Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (8): 1188-1195.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1082
Previous Articles Next Articles
Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics
Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan
- Orthopedic Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2019-03-18Published:2019-03-18 -
Contact:Shi Chenhui, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Orthopedic Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Wang Weishan, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Orthopedic Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Qiu Zhongpeng, Attending physician, Orthopedic Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660374 (to SCH), and 81760404 (to WWS); the Corps Young and Middle-Aged Science and Technology Innovation Leading Talent Construction Project, No. 2016BC001 (to WWS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan. Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1188-1195.
share this article
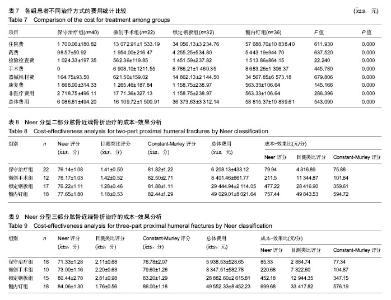
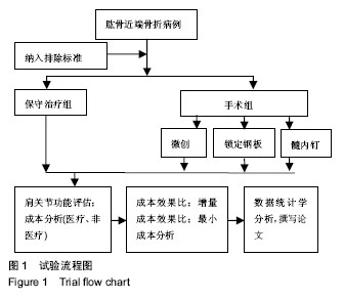
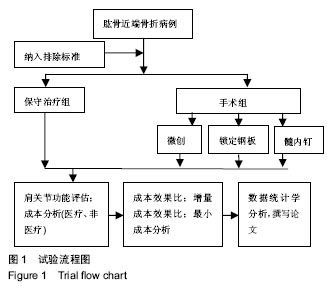
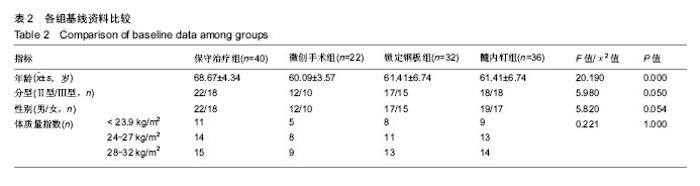
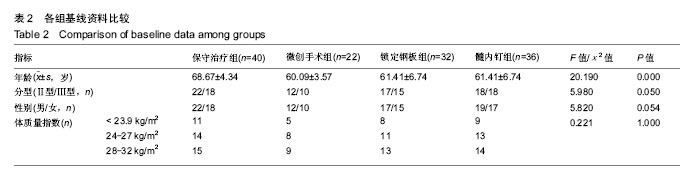
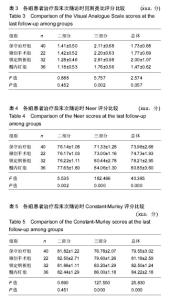
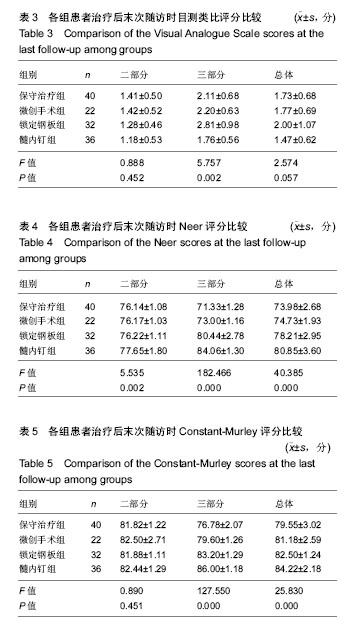
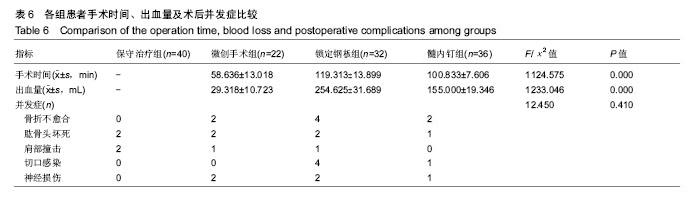
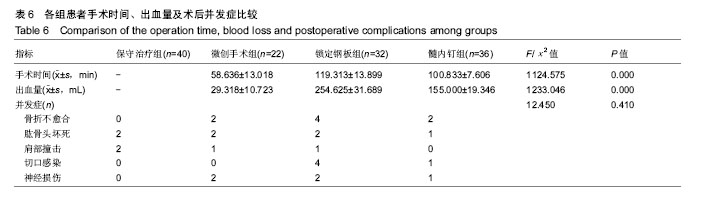
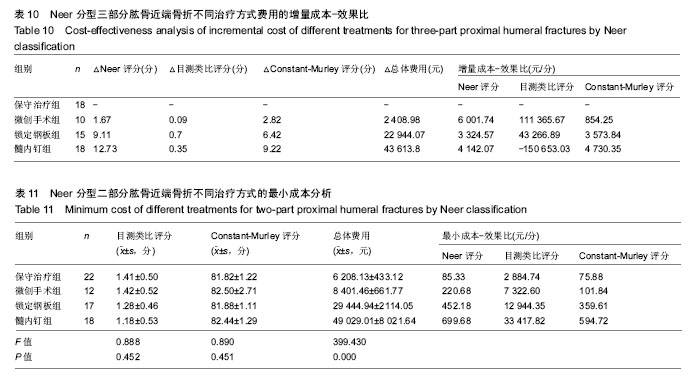
2.5 并发症及生物相容性情况 1年内4组手术干预组并发症明显高于保守治疗组,见表6。 骨折不愈合:微创手术组有2例患者为老年合并骨质疏松患者,骨折不愈合考虑与患者本身骨质疏松,肩关节制动时间不够,不恰当功能锻炼造成。锁定钢板组4例患者骨折未愈合,其中2例发生脱钉,考虑骨折断端未能形成坚强固定制动,严重骨质疏松内固定置入材料选择不当导致;另2例患者考虑手术过程中反复复位,骨折断端周围骨膜剥离过多,肱骨近端血运破坏严重引起。髓内钉组2例患者,其中1例术中计划使用锁定钢板固定,术中更改为髓内钉固定,骨折处血运破坏较重引起;另外1例骨折不愈合,考虑与患者合并糖尿病、骨质疏松多种基础疾病有关。 肱骨头坏死:保守治疗组2例考虑与患者骨折损伤旋肱前动脉的终末枝弓形动脉,以及本身基础疾病有关。微创手术组2例、锁定钢板组2例考虑术中反复复位,破坏肱骨近端血运导致。髓内钉固定组1例与术中操作破坏了肱骨近端血运有关。 肩部撞击并发症:保守治疗组2例考虑手法复位不满意,及局部血肿机化导致。微创手术组1例患者肩缝撞击考虑术中复位不确切及肩峰下血肿机化导致。锁定钢板组1例患者与锁定钢板放置位置不恰当及肩峰处创伤后骨性关节炎有关。髓内钉组患者肩缝撞击综合征考虑与患者术中对肩袖损伤、髓内钉尾帽凸起等原因有关。 切口感染并发症:锁定钢板组4例考虑手术过程创面暴露时间长,术中使用电刀导致脂肪液化坏死,患者合并糖尿病等基础病及自身免疫力等原因导致。髓内钉组1例感染考虑手术持续时间长,术野暴露时间长导致。 神经损伤:微创手术组2例考虑术后置入克氏针临时固定时损伤。锁定钢板组2例考虑术中钢板置入不服帖、过度牵拉、骨折后参照系统不准导致。髓内钉组1例考虑术中肩关节复位过度牵拉及克氏针临时固定时损伤,为预防腋神经损伤,应注意轻柔操作、争取良好复位、注意内固定服帖置入,同时重视术前查体,必要时电生理检查术前术后排除腋神经损伤。术后确诊神经损伤后给予患者营养神经药物对症治疗,在术后1年的随访时间里患者三角肌表面皮肤感觉障碍感觉恢复满意度较低,肩外展功能未见明显受损。 Chowdary等[11]报道50例患者中有8例出现术后并发症,并发症发生率为16%;Matejci?等[12]报道患者随访14-36个月,总并发症发生率为27.1%;Sproul等[13]报道锁定钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折术后并发症发生率为49%,常见的并发症有内翻畸形愈合(16%)、肱骨头缺血性坏死(10%)、螺钉穿出肱骨头(8%)。