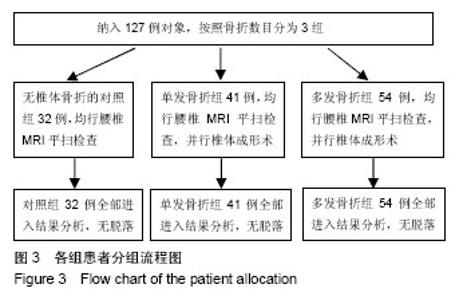
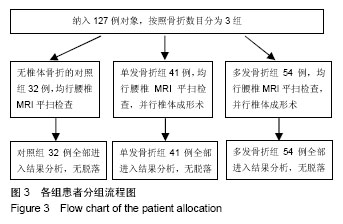
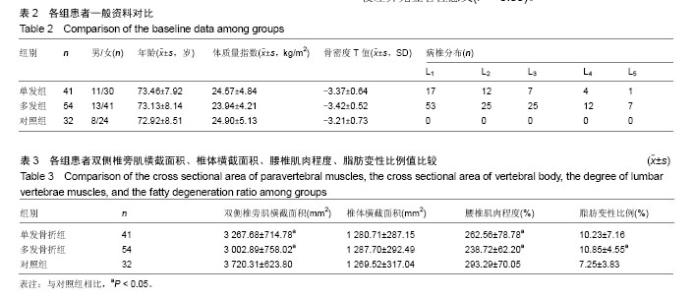
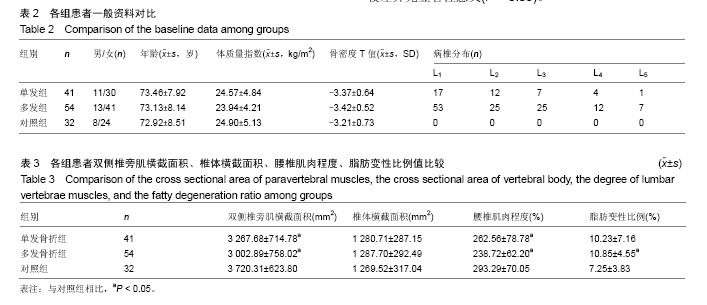
| [1] 国务院人口普查办公室.中国2010年人口普查资料[M].北京:中国统计出版社,2012.[2] Zeytinoglu M, Jain RK, Vokes TJ. Vertebral fracture assessment: Enhancing the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of osteoporosis. Bone. 2017;104:54-65. [3] Al-Sari UA, Tobias J, Clark E. Health-related quality of life in older people with osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(10):2891-2900. [4] Andrei D, Popa I, Brad S, et al. The variability of vertebral body volume and pain associated with osteoporotic vertebral fractures: conservative treatment versus percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty. Int Orthop. 2017;41(5):1-6. [5] Svensson HK, Olofsson EH, Karlsson J, et al. A painful, never ending story: older women’s experiences of living with an osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(5):1-8. [6] Edidin AA, Ong KL, Lau E, et al. Mortality risk for operated and nonoperated vertebral fracture patients in the medicare population J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(7):1617–1626. [7] 叶龙,陈林,吕龙龙,等.绝经后女性骨质疏松性椎体骨折与腰椎体骨密度的相关性[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(6):771-776.[8] Katzman WB, Vittinghoff E, Kado DM, et al. Thoracic kyphosis and rate of incident vertebral fractures: the Fracture Intervention Trial. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(3):899-903. [9] 曹威,朱秀芬,陈新,等.老年人群骨质疏松性骨折与跌倒风险的相关性[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(4):353-358.[10] Jun HS, Kim JH, Ahn JH, et al. The effect of lumbar spinal muscle on spinal sagittal alignment: evaluating muscle quantity and quality. Neurosurgery. 2016;79(6):847. [11] Ismail AA, Cooper C, Felsenberg D, et al. Number and type of vertebral deformities: epidemiological characteristics and relation to back pain and height loss. European Vertebral Osteoporosis Study Group. Osteoporos Int. 1999;9(3):206-213. [12] Genant HK, Wu CY, Van KC, et al. Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res. 1993;8(9): 1137-1148. [13] Cauley JA. Osteoporosis: fracture epidemiology update 2016. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(2):150. [14] Kostuik JP. Anterior kostuik-harrington distraction systems for the treament of kyphotic deformities. Spine. 1990;15(3):169-180. [15] Ross PD. Osteoporosis. Frequency, consequences, and risk factors. Arch Int Med. 1996;156(13):1399-1411. [16] 吴继功.HA/PMMA复合活性骨水泥椎体成形的实验和临床研究[D].广州:第一军医大学,2004.[17] Silva MJ, Keaveny TM, Hayes WC. Load sharing between the shell and centrum in the lumbar vertebral body. Spine.1997; 22(2):140. [18] Leech JA, Dulberg C, Kellie S, et al. Relationship of lung function to severity of osteoporosis in women. Am Rev Respir Dis. 2012; 141(1):68. [19] 唐正午,戴祝,陈志伟,等.绝经后女性股骨近端骨密度与骨质疏松性骨折相关性研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,20(12):1447-1449.[20] Lambrinoudaki I, Flokatoula M, Armeni E, et al. Vertebral fracture prevalence among Greek healthy middle-aged postmenopausal women: association with demographics, anthropometric parameters, and bone mineral density. Spine J. 2015;15(1):86-94. [21] Gómez-De-Tejada Romero MJ, Navarro Rodríguez MD, Saavedra SP, et al. Prevalence of osteoporosis, vertebral fractures and hypovitaminosis D in postmenopausal women living in a rural environment. Maturitas. 