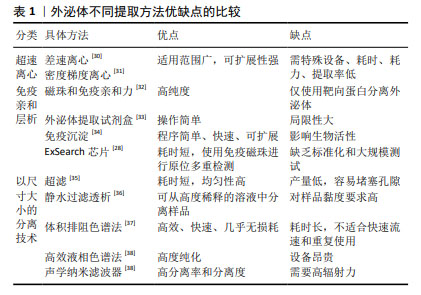
2.1.3 外泌体的分离 目前,超速离心法被认可为外泌体分离的黄金标准,因其高效、可靠的分离效果在研究和临床应用中备受青睐[28]。同时,现有研究已开发出多种新型分离纯化技术,如超滤、免疫亲和层析、尺寸排阻色谱、免疫沉淀及微流控等方法[29]。这些分离方法虽然能够有效提取外泌体,但过程繁琐、耗时较长、提取量少,且对设备要求高,导致整体成本居高不下,无法实现规模化制备[30-38],详述见表1。然而大规模应用是外泌体在临床应用中取得成功的关键,只有通过大规模的生产和应用,才能充分验证外泌体的疗效和安全性,推动其向临床转化。由于高昂的成本和复杂的操作使得外泌体的大规模应用变得困难重重,进而限制了其在临床上的广泛应用。因此,如何降低分离纯化成本、简化操作流程,提高产量成为当前亟待解决的问题。
2.1.4 外泌体表征的分析方法 当前,外泌体表征常用的技术有流式细胞术、蛋白质印迹、纳米颗粒跟踪分析、动态光散射、质谱和显微镜技术等[39]。流式细胞术主要通过标记外泌体表面的特定蛋白或其他标志物(如CD9,CD63和CD81等),对外泌体进行定量和定性分析。而蛋白质印迹也可用于外泌体特定蛋白质的存在和丰度的检测,该方法对于检测外泌体相关标志物(如TSG101和Alix等)的表达有着较高的灵敏度和特异性[40]。质谱技术除可用于鉴定和分析外泌体蛋白成分外,还可鉴定其脂质等成分,以确定其不同成分的组成和丰度[41]。电子显微镜可直接观察外泌体的形态特征,包括其大小、形状和膜结构等,从而进一步提供外泌体的形态学信息[42]。此外,动态光散射可通过分析光的散射模式来确定颗粒的大小分布,从而了解其在样品中的特性。纳米颗粒跟踪分析不仅可以测定外泌体的大小,还可以对其浓度和分布进行定量分析,为外泌体的纯化和定量提供重要的数据支持[43]。在实际的研究工作中,应结合上述不同方法对外泌体进行全面及准确的表征分析。
2.1.5 外泌体的安全性 在生物医学领域,外泌体作为一种新兴的药物递送系统,正逐渐展现出其独特的优势和潜力。然而,尽管外泌体具有天然来源、良好的生物相容性和能够穿越生物屏障等特性,但其在体内的药代动力学和毒理学特性仍需深入研究和全面验证,以确保外泌体作为药物递送系统的安全性和有效性[44]。
目前,药品制造商被要求必须详尽列出药物中所有能触发药理学、免疫学或新陈代谢反应的成分。此外,构成最终制剂使用的非功能性组分(也被称为赋形剂),亦需明确申报,以确保产品的全面可追溯性与安全性。国际细胞外囊泡协会的最新声明,当治疗效果明确源自外泌体所携带的药物分子,而非外泌体载体系统自身时,这些外泌体在特定情境下可被认为是赋形剂。此种情况下,仅需聚焦于药代动力学研究外泌体在生物体内吸收、分布、代谢和排泄过程及其随时间变化和毒理学,验证外泌体对生物体的潜在毒性作用,包括急性毒性、长期毒性、遗传毒性和免疫原性等。通过严格的评估后,如果确保外泌体在临床应用中不会对患者造成不必要的伤害或风险,则可以允许进行Ⅰ期临床试验[45]。
转化同种异体及异种外泌体为安全高效的临床产品,需严密监测,确保亲本细胞筛选严谨、评估免疫原性、致癌风险及病毒污染。当前各实验室与企业间所采用的测试标准与方法测试标准不一[46],这在一定程度上延缓了行业发展的步伐。综上所述,探索新方法以验证外泌体安全性与疗效迫在眉睫。这不仅需要科研人员的共同努力和不断探索,还需要政府、企业和社会的广泛关注和支持,这样才能推动外泌体药物递送系统的发展和应用,为人类的健康事业做出更大的贡献。
2.2 外泌体载药方法 外泌体载药的不同方法,见图5。
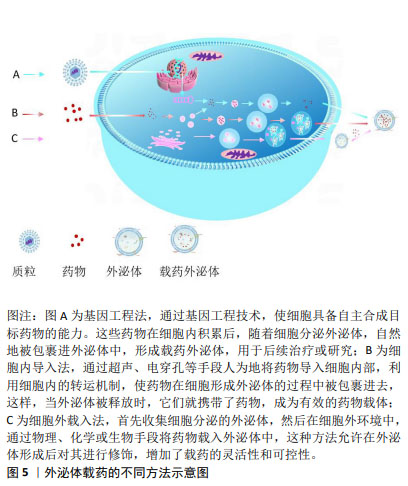
工程化外泌体常见载药方法可分为2种:①直接载药法,通过转染或共孵育方法从母细胞中获取载药外泌体[47-48]。尽管这些方法具有高度可重复性且相对简单,但加载效率通常较低,并且高度依赖于母细胞类型以及货物特性和浓度梯度。②间接载药法,从不同来源的细胞中提取外泌体,并通过共孵育、电穿孔、超声处理、挤出、冻融循环或转染试剂将货物引入细胞外囊泡中[49-50]。这种策略比前者更具可定制性,并最大限度地减少了其他不必要的物质的包含。
2.2.1 直接载药法 在直接载药的过程中,药物可与外泌体的脂质双层相互作用,或者被包裹在外泌体囊泡内部,通过优化载药条件而实现稳定的药物载荷和控制释放。直接载药法简单高效,可供外泌体载药的基础研究和应用研究。在大多数情况下,亲脂性小分子在与外泌体共孵育过程中被动加载到外泌体中[51]。例如,通过共孵育可将具有抗癌活性的姜黄素、白藜芦醇、抗癌剂阿霉素和紫杉醇等药物装载到外泌体中[52-54]。此外,外泌体通常带负电荷,也可吸引带有相反电荷的药物[55]。但也有报道称带有负电荷的分子(如siRNA和DNA)和中性电荷的药物也可被外泌体捕获[56],其具体机制还不清楚。为克服外泌体表面的静电力,可利用脂溶性化合物的亲脂性来实现药物的负载[57]。另外,外泌体还可通过超声处理、电穿孔、挤出、皂苷(透化剂)、冻融循环、热冲击、pH梯度法和低渗透析等方法加载药物[58]。例如通过常温下共孵育、加入皂素后孵育、反复冻融、超声及挤出等多种不同的方法将过氧化氢酶装载到外泌体中。结果显示,外泌体通过超声和挤出两种方式具有较高的载药量,分别为26.1%和22.2%;相比之下,仅通过被动扩散方式实现的载药量较低,仅为4.9%,但在实验中加入具有透皮促进作用的皂素后,外泌体的载药量得到了显著的提升,增加至18.5%[59]。这些研究结果不仅深化了对药物封装技术的理解,更凸显了选择恰当方法对于优化外泌体载药效率与容量的至关重要性,为未来的药物递送系统设计与应用指明了方向。
2.2.2 间接载药法 间接载药法是将药物加载到亲本细胞,使细胞内含有所需药物,然后在外泌体中释放;或者用编码治疗基因转染/感染亲本细胞,由亲本细胞合成相应的治疗性化合物,然后释放的外泌体中会负载药物。通过精心设计载药策略和优化操作流程,可以提高药物的装载效率和稳定性,为外泌体药物递送系统在未来医学研究和临床治疗开辟更广阔的前景。例如将亲本细胞与药物共孵育培养,间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体可以实现对紫杉醇的装载[60]。同样,肝癌细胞与不同抗癌药物(如紫杉醇、依托泊苷、卡铂、伊立替康、表柔比星和米托蒽醌等)一起孵育也显示出类似的结果[60]。通过该方法制备的含药外泌体能够显著抑制胰腺管腺癌细胞系的增殖活性,并引发特异性的自然杀伤细胞反应[61]。最近有团队将含有疏水性药物的融合脂质体对亲本细胞进行处理,进而亲本细胞分泌的外泌体成功负载了载药脂质体,从而实现载药外泌体的细胞外释放[62]。
此外,还可向亲本细胞导入编码治疗活性化合物的基因,进而使亲本细胞合成相应的化合物通过释放的外泌体携带药物进行传递。同时,外泌体作为核酸转移的载体可自然地携带并传递mRNA、miRNA、各种非编码RNA、线粒体DNA以及基因组DNA[63-64]。例如,成功构建能表达狂犬病毒糖蛋白-溶酶体相关膜蛋白的质粒并将其转染到树突状细胞中,获得的外泌体通过膜上的溶酶体相关膜蛋白与神经元特异性狂犬病病毒糖蛋白肽强烈融合。通过电穿孔可将siRNA负载至树突状细胞衍生的外泌体中,该靶向外泌体可以在小鼠模型中有效地将治疗性siRNA递送到大脑[65]。该方法可能伴随着广泛的siRNA聚集体形成,这可能导致高估实际加载到外泌体中的siRNA量[66]。已知外泌体带有负表面电荷,因此排除了静电siRNA络合。有研究建议通过阳离子脂质体对siRNA进行预络合,然后与分离的外泌体融合,以便将siRNA加载到外泌体中[67]。此外,适当的温度条件也可改善siRNA在外泌体中的负荷[68]。
尽管外泌体载药技术已展现出多样化的策略,且通过优化手段能够在一定程度上提升载药量,然而,但是无法大幅度提高其药物装载量。造成这一原因最重要的因素是外泌体作为细胞自然分泌的微小囊泡,其内部空间相对较小[69],因此能够装载的药物量也相应受限。这种容量的限制意味着,外泌体可能无法携带足够量的药物以达到治疗所需的浓度,从而影响了治疗效果的充分发挥。目前,有实验可以通过基因工程技术改造外泌体,增加其载药空间[70],但是还未形成完整的体系,随着对外泌体生物学特性的深入研究,有望发现更多调控外泌体装载容量的新方法和新途径。
2.3 外泌体的靶向修饰 理想的药物载体需要能够逃避宿主免疫系统、实现精准靶向递药和无毒等特性[71]。此外,要实现药物的高效治疗,必须确保外泌体能够精确地将药物输送到目标病变部位,避免对非靶标组织的损伤和药物浪费。外泌体作为天然的纳米载体,其自身具有一定的自然靶向性,但这种靶向性往往不够精确,难以满足复杂疾病治疗的需求,仅靠外泌体的特性不足以满足疾病治疗。
2.3.1 生物改造 生物修饰是一种广泛应用的膜修饰方法,最为常见的是靶向肽和适配体等修饰。利用靶向肽修饰外泌体能够显著提高其组织器官的靶向性和改善化疗药物的累计效应等。例如,环肽(Arg-Gly-Asp-D-Tyr-Lys)能赋予外泌体靶向肿瘤的能力,对肿瘤血管内皮细胞或骨肉瘤细胞表面过表达的αVβ3整合素受体具有高亲和力[72]。同时,外泌体被环肽功能化后能够将阿霉素靶向运输到肿瘤细胞环境中,从而改善了化疗药物的特异性积累[73]。趋化因子受体4与造血干细胞归巢和肿瘤骨转移密切相关。通过基因工程使小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞产生能表达趋化因子受体4抗体的外泌体,并观察到这些表达趋化因子受体4抗体的外泌体能有选择性地富集在骨髓中[74]。同样地,将人表皮生长因子受体2与溶酶体相关膜蛋白2的N端融合后形成融合蛋白并表达在外泌体表面,该融合蛋白可通过表皮生长因子受体介导的肿瘤细胞内吞作用,加速靶向细胞的摄取,从而有效地靶向结肠癌细胞[75]。此外,外泌体经过肽修饰后,在体外可以靶向高度表达间充质-上皮转化因子的三阴性乳腺癌细胞[76];在体内也表现出显著的肿瘤靶向功效[77-78]。
适配体与外泌体膜表面分子连接是一种新兴的外泌体表面功能化方法,它可以实现与特定配体的相互作用。适配体是具有特定三维结构的短单链寡核苷酸或肽,以高亲和力和特异性靶向肿瘤细胞[79]。例如携带人沉默调节蛋白siRNA的E3适配体修饰的外泌体在体内外均对前列腺癌表现出显著的靶向作用[80];包被RNA适配体的外泌体能够与肝细胞癌中的上皮细胞黏附分子结合,显著提高了对肿瘤的靶向性[81];靶向核仁素的核酸适配体修饰的巨噬细胞外泌体在胶质母细胞瘤中具有高效穿透血脑屏障和靶向肿瘤的能力[11]。此外,生物改造与磁场技术的融合正处于蓬勃的探索阶段,尽管尚未迈入具体的临床应用门槛,但其展现出的无限潜力与广阔前景,正引领着医疗科技向更加精准、高效的治疗时代迈进。
