[1] LURETTE O, MARTÍN-JIMÉNEZ R, KHAN M, et al. Aggregation of alpha-synuclein disrupts mitochondrial metabolism and induce mitophagy via cardiolipin externalization. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(11):729.
[2] ANTONY PM, DIEDERICH NJ, KRÜGER R, et al. The hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J. 2013;280(23):5981-5993.
[3] WÜLLNER U, BORGHAMMER P, CHOE CU, et al. The heterogeneity of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2023;130(6):827-838.
[4] XU MM, RYAN P, RUDRAWAR S, et al. Advances in the development of imaging probes and aggregation inhibitors for alpha-synuclein. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41(4):483-498.
[5] VILLAR-PIQUÉ A, LOPES DA FONSECA T, OUTEIRO TF. Structure, function and toxicity of alpha-synuclein: the Bermuda triangle in synucleinopathies. J Neurochem. 2016;139 Suppl 1:240-255.
[6] CHEN R, GU X, WANG X. α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease and advances in detection. Clin Chim Acta. 2022;529:76-86.
[7] VASQUEZ V, MITRA J, WANG H, et al. A multi-faceted genotoxic network of alpha-synuclein in the nucleus and mitochondria of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease: Emerging concepts and challenges. Prog Neurobiol. 2020;185:101729.
[8] WAKABAYASHI K. Where and how alpha-synuclein pathology spreads in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathology. 2020;40(5):415-425.
[9] FUSCO G, PAPE T, STEPHENS AD, et al. Structural basis of synaptic vesicle assembly promoted by α-synuclein. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12563.
[10] CARTELLI D, ALIVERTI A, BARBIROLI A, et al. α-Synuclein is a Novel Microtubule Dynamase. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33289.
[11] TOFARIS GK. Initiation and progression of α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(4):210.
[12] ZHU M, QIN ZJ, HU D, et al. Alpha-synuclein can function as an antioxidant preventing oxidation of unsaturated lipid in vesicles. Biochemistry. 2006; 45(26):8135-8142.
[13] NEGI S, KHURANA N, DUGGAL N. The misfolding mystery: α-synuclein and the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int. 2024;177:105760.
[14] VAN ROOIJEN BD, CLAESSENS MM, SUBRAMANIAM V. Membrane interactions of oligomeric alpha-synuclein: potential role in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010;11(5):334-342.
[15] KAWAHATA I, FINKELSTEIN DI, FUKUNAGA K. Pathogenic Impact of α-Synuclein Phosphorylation and Its Kinases in α-Synucleinopathies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6216.
[16] CAVALLARIN N, VICARIO M, NEGRO A. The role of phosphorylation in synucleinopathies: focus on Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010;9(4):471-481.
[17] JUNQUEIRA SC, CENTENO EGZ, WILKINSON KA, et al. Post-translational modifications of Parkinson’s disease-related proteins: Phosphorylation, SUMOylation and Ubiquitination. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(8):2001-2007.
[18] CHEN G, AHN EH, KANG SS, et al. UNC5C Receptor Proteolytic Cleavage by Active AEP Promotes Dopaminergic Neuronal Degeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(7):e2103396.
[19] NWABUFO CK, AIGBOGUN OP. Diagnostic and therapeutic agents that target alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2022;269(11):5762-5786.
[20] KRÜGER R, KUHN W, MÜLLER T, et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet. 1998;18(2):106-108.
[21] GHOSH D, SAHAY S, RANJAN P, et al. The newly discovered Parkinson’s disease associated Finnish mutation (A53E) attenuates α-synuclein aggregation and membrane binding. Biochemistry. 2014;53(41):6419-6421.
[22] GHOSH D, MONDAL M, MOHITE GM, et al. The Parkinson’s disease-associated H50Q mutation accelerates α-Synuclein aggregation in vitro. Biochemistry. 2013;52(40):6925-6927.
[23] SAHAY S, GHOSH D, SINGH PK, et al. Alteration of Structure and Aggregation of α-Synuclein by Familial Parkinson’s Disease Associated Mutations. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(7):656-676.
[24] POLYMEROPOULOS MH, LAVEDAN C, LEROY E, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science. 1997;276(5321):2045-2047.
[25] SIMON C, SOGA T, OKANO HJ, et al. α-Synuclein-mediated neurodegeneration in Dementia with Lewy bodies: the pathobiology of a paradox. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):196.
[26] MALPARTIDA AB, WILLIAMSON M, NARENDRA DP, et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitophagy in Parkinson’s Disease: From Mechanism to Therapy. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021;46(4):329-343.
