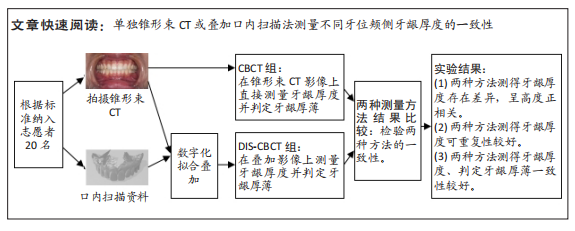
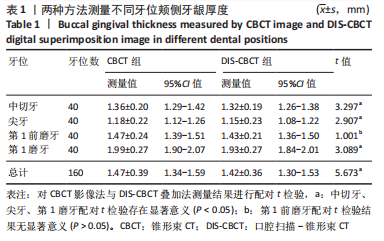
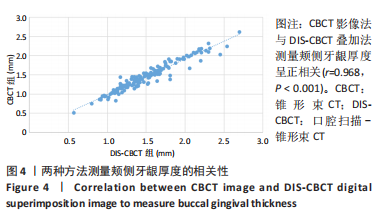
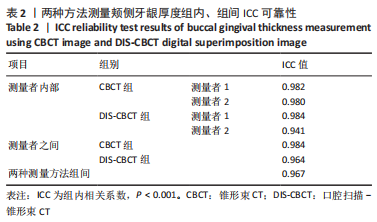
[1] CORTELLINI P, BISSADA NF. Mucogingival conditions in the natural dentition: Narrative review, case definitions, and diagnostic considerations. J Periodontol. 2018;89 Suppl 1: S204-S213.
[2] WEINLÄNDER M, LEKOVIC V, SPADIJER-GOSTOVIC S, et al. Gingivomorphometry - esthetic evaluation of the crown-mucogingival complex: a new method for collection and measurement of standardized and reproducible data in oral photography. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(5):526-530.
[3] BARRIVIERA M, DUARTE WR, JANUÁRIO AL, et al. A new method to assess and measure palatal masticatory mucosa by cone-beam computerized tomography. J Clin Periodontol. 2009;36(7):564-568.
[4] RONAY V, SAHRMANN P, BINDL A, et al. Current status and perspectives of mucogingival soft tissue measurement methods. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2011;23(3):146-156.
[5] 陈子圆,钟金晟,欧阳翔英,等.牙龈退缩患牙的牙龈厚度评估[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2020,52(2):339-345.
[6] TATTAN M, SINJAB K, LEE E, et al. Ultrasonography for chairside evaluation of periodontal structures: A pilot study. J Periodontol. 2020;91(7):890-899.
[7] ALVES PHM, ALVES TCLP, PEGORARO TA, et al. Measurement properties of gingival biotype evaluation methods. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(3):280-284.
[8] GÜRLEK Ö, SÖNMEZ Ş, GÜNERI P, et al. A novel soft tissue thickness measuring method using cone beam computed tomography. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2018;30(6):516-522.
[9] WANG L, RUAN Y, CHEN J, et al. Assessment of the relationship between labial gingival thickness and the underlying bone thickness in maxillary anterior teeth by two digital techniques. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):709.
[10] KIM YJ, PARK JM, CHO HJ, et al. Correlation analysis of periodontal tissue dimensions in the esthetic zone using a non-invasive digital method. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2021;51(2):88-99.
[11] KIM YJ, PARK JM, KIM S, et al. New method of assessing the relationship between buccal bone thickness and gingival thickness. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016;46(6):372-381.
[12] KIM SH, LEE JB, KIM MJ, et al. Combining virtual model and cone beam computed tomography to assess periodontal changes after anterior tooth movement. BMC Oral Health. 2018;18(1):180.
[13] 沈宇清,余优成,孙健,等.口内扫描与锥形束CT重建牙颌数字化模型的测量分析[J].精准医学杂志,2020,35(5):428-431,436.
[14] 匡博渊.实用新型的CBCT重建模型与激光扫描牙齿STL模型的融合方法[D].济南:山东大学,2017.
[15] SIN YW, CHANG HY, YUN WH, et al. Association of gingival biotype with the results of scaling and root planing. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013;43(6):283-290.
[16] CLAFFEY N, SHANLEY D. Relationship of gingival thickness and bleeding to loss of probing attachment in shallow sites following nonsurgical periodontal therapy. J Clin Periodontol. 1986;13(7):654-657.
[17] AMID R, MIRAKHORI M, SAFI Y, et al. Assessment of gingival biotype and facial hard/soft tissue dimensions in the maxillary anterior teeth region using cone beam computed tomography. Arch Oral Biol. 2017;79:1-6.
[18] COUSO-QUEIRUGA E, TATTAN M, AHMAD U, et al. Assessment of gingival thickness using digital file superimposition versus direct clinical measurements. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(4):2353-2361.
[19] NIKIFORIDOU M, TSALIKIS L, ANGELOPOULOS C, et al. Classification of periodontal biotypes with the use of CBCT. A cross-sectional study. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(8):2061-2071.
[20] VANDANA KL, SAVITHA B. Thickness of gingiva in association with age, gender and dental arch location. J Clin Periodontol. 2005;32(7):828-830.
[21] RATHOD SR, GONDE NP, KOLTE AP, et al. Quantitative analysis of gingival phenotype in different types of malocclusion in the anterior esthetic zone. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2020;24(5):414-420.
[22] KAYA Y, ALKAN Ö, ALKAN EA, et al. Gingival thicknesses of maxillary and mandibular anterior regions in subjects with different craniofacial morphologies. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018;154(3):356-364.
[23] AGUILAR-DURAN L, MIR-MARI J, FIGUEIREDO R, et al. Is measurement of the gingival biotype reliable? Agreement among different assessment methods. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2020;25(1):e144-e149.
[24] WANG J, CHA S, ZHAO Q, et al. Methods to assess tooth gingival thickness and diagnose gingival phenotypes: A systematic review. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2022;34(4):620-632.
[25] ROSIN M, SPLIETH CH, HESSLER M, et al. Quantification of gingival edema using a new 3-D laser scanning method. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29(3):240-246.
[26] MEHL A, GLOGER W, KUNZELMANN KH, et al. A new optical 3-D device for the detection of wear. J Dent Res. 1997;76(11):1799-1807.
[27] 刘怡,JAMES MAH,许天民.锥形束计算机断层扫描中牙齿的分割精度[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2010,42(1):98-102.
[28] 马寅耀. CBCT数字化牙颌模型精度及测量信度和效度研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2013.
[29] STUDER SP, ALLEN EP, REES TC, et al. The thickness of masticatory mucosa in the human hard palate and tuberosity as potential donor sites for ridge augmentation procedures. J Periodontol. 1997;68(2):145-151.
[30] 李镒冲,李晓松.两种测量方法定量测量结果的一致性评价[J].现代预防医学, 2007,34(17):3263-3266,3269.
|