2.3.2 物理修改 工程化外泌体可在外部物理条件下实现更准确的肿瘤靶向效果,如静电、磁场、超声和激光照射。例如,将阳离子脂质融合到外泌体表面可以赋予外泌体表面正电荷,这提高了包裹葡聚糖大分子的外泌体在细胞间的摄取以及细胞内释放的效率[82]。在外部磁场的作用下,中性粒细胞来源的外泌体被超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒修饰后能够选择性地积聚在肿瘤部位[83]。同样地,肿瘤坏死因子负载和被超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒修饰的外泌体可以在外部磁场下显著增强肿瘤的靶向性,同时减轻体内外的毒性[84]。此外,研究人员利用超声波的聚焦效应引导声敏外泌体在特定位置进行递送,设计了一种功能化的智能声敏外泌体。在同型肿瘤细胞衍生的外泌体表面加载了华卟啉钠,利用体外超声设备可以非侵入性地提高智能声敏外泌体对肿瘤的靶向性,这为体外引导靶向外泌体提供了新的思路[85]。此外,外部激光照射同样可以达到肿瘤靶向治疗效果,尤其是在光热治疗中。例如,外泌体与载药的热敏脂质体混合后能够显著靶向小鼠的肿瘤部位,在此过程中,在激光照射下,负载到工程化外泌体中的光热剂可以达到优异的光热治疗效果[86]。同样,外部近红外照射可以调控触发神经胶质瘤中化疗药物的释放[87]。然而,值得注意的是,尽管激光照射技术以其靶向药物递送与药物释放的高度可控性而备受瞩目,但其临床应用却面临辐射损伤风险及高昂成本的双重挑战,加之重复操作性的局限,这些因素共同制约了该技术在临床领域的广泛推广与应用。
2.3.3 化学改性 肿瘤微环境相对偏酸性,可能是由于糖酵解率高和乳酸增加引起的[88],这为工程化外泌体的肿瘤靶向修饰提供了条件。i序列是一种富含胞嘧啶且对pH敏感的DNA链[89],可将涂有i序列的外泌体递送至乳腺癌并在酸性环境下释放阿霉素[90]。碳酸氢钠装载在外泌体中可产生二氧化碳,通过内吞作用进入癌细胞后迅速起泡,有效释放紫杉醇等药物[91]。研究还发现了一种对pH和温度敏感的聚合物黏合剂,该黏合剂在pH 6.8下与肿瘤细胞结合,但在pH 7.4下不能与肿瘤细胞结合,这种黏合剂可作为工程外泌体修饰的重要组成部分[49]。由此可见,利用酸性肿瘤微环境实现药物的可控释放,为开发针对临床分期的高效药物递送系统开辟了一条极具前景的道路。
点击化学是一种常见的外泌体表面修饰技术,通过化学方法将靶向肽等物质与外泌体表面蛋白结合,进而实现有效调控其结构和功能的目的。研究表明,将超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子和姜黄素加载到外泌体中,然后通过点击化学将外泌体膜与神经纤毛蛋白1靶向肽偶联,可以获得具有成像和治疗功能的胶质瘤靶向外泌体[92]。另有研究使用点击化学方法开发了一种结合了氨基聚乙二醇并携带紫杉醇的外泌体,该外泌体能够靶向肺癌细胞高表达的sigma受体,经全身给药后,外泌体能在癌细胞中积累,并提高治疗效果[93]。此外,通过外泌体表面的修饰可以增强对肿瘤细胞的免疫应答。肿瘤细胞表面的CD47表面蛋白与吞噬细胞上的信号调节蛋白α相互作用,导致巨噬细胞的吞噬活性下降。通过点击化学将二苯环辛炔衍生的信号调节蛋白α抗体与叠氮化物修饰的外泌体结合,可以抑制肿瘤细胞的增长[94]。相较于传统化学反应中温度与压力的波动以及盐浓度不当可能引发的渗透压变化,这些不利因素往往损害外泌体膜的完整性或促使其聚集,点击化学反应则展现出了显著的优势:其高效性、短反应时间不仅提升了操作效率,更关键的是,共轭反应过程对外泌体的大小保持中性影响,确保了外泌体的完整性,同时不影响其在靶细胞中的有效摄取,为外泌体在生物医学领域的应用提供了更为可靠与高效的修饰手段。
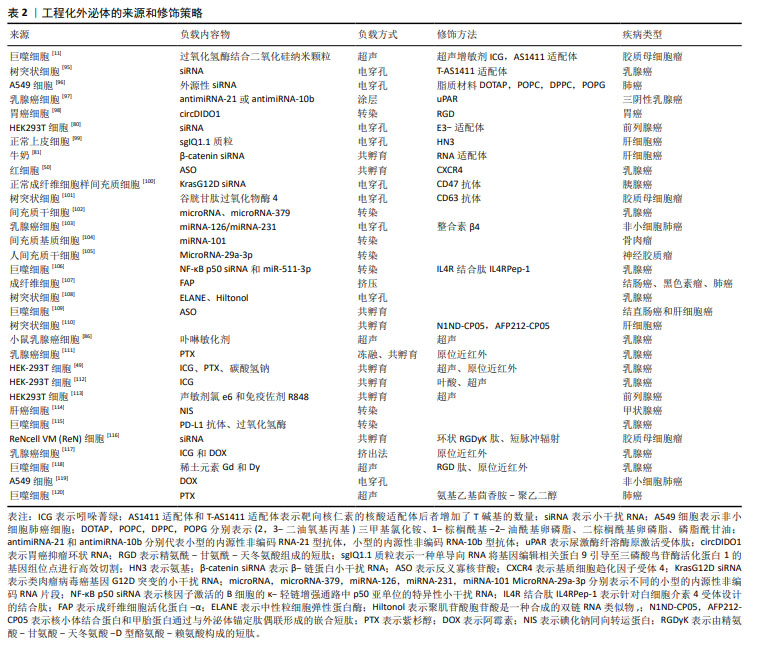
当前,外泌体来源多样,均具备工程化修饰的潜力。依据药物特性与治疗目标,可灵活选用适宜的负载技术,确保药物高效负载。同时,针对多样化的治疗需求,采取差异化的修饰策略,以优化外泌体功能,实现精准医疗的愿景[95-120],见表2。然而,通过工程化改造在提升外泌体靶向性的同时,也带来了新的挑战。首先,工程化改造过程可能会对外泌体的稳定性产生影响,包括其膜结构的完整性和内部封装货物的稳定性,这直接关系到外泌体在体内的循环时间和递送效率。其次,工程化改造可能改变外泌体与细胞膜的相互作用方式,进而影响其细胞进入途径,包括内吞、膜融合或直接信号传导等,这些机制的变化将直接影响药物的递送效率和细胞内的生物利用度。最后,工程化改造还可能影响外泌体在体内的组织分布,特别是在复杂疾病环境中,如何确保外泌体能够穿越生理屏障,如血脑屏障,并准确到达靶标组织,是亟待解决的问题。要实现外泌体在精准医疗中的广泛应用,还需要进一步深入研究表面工程对外泌体稳定性、细胞进入途径和体内组织分布的具体影响,并不断优化表面修饰策略,以提高外泌体的靶向效率和治疗效果。
目前已经开发了各种用于改造外泌体的策略,包括生物改造、物理修改和化学改性等方法,见表2,以确保外泌体在靶组织或器官中的积累。如上所述,这些方法可以让药物在靶细胞中积累更多,从而减少脱靶效应并提高其疗效。
2.4 外泌体递送系统抗肿瘤的应用现状 众所周知,外泌体以其独特的生物学特性,已成为治疗广泛疾病谱中诸多病症的极具潜力的候选载体。在正式踏入临床试验之前,众多临床前研究已充分彰显了外泌体在肿瘤治疗领域所展现出的空间精准性与时间敏感性的双重显著优势。此外,当前已有临床试验展开,进一步探索并验证外泌体在肿瘤治疗中的实际疗效与安全性。这些临床试验不仅是对前期研究成果的延伸与拓展,更是推动外泌体疗法从实验室走向临床、从理论走向实践的关键一步。
2.4.1 工程化外泌体在空间上靶向肿瘤部位 工程化外泌体的空间靶向递送取决于其表面的靶向分子,用特定靶向分子修饰的外泌体可以实现更精确的治疗性药物递送。该策略使得工程化外泌体在肿瘤内的浓度更高,而在其他健康器官(如肝脏、脾脏和肾脏)中的浓度较低。例如,外泌体被人表皮生长因子受体2修饰后,负载治疗性药物,使其能够黏附在人喉癌细胞表面的人表皮生长因子受体2上,并优先进入人表皮生长因子受体2阳性细胞;更重要的是,与没有靶向肽的外泌体相比,人表皮生长因子受体2修饰的外泌体会激发更有效的抗癌作用[121]。再例如,利用超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒修饰的携带多柔比星的中性粒细胞外泌体,这种外泌体在外部磁场的作用下能够有选择性地聚集在肿瘤部位,从而有效地抑制了肿瘤的生长,显著延长了小鼠的存活时间[82]。在另一项研究中,成功合成了一种用于基因治疗肺癌的新型靶向程序性细胞死亡蛋白1的siRNA外泌体纳米囊泡;研究表明,携带siRNA的靶向外泌体纳米囊泡具有低毒性和高装载率的特点,适合肿瘤细胞的基因治疗[122]。也可以利用转铁蛋白-转铁蛋白受体的相互作用,将被转铁蛋白修饰的超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒结合到肿瘤坏死因子α外泌体上,形成了良好水分散性的结合载体;在小鼠黑色素瘤皮下模型中,这种复合物能够提高对肿瘤的靶向能力,抑制肿瘤生长,并同时减少毒性的表现[83]。尽管有越来越多关于工程化外泌体策略的报道,但缺乏理想的靶分子来引导外泌体准确到达肿瘤部位,并尽可能减少在正常组织中的吸收。
2.4.2 工程化外泌体在时间上靶向肿瘤部位 工程化的外泌体到达肿瘤组织后,如何更好地发挥抗肿瘤功能仍存在问题。为应对这一挑战,用特定靶分子对外泌体进行修饰,可以使得工程化外泌体能够时间可控的将治疗性药物输送到肿瘤部位。外泌体与载药的热敏脂质体融合,称为杂交治疗性纳米囊泡。该杂交工程外泌体能够以可控的时间方式精准释放抗肿瘤药物,例如杂交治疗性纳米囊泡在1,6 h表现出更高的药物释放率[83],这种可控释放药物的方法有助于临床医生调节患者体内的药代动力学。同样的,化疗药物和热敏药物的组合也以可控的时间方式发挥显著的抗肿瘤作用。姜黄素和吲哚菁绿共同负载的工程化外泌体在体内神经胶质瘤中能够有效地积累[123],通过局部的热疗显著影响了工程化外泌体膜的通透性,触发了药物释放,并维持了持续的化疗效果。与激光相比,超声波具有许多优点,包括无辐射和低成本[123]。表面用外泌体锚定蛋白修饰的骨形态发生蛋白7 mRNA和氯化e6的外泌体可被超声波局部降解,并将骨形态发生蛋白7 mRNA精确递送至肥胖C57BL/6小鼠的网膜脂肪组织[124]。总之,工程化外泌体已被证明可通过表面的靶向分子和物理照射在时间和空间上释放生物活性治疗分子到肿瘤部位。尽管在空间和时间存在着靶向性较差的问题,但通过一系列的新型策略探索,工程化外泌体有望开辟分子靶向药物的新领域。
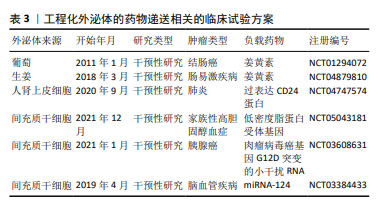
2.4.3 工程化外泌体的临床应用 外泌体作为已开发的用于递送治疗剂的生物纳米平台,目前有多项临床试验正在评估外泌体作为递送载体的安全性和有效性[125]。例如,有37项外泌体抗肿瘤相关临床试验在 ClinicalTrials.gov 资源https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/home)中注册并完成,见表3。其中2项临床试验旨在将姜黄素封装到植物来源的外泌体中,用于治疗结肠癌和肠易激疾病。此外,许多研究报告称,植物来源的外泌体与哺乳动物来源的外泌体具有相似的尺寸分布、电荷、形状和成分,一些临床试验正在进行中(NCT04879810,NCT04698447,NCT01668849) [126]。 由于它毒性低,生物相容性和稳定性好,可食用。因此,适当的植物源性细胞外囊泡可以作为对抗各种疾病的天然治疗剂。值得注意的是,一些临床试验被记录在国际外泌体协会发布指南之前,使用来自肿瘤细胞的微粒来递送药物(例如NCT02657460和NCT01854866).这些研究使用了微粒,而不是外泌体。工程化外泌体的出现,不仅为传统治疗手段带来了革命性的突破,更为个性化医疗、精准治疗等前沿领域的发展开辟了全新的道路。随着研究的深入与技术的成熟,工程化外泌体将在未来临床实践中发挥不可估量的价值,引领人类健康事业迈向新的高度。