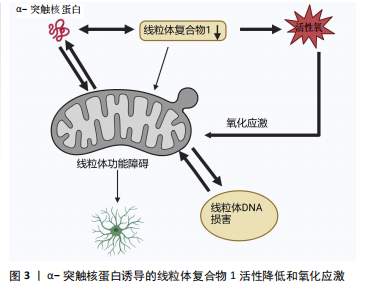
[27] SOHRABI T, MIRZAEI-BEHBAHANI B, ZADALI R, et al. Common Mechanisms Underlying α-Synuclein-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. J Mol Biol. 2023;435(12):167992.
[28] SCHAPIRA AH, COOPER JM, DEXTER D, et al. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 1989;1(8649):1269.
[29] PRZEDBORSKI S, KOSTIC V, JACKSON-LEWIS V, et al. Transgenic mice with increased Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase activity are resistant to N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 1992;12(5):1658-1667.
[30] SURMEIER DJ, GUZMAN JN, SANCHEZ-PADILLA J, et al. The role of calcium and mitochondrial oxidant stress in the loss of substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2011;198:221-231.
[31] XIE W, CHUNG KK. Alpha-synuclein impairs normal dynamics of mitochondria in cell and animal models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2012;122(2): 404-414.
[32] PESAH Y, PHAM T, BURGESS H, et al. Drosophila parkin mutants have decreased mass and cell size and increased sensitivity to oxygen radical stress. Development. 2004;131(9):2183-2194.
[33] DI MAIO R, BARRETT PJ, HOFFMAN EK, et al. α-Synuclein binds to TOM20 and inhibits mitochondrial protein import in Parkinson’s disease. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(342):342ra78.
[34] SUBRAMANIAM SR, CHESSELET MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2013;106-107:17-32.
[35] SUBRAHMANIAN N, LAVOIE MJ. Is there a special relationship between complex I activity and nigral neuronal loss in Parkinson’s disease? A critical reappraisal. Brain Res. 2021;1767:147434.
[36] BURTSCHER J, SYED MMK, KELLER MA, et al. Fatal attraction - The role of hypoxia when alpha-synuclein gets intimate with mitochondria. Neurobiol Aging. 2021;107:128-141.
[37] THORNE NJ, TUMBARELLO DA. The relationship of alpha-synuclein to mitochondrial dynamics and quality control. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15: 947191.
[38] YE H, ROBAK LA, YU M, et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Syndrome. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023;18:95-121.
[39] LAPOINTE N, ST-HILAIRE M, MARTINOLI MG, et al. Rotenone induces non-specific central nervous system and systemic toxicity. FASEB J. 2004; 18(6):717-719.
[40] IMBRIANI P, MARTELLA G, BONSI P, et al. Oxidative stress and synaptic dysfunction in rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2022; 173:105851.
[41] BORSCHE M, PEREIRA SL, KLEIN C, et al. Mitochondria and Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical, Molecular, and Translational Aspects. J Parkinsons Dis. 2021;11(1):45-60.
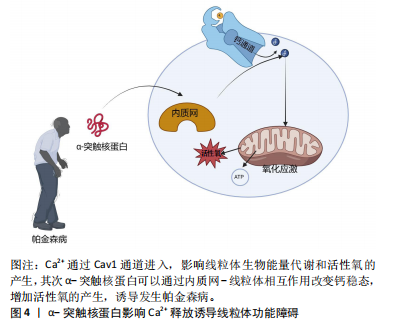
[42] SURMEIER DJ, SCHUMACKER PT, GUZMAN JD, et al. Calcium and Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;483(4):1013-1019.
[43] SURMEIER DJ, HALLIDAY GM, SIMUNI T. Calcium, mitochondrial dysfunction and slowing the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol. 2017; 298(Pt B):202-209.
[44] WILSON EL, METZAKOPIAN E. ER-mitochondria contact sites in neurodegeneration: genetic screening approaches to investigate novel disease mechanisms. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(6):1804-1821.
[45] TSUNEMI T, PEREZ-ROSELLO T, ISHIGURO Y, et al. Increased Lysosomal Exocytosis Induced by Lysosomal Ca2+ Channel Agonists Protects Human Dopaminergic Neurons from α-Synuclein Toxicity. J Neurosci. 2019;39(29): 5760-5772.
[46] LIN KJ, LIN KL, CHEN SD, et al. The Overcrowded Crossroads: Mitochondria, Alpha-Synuclein, and the Endo-Lysosomal System Interaction in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(21):5312.
[47] GANGULY G, CHAKRABARTI S, CHATTERJEE U, et al. Proteinopathy, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: cross talk in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017;11:797-810.
[48] LUTH ES, STAVROVSKAYA IG, BARTELS T, et al. Soluble, prefibrillar α-synuclein oligomers promote complex I-dependent, Ca2+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(31):21490-21507.
[49] BARAZZUOL L, GIAMOGANTE F, BRINI M, et al. PINK1/Parkin Mediated Mitophagy, Ca2+ Signalling, and ER-Mitochondria Contacts in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(5):1772.