2014;77(3):282-286. [22] Patel PJ, Bhatt T. Does aging with a cortical lesion increase fall-risk: Examining effect of age versus stroke on intensity modulation of reactive balance responses from slip-like perturbations. Neuroscience. 2016;333:252-263. [23] Scott D, Hayes A, Sanders KM, et al. Operational definitions of sarcopenia and their associations with 5-year changes in falls risk in community-dwelling middle-aged and older adults. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(1):187. [24] Hida T, Shimokata H, Sakai Y, et al. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic leg as potential risk factors for acute osteoporotic vertebral fracture among older women. Eur Spine J. 2015;25(11):1-8. [25] Melzer I, Oddsson LI. Altered characteristics of balance control in obese older adults. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2016;10(2):151-158. [26] 王亮,马远征,张妍,等.北京海淀地区中老年妇女骨质疏松性骨折情况调查研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(5):580-582.[27] 张义龙,孙志杰,王雅辉,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折:椎体骨折数目和C_7矢状位比值的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(22): 3315-3321.[28] 韦祎,田伟,张贵林,等.绝经期女性胸腰椎后凸与椎体压缩骨折相关性分析[J].临床军医杂志,2016,44(7):728-730.[29] Bruno AG, Anderson DE, D'agostino J, et al. The effect of thoracic kyphosis and sagittal plane alignment on vertebral compressive loading. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(10):2144-2151. [30] van der Jagt-Willems HC, de Groot MH, van Campen JP, et al. Associations between vertebral fractures, increased thoracic kyphosis, a flexed posture and falls in older adults: a prospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2015;15(1):1-6. [31] Hultman G, Nordin M, Saraste H, et al. Body composition, endurance, strength, cross-sectional area, and density of MM erector spinae in men with and without low back pain. J Spinal Disord. 1993;6(2):114. [32] Anderson D, Allaire B, Bruno A, et al. Low trunk muscle density is associated with prevalent vertebral fractures in older adults. Meeting of the American-Society-For-Bone-And-Mineral-Research, 2013. [33] Mokhtarzadeh H, Anderson DE. The Role of Trunk Musculature in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures: Implications for Prediction, Prevention, and Management. Curr Osteoporos Reports. 2016; 14(3): 67. [34] Sinaki M, Itoi E, Wahner HW, et al. Stronger back muscles reduce the incidence of vertebral fractures: a prospective 10 year follow-up of postmenopausal women. Bone. 2002;30(6):836-841. [35] Panjabi MM. The stabilizing system of the spine. Part II. Neutral zone and instability hypothesis. J Spinal Disord. 1992;5(4):383. [36] Zazulak BT, Hewett TE, Reeves NP, et al. The effects of core proprioception on knee injury: a prospective biomechanical- epidemiological study. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):368. [37] Borghuis J, Hof AL, Lemmink KA. The importance of sensory-motor control in providing core stability: implications for measurement and training. Sports Med. 2008;38(11):893-916. [38] 王雪鹏,王圣杰,晏鹏,等.椎旁肌肉损伤对腰椎椎体骨质量的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2016,96(43):3515-3518.[39] Lescher S, Bender B, Eifler R, et al. Isometric non-machine-based prevention training program: effects on the cross-sectional area of the paravertebral muscles on magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Neuroradiol. 2011;21(4):217-222. |