| [1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [2] PRAKASH V, BOSE C, SUNILKUMAR D, et al. Resveratrol as a promising nutraceutical: implications in gut microbiota modulation, inflammatory disorders, and colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(6):3370. [3] GUTIERREZ-MILLAN C, CALVO DíAZ C, LANAO JM, et al. Advances in exosomes-based drug delivery systems. Macromol Biosci. 2021; 21(1):e2000269. [4] PATRA S, PRADHAN B, NAYAK R, et al. Chemotherapeutic efficacy of curcumin and resveratrol against cancer: chemoprevention, chemoprotection, drug synergism and clinical pharmacokinetics. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;73(3):310-320. [5] ZHONG L, LI Y, XIONG L, et al. Small molecules in targeted cancer therapy: advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):201. [6] MENG W, HE C, HAO Y, et al. Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: considering cell source. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):585-598. [7] RILEY RS, JUNE CH, LANGER R, et al. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019;18(3):175-196. [8] YAMAMOTO K, IMAOKA T, TANABE M, et al. New horizon of nanoparticle and cluster catalysis with dendrimers. Chem Rev. 2020; 120(2):1397-1437. [9] SABBAGH F, KIM BS. Recent advances in polymeric transdermal drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2022;341(6):132-146. [10] YANG E, WANG X, GONG Z, et al. Exosome-mediated metabolic reprogramming: the emerging role in tumor microenvironment remodeling and its influence on cancer progression. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):242. [11] WU T, LIU Y, CAO Y, et al. Engineering macrophage exosome disguised biodegradable nanoplatform for enhanced sonodynamic therapy of glioblastoma. Adv Mater. 2022;34(15):e2110364. [12] BAHADORANI M, NASIRI M, DELLINGER K, et al. Engineering exosomes for therapeutic applications: decoding biogenesis, content modification, and cargo loading strategies. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19(11): 7137-7164. [13] LIANG Y, XU X, XU L, et al. Chondrocyte-specific genomic editing enabled by hybrid exosomes for osteoarthritis treatment. Theranostics. 2022;12(11):4866-4878. [14] PATHAN M, FONSEKA P, CHITTI SV, et al. Vesiclepedia 2019: a compendium of RNA, proteins, lipids and metabolites in extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D516-D519. [15] CHARGAFF E, WEST R. The biological significance of the thromboplastic protein of blood. J Biol Chem. 1946;166(1):189-197. [16] WOLF P. The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. Br J Haematol. 1967;13(3):269-288. [17] NUNEZ EA, WALLIS J, GERSHON MD. Secretory processes in follicular cells of the bat thyroid. 3. the occurrence of extracellular vesicles and colloid droplets during arousal from hibernation. Am J Anat. 1974;141(2):179-201. [18] HARDING C, HEUSER J, STAHL P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983;97(2):329-339. [19] JOHNSTONE RM, MATHEW A, MASON AB, et al. Exosome formation during maturation of mammalian and avian reticulocytes: evidence that exosome release is a major route for externalization of obsolete membrane proteins. J Cell Physiol. 1991;147(1):27-36. [20] MACKENZIE A, WILSON HL, KISS-TOTH E, et al. Rapid secretion of interleukin-1beta by microvesicle shedding. Immunity. 2001;15(5): 825-835. [21] SKOKOS D, BOTROS HG, DEMEURE C, et al. Mast cell-derived exosomes induce phenotypic and functional maturation of dendritic cells and elicit specific immune responses in vivo. J Immunol. 2003;170(6): 3037-3045. [22] LöTVALL J, HILL AF, HOCHBERG F, et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: a position statement from the international society for extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3(3):26913. [23] JIANG D, JIANG Z, LU D, et al. Migrasomes provide regional cues for organ morphogenesis during zebrafish gastrulation. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(8):966-977. [24] CHEN C, LIU J, LIN X, et al. Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and regulated cell death in tumors: insights into apoptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis, and pyroptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2024;10(1):189. [25] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [26] CHAUDHARY PK, KIM S, KIM S. Shedding light on the cell biology of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles and their biomedical applications. Life (Basel). 2023;13(6):1403. [27] 尚志,章瑾,杨明睿,等.小细胞外囊泡在乳腺癌诊断与治疗中的研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2024,44(4):54-66. [28] KUMAR MA, BABA SK, SADIDA HQ, et al. Extracellular vesicles as tools and targets in therapy for diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):27. [29] CHEN J, LI P, ZHANG T, et al. Review on strategies and technologies for exosome isolation and purification. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021; 9(5):811971. [30] KUKLIN V, SOVERSHAEV M, BJERNER J, et al. Influence of therapeutic plasma exchange treatment on short-term mortality of critically ill adult patients with sepsis-induced organ dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2024;28(1):12. [31] ZHU L, SUN H T, WANG S, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes for cancer research. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):152. [32] RYU KJ, LEE JY, PARK C, et al. Isolation of small extracellular vesicles from human serum using a combination of ultracentrifugation with polymer-based precipitation. Ann Lab Med. 2020;40(3):253-258. [33] TURKIEH A, BESEME O, SAURA O, et al. LIPCAR levels in plasma-derived extracellular vesicles is associated with left ventricle remodeling post-myocardial infarction. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):31. [34] FORTUNATO D, GIANNOUKAKOS S, GIMéNEZ-CAPITáN A, et al. Selective isolation of extracellular vesicles from minimally processed human plasma as a translational strategy for liquid biopsies. Biomark Res. 2022;10(1):57. [35] SHU S, YANG Y, ALLEN CL, et al. Purity and yield of melanoma exosomes are dependent on isolation method. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9(1): 1692401. [36] LIU J L, ZHANG L, HUANG Y, et al. Epsin1-mediated exosomal sorting of Dll4 modulates the tubular-macrophage crosstalk in diabetic nephropathy. Mol Ther. 2023;31(5):1451-1467. [37] YOSHITAKE J, AZAMI M, SEI H, et al. Rapid isolation of extracellular vesicles using a hydrophilic porous silica gel-based size-exclusion chromatography column. Anal Chem. 2022;94(40):13676-13681. [38] HOSSEIN F, ANGELI P. A review of acoustofluidic separation of bioparticles. Biophys Rev. 2023;15(6):2005-2025. [39] NIEUWLAND R, SILJANDER PR. A beginner’s guide to study extracellular vesicles in human blood plasma and serum. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024;13(1):e12400. [40] LIU Y, LI M, LIU H, et al. Cancer diagnosis using label-free SERS-based exosome analysis. Theranostics. 2024;14(5):1966-1981. [41] GOO J, LEE Y, LEE J, et al. Extracellular vesicles in therapeutics: a comprehensive review on applications, challenges, and clinical progress. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(3):311. [42] PATIL SM, SAWANT SS, KUNDA NK. Exosomes as drug delivery systems: a brief overview and progress update. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020; 154(8):259-269. [43] DAßLER-PLENKER J, KüTTNER V, EGEBLAD M. Communication in tiny packages: exosomes as means of tumor-stroma communication. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020;1873(2):188340. [44] HERRMANN IK, WOOD MJA, FUHRMANN G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021; 16(7):748-759. [45] SILVA AKA, MORILLE M, PIFFOUX M, et al. Development of extracellular vesicle-based medicinal products: a position paper of the group “Extracellular Vesicle translatiOn to clinicaL perspectiVEs - EVOLVE France”. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;179(6):114001. [46] SHEARN A I U, ADAY S, BEN-AICHA S, et al. Analysis of neat biofluids obtained during cardiac surgery using nanoparticle tracking analysis: methodological considerations. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8(3):367. [47] LUO N, LI J, CHEN Y, et al. Hepatic stellate cell reprogramming via exosome-mediated CRISPR/dCas9-VP64 delivery. Drug Deliv. 2021; 28(1):10-18. [48] LI M, CHEN F, YANG Q, et al. Biomaterial-based CRISPR/Cas9 delivery systems for tumor treatment. Biomater Res. 2024;30(28):23. [49] SADEGHI S, TEHRANI FR, TAHMASEBI S, et al. Exosome engineering in cell therapy and drug delivery. Inflammopharmacology. 2023;31(1): 145-169. [50] MCANDREWS KM, XIAO F, CHRONOPOULOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 for targeting of oncogenic Kras(G12D) in pancreatic cancer. Life Sci Alliance. 2021;4(9):e202000875. [51] GODSE S, ZHOU L, SAKSHI S, et al. Nanocarrier-mediated curcumin delivery: an adjuvant strategy for CNS disease treatment. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023;248(22):2151-2166. [52] GONZáLEZ-SARRíAS A, IGLESIAS-AGUIRRE C E, CORTéS-MARTíN A, et al. Milk-derived exosomes as nanocarriers to deliver curcumin and resveratrol in breast tissue and enhance their anticancer activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2860. [53] WEI H, CHEN F, CHEN J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes as nanodrug carrier of doxorubicin for targeted osteosarcoma therapy via SDF1-CXCR4 axis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17(8):3483-3495. [54] SUN H, BHANDARI K, BURROLA S, et al. Pancreatic ductal cell-derived extracellular vesicles are effective drug carriers to enhance paclitaxel’s efficacy in pancreatic cancer cells through cathrin-mediated endocytosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):4773. [55] JIN Z, NA J, LIN X, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanovesicles: a novel nanotool for disease therapy. Heliyon. 