此次研究中,患者总并发症发生率为22%,与文献报道相比并发症发生率较高,考虑与手术医生操作熟练程度、患者本身基础疾病、内固定材料选择、治疗方案选择及患者术后康复等因素相关。 此次研究中的3种植入物生物相容性良好,各组患者均未出现植入物周围感染、过敏反应、免疫反应及排斥反应。 2.6 费用统计 见表7。 此次研究中5例患者再次入院,其中微创手术组内固定克氏针脱落1例,锁定钢板组创面感染4例入院给予清创手术治疗。1年内微创手术组、锁定钢板组、髓内钉组总体费用均高于保守治疗组(P=0.000),各手术干预组的非医疗费用和康复费用较保守治疗组明显偏低,其中非医疗费用主要包含家庭护理费用,保守治疗组患者院外康复及关节制动时间较长,是家庭护理费用高的原因;手术干预组的制动时间短,康复时间也短,是非医疗费用及康复费用花费较少的原因。 2.7 成本-效果分析、增量成本效果比 对于Neer二部分肱骨近端骨折,各手术干预组与保守治疗组疗效差异无显著性意义,但保守治疗组患者治疗支付成本更低,提示Neer二部分肱骨近端骨折采取保守治疗是更经济、有效的治疗方案,见表8。 Neer三部分肱骨近端骨折,各手术干预组治疗效果优于保守治疗组,但手术干预组患者治疗支付成本比保守治疗组更高,见表9。 根据增量成本-效果比结果,对于Neer 分型三部分肱骨近端骨折,微创手术组、锁定钢板组、髓内钉组患者肩关节功能Constant-Murley评分每提高1分需分别花费854.25,3 573.84,4730.35元,见表10。 "
| [1] Südkamp N, Bayer J, Hepp P, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with use of the locking proximal humerus plate. Results of a prospective, multicenter, observational study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;91(6):85-95.[2] Burkhart KJ, Dietz SO, Bastian L, et al. The treatment of proximal humeral fracture in adults. Deutsch Arztebl Int. 2013;110(35-36):591.[3] 卡纳莱. 坎贝尔骨科手术学[M]. 北京:人民军医出版社, 2013.[4] 赵星,储伟,祝少博. 肱骨近端骨折的手术治疗方案及研究进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2017, 11(7):1221-1226.[5] 俞思祎,姜海涛,李四波,等. 肱骨近端骨折治疗进展[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2018,27(16):1819-1822.[6] 李大鹏,吴燕,岳佳伟,等. PHILOS接骨板治疗47例NeerⅡ、Ⅲ部分肱骨近端骨折的临床研究[J]. 重庆医学,2017,46(32):4511-4513.[7] 熊杰鹏,王静成,颜连启. 骨质疏松性肱骨近端骨折治疗的研究进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2017 11(5):788-793.[8] Von KA, Vrahas MS, Weaver MJ. Surgical versus nonsurgical treatment of adults with displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: the profher randomized clinical trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(4):e143.[9] 吴欣,程薇,赵丽颖. 总额预付影响供方行为的经济学分析[J]. 医学与社会, 2013, 26(2):52-54.[10] 贾柯,徐克武,胡翔. 老年肱骨近端骨折分部分及临床治疗进展[J]. 中医正骨, 2017, 29(3):24-27.[11] Chowdary U, Prasad H, Subramanyam PK. Outcome of locking compression plating for proximal humeral fractures: a prospective study. J Orthop Surg. 2014;22(1):4-8.[12] Matejci? A, Vidovi? D, Ivica M, et al. Internal fixation with locking plate of 3- and 4-part proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: complications and functional outcome. Acta Clinica Croatica. 2013;52(1):17-22.[13] Sproul RC, Iyengar JJ, Devcic Z, et al. A systematic review of locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Injury. 