[50] GIORGI C, MARCHI S, PINTON P. The machineries, regulation and cellular functions of mitochondrial calcium. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(11):713-730.
[51] BOHUSH A, LEŚNIAK W, WEIS S, et al. Calmodulin and Its Binding Proteins in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):3016.
[52] WU Y, WHITEUS C, XU CS, et al. Contacts between the endoplasmic reticulum and other membranes in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017; 114(24):E4859-E4867.
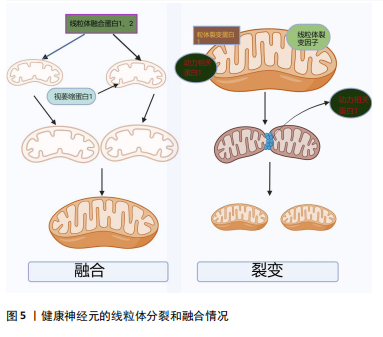
[53] MEYER JN, LEUTHNER TC, LUZ AL. Mitochondrial fusion, fission, and mitochondrial toxicity. Toxicology. 2017;391:42-53.
[54] YAPA NMB, LISNYAK V, RELJIC B, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics in health and disease. FEBS Lett. 2021;595(8):1184-1204.
[55] POZO DEVOTO VM, FALZONE TL. Mitochondrial dynamics in Parkinson’s disease: a role for α-synuclein? Dis Model Mech. 2017;10(9):1075-1087.
[56] KAMP F, EXNER N, LUTZ AK, et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial fusion by α-synuclein is rescued by PINK1, Parkin and DJ-1. EMBO J. 2010;29(20): 3571-3589.
[57] ADEBAYO M, SINGH S, SINGH AP, et al. Mitochondrial fusion and fission: The fine-tune balance for cellular homeostasis. FASEB J. 2021;35(6):e21620.
[58] CLARK EH, VÁZQUEZ DE LA TORRE A, HOSHIKAWA T, et al. Targeting mitophagy in Parkinson’s disease. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100209.
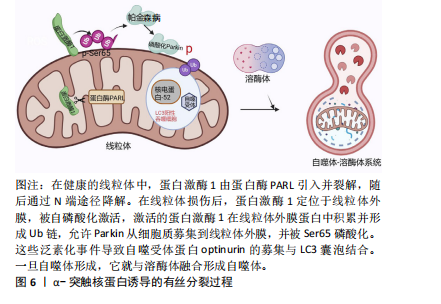
[59] LIU J, LIU W, LI R, et al. Mitophagy in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Treatment. Cells. 2019;8(7):712.
[60] GRÜNEWALD A, KUMAR KR, SUE CM. New insights into the complex role of mitochondria in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2019;177:73-93.
[61] WILKANIEC A, LENKIEWICZ AM, CZAPSKI GA, et al. Extracellular Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers Induce Parkin S-Nitrosylation: Relevance to Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease Etiopathology. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(1):125-140.
[62] WILKANIEC A, LENKIEWICZ AM, BABIEC L, et al. Exogenous Alpha-Synuclein Evoked Parkin Downregulation Promotes Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Neuronal Cells. Implications for Parkinson’s Disease Pathology. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:591475.
[63] KRZYSTEK TJ, BANERJEE R, THURSTON L, et al. Differential mitochondrial roles for α-synuclein in DRP1-dependent fission and PINK1/Parkin-mediated oxidation. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(9):796.
[64] RAY B, BHAT A, MAHALAKSHMI AM, et al. Mitochondrial and Organellar Crosstalk in Parkinson’s Disease. ASN Neuro. 2021;13:17590914211028364.
[65] HSIEH CH, SHALTOUKI A, GONZALEZ AE, et al. Functional Impairment in Miro Degradation and Mitophagy Is a Shared Feature in Familial and Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;19(6):709-724.
[66] SHALTOUKI A, HSIEH CH, KIM MJ, et al. Alpha-synuclein delays mitophagy and targeting Miro rescues neuron loss in Parkinson’s models. Acta Neuropathol. 2018;136(4):607-620.
[67] DE MIRANDA BR, ROCHA EM, CASTRO SL, et al. Protection from α-Synuclein induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration by overexpression of the mitochondrial import receptor TOM20. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2020;6(1):38.
[68] COPELAND WC, LONGLEY MJ. Mitochondrial genome maintenance in health and disease. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014;19:190-198.
[69] PASCHEN SA, NEUPERT W. Protein import into mitochondria. IUBMB Life. 2001;52(3-5):101-112.
[70] WIEDEMANN N, PFANNER N. Mitochondrial Machineries for Protein Import and Assembly. Annu Rev Biochem. 2017;86:685-714. |