2024;10(9):e30630. [56] YI C, LU L, LI Z, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles for microRNA delivery in cancer treatment. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024; 11(7):13346. [57] DAD HA, GU TW, ZHU AQ, et al. Plant exosome-like nanovesicles: emerging therapeutics and drug delivery nanoplatforms. Mol Ther. 2021;29(1):13-31. [58] XI XM, XIA SJ, LU R. Drug loading techniques for exosome-based drug delivery systems. Pharmazie. 2021;76(2):61-67. [59] SONG Y, HU J, MA C, et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes as advanced therapeutics for inflammation: current progress and future perspectives. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:1597-1627. [60] YANG Q, LI S, OU H, et al. Exosome-based delivery strategies for tumor therapy: an update on modification, loading, and clinical application. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):41. [61] BAGHERI E, ABNOUS K, FARZAD S A, et al. Targeted doxorubicin-loaded mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes as a versatile platform for fighting against colorectal cancer. Life Sci. 2020;261(5):118369. [62] ZHENG C, ZHONG Q, YI K, et al. Anti-phagocytosis-blocking repolarization-resistant membrane-fusogenic liposome (ARMFUL) for adoptive cell immunotherapy. Sci Adv. 2023;9(32):eadh2413. [63] SAFAEI S, FADAEE M, FARZAM OR, et al. Exploring the dynamic interplay between exosomes and the immune tumor microenvironment: implications for breast cancer progression and therapeutic strategies. Breast Cancer Res. 2024;26(1):57. [64] BOLUMAR D, MONCAYO-ARLANDI J, GONZALEZ-FERNANDEZ J, et al. Vertical transmission of maternal DNA through extracellular vesicles associates with altered embryo bioenergetics during the periconception period. Elife. 2023;12(6):RP88008. [65] WANG Z, HE Z, WAN J, et al. EphA2-specific microvesicles derived from tumor cells facilitate the targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs for osteosarcoma therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):89. [66] XIE X, CHENG P, HU L, et al. Bone-targeting engineered small extracellular vesicles carrying anti-miR-6359-CGGGAGC prevent valproic acid-induced bone loss. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):24. [67] ZHANG Y, BELAID M, LUO X, et al. Probing milk extracellular vesicles for intestinal delivery of RNA therapies. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023; 21(1):406. [68] LI Z, GUO K, GAO Z, et al. Colocalization of protein and microRNA markers reveals unique extracellular vesicle sub-populations for early cancer detection. bioRxiv. 2024;10(9):eadh8689. [69] YANG B, CHEN Y, SHI J. Exosome Biochemistry and advanced nanotechnology for next-generation theranostic platforms. Adv Mater. 2019;31(2):e1802896. [70] KOMURO H, AMINOVA S, LAURO K, et al. Advances of engineered extracellular vesicles-based therapeutics strategy. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2022;23(1):655-681. [71] 赖威,彭敦钰,李晶,等.肺癌微环境中肿瘤源性外泌体的通讯与免疫调节作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2024,41(4):881-884. [72] HUANG X, WU W, JING D, et al. Engineered exosome as targeted lncRNA MEG3 delivery vehicles for osteosarcoma therapy. J Control Release. 2022;343(3):107-117. [73] KANG C, HAN P, LEE J S, et al. Anchor, spacer, and ligand-modified engineered exosomes for trackable targeted therapy. Bioconjug Chem. 2020;31(11):2541-2552. [74] HU Y, LI X, ZHANG Q, et al. Exosome-guided bone targeted delivery of antagomir-188 as an anabolic therapy for bone loss. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(9):2905-2913. [75] LIANG G, ZHU Y, ALI D J, et al. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):10. [76] LI S, WU Y, DING F, et al. Engineering macrophage-derived exosomes for targeted chemotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer. Nanoscale. 2020;12(19):10854-10862. [77] PARK J, CHANG ES, KIM JY, et al. C-MET-positive circulating tumor cells and cell-free DNA as independent prognostic factors in hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2024;26(1):13. [78] NONAKA T. Application of engineered extracellular vesicles to overcome drug resistance in cancer. Front Oncol. 2022;12(15):1070479. [79] WANG J, CHEN D, HUANG W, et al. Aptamer-functionalized field-effect transistor biosensors for disease diagnosis and environmental monitoring. Exploration (Beijing). 