2011; 42(4):408-413.[14] Whiting PS. Fractures of the Proximal Humerus[M]// Orthopaedic Trauma in the Austere Environment. Springer International Publishing, 2016.[15] 李洪飞.手术与非手术治疗肱骨近端骨折疗效对比分析[J].中国卫生产业,2014,11(29):154-155.[16] 李强,王跃文,包毅敏,等. 高龄患者肱骨近端3、4部分骨折内固定治疗与非手术治疗疗效的系统评价[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2015, 23(12):1072-1077.[17] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 关于开展基本医疗保险付费总额控制的意见[J]. 中国实用乡村医生杂志, 2013,20(12):22-25.[18] Kelley R. Where can $700 billion in waste be cut annually from the u.s. healthcare system? Thompson Reuters White Paper, 2009: 1-29.[19] 邵蓉,唐吉锋,施孝金,等. 总额预付制下医保费用管理措施对医疗服务行为影响[J]. 中国医院管理, 2016, 36(7):19-22.[20] Madrid I, Velázquez G, Fefer E. Pharmaceuticals and health sector reform in the Americas: an economic perspective. Revista Panamericana De Salud Pública. 1998; 3(5):343-350.[21] Ford ES, Ajani UA, Croft JB, et al. Explaining the decrease in U.S. deaths from coronary disease, 1980-2000. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356(23):2388-2398.[22] Zyto K. Non-operative treatment of comminuted fractures of the proximal humerus in elderly patients. Injury. 1998;29(5):349-352.[23] Gaebler C, Mcqueen MM, Court-Brown CM. Minimally displaced proximal humeral fractures: epidemiology and outcome in 507 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74(5):580-585.[24] Koval KJ, Gallagher MA, Marsicano JG, et al. Functional outcome after minimally displaced fractures of the proximal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(2):203-207.[25] Habermeyer P. [Fracture of the head of the humerus]. Der Unfallchirurg. 1997; 100(10):820-837.[26] Corbacho B, Duarte A, Keding A, et al. Cost effectiveness of surgical versus non-surgical treatment of adults with displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: economic evaluation alongside the PROFHER trial. Bone Joint J. 2016; 98-B(2):152.[27] Krieg JC. Surgical and Nonsurgical Treatment Produced Similar Outcomes for Proximal Humeral Fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(22):1890. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Li Jun, Zuo Xinhui, Liu Xiaoyuan, Zhang Kai, Han Xiangzhen, He Huiyu, . Effect of over expression of miR-378a on osteogenic and vascular differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheet [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4939-4944. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||