2023;3(3):20210027. [80] HAN Q, XIE QR, LI F, et al. Targeted inhibition of SIRT6 via engineered exosomes impairs tumorigenesis and metastasis in prostate cancer. Theranostics. 2021;11(13):6526-6541. [81] ISHIGURO K, YAN IK, LEWIS-TUFFIN L, et al. Targeting liver cancer stem cells using engineered biological nanoparticles for the treatment of hepatocellular cancer. Hepatol Commun. 2020;4(2):298-313. [82] TAN F, LI X, WANG Z, et al. Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):17. [83] ZHANG J, JI C, ZHANG H, et al. Engineered neutrophil-derived exosome-like vesicles for targeted cancer therapy. Sci Adv. 2022;8(2):eabj8207. [84] ZHUANG M, CHEN X, DU D, et al. SPION decorated exosome delivery of TNF-α to cancer cell membranes through magnetism. Nanoscale. 2020;12(1):173-188. [85] LIU Y, BAI L, GUO K, et al. Erratum: focused ultrasound-augmented targeting delivery of nanosonosensitizers from homogenous exosomes for enhanced sonodynamic cancer therapy: erratum. Theranostics. 2022;12(17):7643-7644. [86] CHENG L, ZHANG X, TANG J, et al. Gene-engineered exosomes-thermosensitive liposomes hybrid nanovesicles by the blockade of CD47 signal for combined photothermal therapy and cancer immunotherapy. Biomaterials. 2021;275(12):120964. [87] LI G, WANG J, XU M, et al. Engineered exosome for NIR-triggered drug delivery and superior synergistic chemo-phototherapy in a glioma model. Applied Materials Today. 2020;20(13):100723. [88] ADITI K, SABOOR K, NANDINI P, et al. Dual pH and ultrasound responsive nanocarriers: a smart approach in cancer theranostics, Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2024;95(2):105560. [89] ESSOLA JM, ZHANG M, YANG H, et al. Exosome regulation of immune response mechanism: Pros and cons in immunotherapy. Bioact Mater. 2024;32(12):124-146. [90] LEI P, CHENXV Z, GUANLUN Z, et al. The modulation of tumor-associated macrophages via natural nanomodulators by neutralizing the acidic tumor microenvironment for tumor treatment. Mater Adv. 2024;5(1):329-335. [91] NGUYEN CAO TG, KANG JH, KIM W, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicle-based sonotheranostics for dual stimuli-sensitive drug release and photoacoustic imaging-guided chemo-sonodynamic cancer therapy. Theranostics. 2022;12(3):1247-1266. [92] WU W, ZHONG S, GONG Y, et al. A new molecular probe: an NRP-1 targeting probe for the grading diagnosis of glioma in nude mice. Neurosci Lett. 2020;714(1):134617. [93] YE Y, GAO M, SHI W, et al. The immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Immunol. 2023;14(6):1325530. [94] HE S, ZHAO Z. Genetically engineered cell-derived nanovesicles for cancer immunotherapy. Nanoscale. 2024;16(17):8317-8334. [95] KIM SY, GUK D, JEONG Y, et al. Engineered hybrid vesicles and cellular internalization in mammary cancer cells. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(4):440. [96] BOSE RJ, KUMAR US, GARCIA-MARQUES F, et al. Engineered cell-derived vesicles displaying targeting peptide and functionalized with nanocarriers for therapeutic microRNA delivery to triple-negative breast cancer in mice. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(5):e2101387. [97] GUO Z, ZHANG Y, XU W, et al. Engineered exosome-mediated delivery of circDIDO1 inhibits gastric cancer progression via regulation of MiR-1307-3p/SOCS2 axis. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):326. [98] HE C, JAFFAR ALI D, LI Y, et al. Engineering of HN3 increases the tumor targeting specificity of exosomes and upgrade the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib on huh-7 cells. PeerJ. 2020;8(3):e9524. [99] JAYASINGHE MK, PIRISINU M, YANG Y, et al. Surface-engineered extracellular vesicles for targeted delivery of therapeutic RNAs and peptides for cancer therapy. Theranostics. 2022;12(7):3288-3315. [100] LI B, CHEN X, QIU W, et al. Synchronous disintegration of ferroptosis defense axis via engineered exosome-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for glioblastoma therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(17):e2105451. [101] GHARAVI AT, IRIAN S, NIKNEJAD A, et al. Harnessing exosomes as a platform for drug delivery in breast cancer: a systematic review for in vivo and in vitro studies. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024;32(2):200800. [102] YAN Z, XIAO P, JI P, et al. Enhanced breast cancer therapy using multifunctional lipid-coated nanoparticles combining curcumin chemotherapy and nitric oxide gas delivery. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):18107. [103] WANG Y, ZHANG T, HE X. Advances in the role of microRNAs associated with the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2023;13(6):1279822. [104] ZHANG K, DONG C, CHEN M, et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated delivery of miR-101 inhibits lung metastasis in osteosarcoma. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):411-425. [105] GUNASSEKARAN GR, POONGKAVITHAI VADEVOO SM, BAEK MC, et al. M1 macrophage exosomes engineered to foster M1 polarization and target the IL-4 receptor inhibit tumor growth by reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages into M1-like macrophages. Biomaterials. 2021;278(11):121137. [106] HU S, MA J, SU C, et al. Engineered exosome-like nanovesicles suppress tumor growth by reprogramming tumor microenvironment and promoting tumor ferroptosis. Acta Biomater. 2021;135(11):567-581. [107] HUANG L, RONG Y, TANG X, et al. Engineered exosomes as an in situ DC-primed vaccine to boost antitumor immunity in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):45. [108] QIU J, JIANG Y, YE N, et al. Leveraging the intratumoral microbiota to treat human cancer: are engineered exosomes an effective strategy?. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):728. [109] KAMERKAR S, LENG C, BURENKOVA O, et al. Exosome-mediated genetic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages by exoASO-STAT6 leads to potent monotherapy antitumor activity. Sci Adv. 2022; 8(7):eabj7002. [110] ZUO B, ZHANG Y, ZHAO K, et al. Universal immunotherapeutic strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma with exosome vaccines that engage adaptive and innate immune responses. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15(1):46. [111] NGUYEN CAO TG, KANG JH, YOU JY, et al. Safe and targeted sonodynamic cancer therapy using biocompatible exosome-based nanosonosensitizers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(22):25575-25588. [112] WANG D, WAN Z, YANG Q, et al. Sonodynamical reversion of immunosuppressive microenvironment in prostate cancer via engineered exosomes. Drug Deliv. 2022;29(1):702-713. [113] LEE JH, JUNG KH, MINA K, et al. Extracellular vesicles deliver sodium iodide symporter protein and promote cancer cell radioiodine therapy. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11190. [114] MA X, YAO M, GAO Y, et al. Functional immune cell-derived exosomes engineered for the trilogy of radiotherapy sensitization. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(23):e2106031. [115] TIAN T, LIANG R, EREL-AKBABA G, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibition in GBM primed with radiation by engineered extracellular vesicles. ACS Nano. 2022;16(2):1940-1953. [116] TIAN R, WANG Z, NIU R, et al. Tumor exosome mimicking nanoparticles for tumor combinatorial chemo-photothermal therapy. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8(12):1010. [117] YANG M, WANG X, PU F, et al. Engineered exosomes-based photothermal therapy with MRI/CT imaging guidance enhances anticancer efficacy through deep tumor nucleus penetration. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(10):1593. [118] WANG L, ZHOU X, ZOU W, et al. Exosomes containing miRNAs targeting HER2 synthesis and engineered to adhere to HER2 on tumor cells surface exhibit enhanced antitumor activity. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):153. [119] LIU X, XIAO C, XIAO K. Engineered extracellular vesicles-like biomimetic nanoparticles as an emerging platform for targeted cancer therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):287. [120] ZHENG W, ZHU T, TANG L, et al. Inhalable CAR-T cell-derived exosomes as paclitaxel carriers for treating lung cancer. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):383. [121] LIN X, LIN L, WU J, et al. A targeted siRNA-loaded PDL1-exosome and functional evaluation against lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. 2022; 13(11):1691-1702. [122] LV Q, CHENG L, LU Y, et al. Thermosensitive exosome-liposome hybrid nanoparticle-mediated chemoimmunotherapy for improved treatment of metastatic peritoneal cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(18):2000515. [123] NENE LC, ABRAHAMSE H. Design consideration of phthalocyanines as sensitizers for enhanced sono-photodynamic combinatorial therapy of cancer. Acta Pharm Sinb. 2024;14(3):1077-1097. [124] GUO Y, WAN Z, ZHAO P, et al. Ultrasound triggered topical delivery of Bmp7 mRNA for white fat browning induction via engineered smart exosomes. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):402. [125] HILLMAN T. The application of plant-exosome-like nanovesicles as improved drug delivery systems for cancer vaccines. Discov Oncol. 2024;15(1):136. [126] LIU X, LOU K, ZHANG Y, et al. Unlocking the medicinal potential of plant-derived extracellular vesicles: current progress and future perspectives. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19(7):4877-4892. [127] AIMALETDINOV A, GOMZIKOVA M. Tracking of extracellular vesicles’ biodistribution: new methods and approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 25(19):11312. [128] ZIMMERMAN A, OLIVEIRA G, SU X, et al. Multimode chromatography-based techniques for high purity isolation of extracellular vesicles from human blood plasma. J Extracell Biol. 2024;3(3):e147. [129] CHEN H, WANG L, ZENG X, et al. Exosomes, a new star for targeted delivery. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;8(9):751079. [130] LIU J, REN L, LI S, et al. The biology, function, and applications of exosomes in cancer. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(9):2783-2797. [131] RAJPUT A, VARSHNEY A, BAJAJ R, et al. Exosomes as new generation vehicles for drug delivery: biomedical applications and future perspectives. Molecules. 2022;27(21):7289. [132] RHIM W, KIM J, LEE S, et al. Recent advances in extracellular vesicle engineering and its applications to regenerative medicine. Biomater Res. 2023;11;27(1):130. |
| No related articles found! |
外泌体作为药物递送载体有着独特优势,如优异的生物相容性、较高的生物利用度、可生物降解性以及跨越生物屏障的能力等,有开发为肿瘤高精度递送载体的潜力[11]。外泌体将药物包裹在其磷脂双层膜中实现药物的低清除率和长期循环,同时通过其表面的高表达信号分子实现靶向治疗[12]。外泌体具有很强的可修饰性和内化作用,几乎没有不良的免疫反应,生物安全性高[13]。外泌体可负载不同的物质,包括短干扰RNA、反义寡核苷酸、化学治疗药和免疫调节剂等[14]。但由于许多外源性和内源性障碍使得外泌体的应用有限,故采用工程化外泌体负载药物以实现高效、精确地肿瘤部位递送,同时减少与治疗相关的不良反应。
随着肿瘤治疗技术的不断进步,工程化外泌体作为新兴的生物纳米载体,正逐步展现出在抗肿瘤领域的巨大潜力。工程化外泌体通过精准设计与改造,提高治疗的靶向性和精准度,提升抗肿瘤治疗的整体效果,为肿瘤治疗提供了新的思路和方法。作为新型的药物递送平台,工程化外泌体不仅优化了药物的传输效率,还促进了抗肿瘤新药的研发进程,为药物科学家开辟了多靶点治疗策略的新途径。文章对工程化外泌体靶向载药研究作一全面综述,并阐述了其在肿瘤治疗中的最新进展及推动肿瘤治疗创新方面的价值,为肿瘤治疗领域的发展贡献新的思路与策略。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024年8月检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时限为2016-2024年。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed及中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“Exosomal,tumor,microvesicle,extracellular vesicles,engineered,therapeutics,characterization,isolation,drug delivery,targeting,modification strategies, physics,chemistry, biology”为英文检索词,以“外泌体,药物递送,肿瘤”为中文检索词。
1.1.5 检索类型 研究原著、综述、学位论文。
1.1.6 手工检索 无。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检索共获得文献976篇。
1.1.8 文献检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①纳入文献聚焦肿瘤与外泌体最新进展,涵盖肿瘤生物学及外泌体角色等;②考察外泌体生物发生、提取、载药技术及靶向修饰等关键技术;③重视外泌体作为药物载体在肿瘤治疗中的创新应用与成果,旨在为未来研究提供宝贵参考。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①排除内容重复、缺乏新见解或创新性的文献;②排除与主题不相关或相关性较低的文献;③排除实验设计存在明显缺陷、数据不足或数据质量不高的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 基于上述关键词的初步检索,共获得了976篇参考文献。根据文章题目及摘要进行初步筛选,然后经过泛读挑选出与此次研究主题相关的实验论文、综述和专利成果,排除了权威性不足及重复出现的文献,最终通过精读确定了132篇文献作为文章的核心参考,并对其进行了深入的归纳总结与探讨。具体筛选结果见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
战[130],亟需深入评估与解决;④用于治疗人类疾病或者病症的外泌体产品都需要受到严格监管,目前仍然没有任何的外泌体产品能够在美国食品药品监督管理局找到[131],距离外泌体产品的正式面世还有一段很长的路要走。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 过往文献中不乏关于外泌体分离提纯技术、靶向策略等详尽探讨,然而,文章独辟蹊径,聚焦于外泌体在肿瘤学领域的临床转化的研究进展。文章不仅全面梳理了工程化外泌体的改造策略,更深刻剖析了其在迈向临床转化过程中所面临的种种问题与挑战。
3.3 综述的局限性 该综述整合了近年工程化外泌体与肿瘤发生发展方面的相关文献,未能将其他疾病与工程化外泌体的应用相关文章纳入,因此,工程化外泌体相关的改造方法可能不够全面。
3.4 综述的重要意义 恶性肿瘤已成为全球病患死亡的主要原因,许多药物在杀伤肿瘤细胞的同时会对正常细胞造成损伤,因此亟待寻找一种高效、安全的治疗策略。工程化外泌体因天然来源、低毒性和出色的生物相容性而成为一种新型且有前途的靶向药物递送平台。目前工程化外泌体主要分为4种类型:①基因编辑工程化:通过使细胞产生所需的药物来改造外泌体功能;②内源性工程化:可分为2种主要方法,即炎症因子和非炎症相关因子预处理,可用于增强药物稳定性并提高其向靶位点的递送效率;③外源性工程化:在外泌体溶液中直接孵育药物以包封在外泌体中;④混合工程化:将分离的外泌体与另一种脂质纳米颗粒反应形成新的复合纳米颗粒,从而使外泌体功能化,这种方法经常与已建立的工程化方法一起使用[132]。部分工程化外泌体已进入临床试验阶段,例如用于癌症治疗,由于外泌体的产量、药物负载量和生物安全性等挑战,这些临床试验多数仍处于早期阶段。目前没有研究明确指出工程化外泌体的最佳改造方式。选择合适的外泌体类型取决于具体的治疗需求、药物性质以及靶标细胞的特性。整体而言,基因工程化外泌体因较高的靶向性和定制化潜力,通常被认为在未来的药物递送中具有较大的应用前景[105]。文章综述了近年来工程化外泌体的改造策略,以及其应用现状,旨在为肿瘤治疗提供一种新的治疗策略。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 尽管外泌体药物递送系统在肿瘤治疗方面有巨大潜力,但将其用于临床试验之前仍有许多问题需要完善。第一,加强基础研究,应继续深化在生物学、医学和药学领域的基础研究,以全面理解外泌体的生成机制、独特功能、稳定性以及安全性等核心特性。这些研究将为外泌体药物递送系统的进一步优化和应用奠定坚实的基础。第二,优化工程化改造技术,应当鼓励研发创新的外泌体改造技术,旨在提升载药效率、增强靶向性并保障稳定性,同时简化生产流程、降低成本,以推动其在药物递送领域的广泛应用。第三,推动建立外泌体药物递送系统的标准化生产、纯化和检测流程,以确保产品质量和一致性,为临床应用提供可靠保障。第四,在积极推进外泌体药物递送系统的研发与临床应用过程中,必须高度关注伦理和法规问题。确保所有研究活动均遵循伦理规范,尊重患者权益,同时严格遵守国家及国际相关法律法规,为科技创新提供坚实的道德和法律保障。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
外泌体:由细胞分泌的微小囊泡,内含丰富的蛋白质、脂质和核酸,直径为40-160 nm,能够轻松穿越生物屏障。作为纳米级药物递送载体,外泌体不仅具有高度的生物相容性和低免疫原性,还能实现药物的在治疗过程中的精准靶向和缓释,从而显著提高药物的疗效并降低不良反应。因此,外泌体在药物递送领域展现出巨大的应用潜力。#br#工程化外泌体:是天然外泌体经过生物工程技术精细改造后的产物。这些改造后的外泌体不仅保留了原有的特性,还具备了更高的载药效率、更精准的靶向性和更强的抵抗机体清除能力。通过调整其膜负载物或内容物,工程化外泌体能够针对特定疾病或治疗需求进行定制,为药物递送和疾病治疗提供了新的高效途径。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
工程化外泌体在靶向递送药物抗肿瘤领域取得显著进展。通过生物、物理和化学等修饰,外泌体被赋予特定靶向性,实现药物高效和精准递送。这一创新技术为癌症治疗提供了新策略,展现出巨大的临床应用潜力。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||