| [1] Charnley J, Feagin JA. Low-friction arthroplasty in congenital subluxation of the hip. Clin Orthop. 1973;(91):98-113.
[2] Sochart DH, Porter ML. The long-term results of Charnley low-friction arthroplasty in young patients who have congenital dislocation, degenerative osteoarthrosis, or rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(11): 1599-1617.
[3] Harris WH, Crothers O, Oh I. Total hip replacement and femoralhead bone-grafting for severe acetabular deformity in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59(6):752-759.
[4] Pagnano MW, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG, et al. The effect of superior placement of the acetabular component on the rate of loosening after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(7):1004-1014.
[5] Becker DA, Gustilo RB. Double-chevron subtrochanteric shortening derotational osteotomy combined with total hip arthroplasty for treatment of complete congenital dislocation of the hip in the adult. J Arthroplasty. 1995;10(3): 313-318.
[6] Reikeraas O, Lereim P, Gabor I, et al. Femoral shortening in total arthroplasty for completely dislocated hips: 3–7 years results in 25 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996; 67(1): 33-36.
[7] Eskelinen A, Helenius I, Remes V, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients with high congenital hip dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(1):80-91.
[8] Makita H, Inaba Y, Hirakawa K, et al. Results on total hip arthroplasties with femoral shortening for Crowe's group IV dislocated hips. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(1):32-38.
[9] Linde F, Jensen J. Socket loosening in arthroplasty for congenital dislocation of the hip. Acta Orthop Scand. 1988; 59(3):254-257.
[10] Hartofilakidis G, Stamos K, Ioannidis TT. Low-friction arthroplasty for old untreated congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988;70(2):182-186.
[11] Hartofilakidis G, Karachalios T. Total hip arthroplasty for congenital hip disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(2): 242-250.
[12] Pagnano MW, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG, et al. The effect of superior placement of the acetabular component on the rate of loosening after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1996;78(7):1004-1014.
[13] Yoder SA, Brand RA, Pedersen DR, et al. Total hip acetabular component position affects component loosening rates. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;(228):79-87.
[14] Symeonides PP, Pournaras J, Petsatodes G, et al. Total hip arthroplasty in neglected congenital dislocation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1997;(341):55-61.
[15] Reikeeraas O, Lereim P, Gabor I, et al. Femoral short ening in total arthroplasty for completely dislocated hips: 3-7 year result s in 25 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996;67(1):33-36.
[16] Baz AB, Senol V, Akalin S, et al. Treatment of high hip dislocation with a cementless stem combined with a shortening osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132 (10):1481-1486.
[17] Sonohata M, Tajima T, Kitajima M, et al. Total hip arthroplasty combined with double-chevron subtrochanteric osteotomy. J Orthop Sci. 2012;17(4):382-389.
[18] Macheras GS, Kateros K, Koutsostathis SD,et al.The Trabecular Metal Monoblock acetabular component in patients with high congenital hip dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(5):624-628.
[19] Stans AA, Pagnano MW, Shaughnessy WJ, et al. Results of total hip arthroplasty for Crowe Type III developmental hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(348):149-157.
[20] Yoder SA, Brand RA, Pedersen DR, et al. Total hip acetabular component position affects component loosening rates. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;(228):79-87.
[21] Lai KA, Shen WJ, Huang LW, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty and limb-length equalization in patients with unilateral Crowe type-IV hip dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(2):339-345.
[22] Lewallen DG. Neurovascular injury associated with hip arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 1988;47:275-283.
[23] Edwards BN, Tullos HS, Noble PC. Contributory factors and etiology of sciatic nerve palsy in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop. 1987;(218):136-141.
[24] Tanoue M, Yamaga M, Ide J, et al. Acute stretching of peripheral nerve inhibits retrograde axonal transport. J Hand Surg Br. 1996;21(3):358-363.
[25] Kiliço?lu O?, Türker M, Akgül T, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty with modified oblique femoral shortening osteotomy in Crowe type IV congenital hip dislocation. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(1):117-125.
[26] Akiyama H, Kawanabe K, Yamamoto K, et al. Cemented total hip arthroplasty with subtrochanteric femoral shortening transverse osteotomy for severely dislocated hips: outcome with a 3- to 10-year follow-up period. J Orthop Sci. 2011;16(3): 270-277.
[27] Eggli S, Hankemayer S, Müller ME. Nerve palsy after leg lengthening in total replacement arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(5):843-845.
[28] Hartofilakidis G, Babis GC, Georgiades G, et al. Trochanteric osteotomy in total hip replacement for congenital hip disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(5):601-607.
[29] Koulouvaris P, Stafylas K, Sculco T, et al. Distal femoral shortening in totalhip arthroplasty for complex primary hip reconstruction: a new surgical technique. J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23(7):992-998.
[30] Anwar MM, Sugano N, Masuhara K, et al. Total hip arthroplasty in the neglected congenital dislocation of the hip. A five- to 14-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (295):127-134.
[31] Kilicarslan K, Yalcin N, Cicek H, et al. What happens at the adjacent knee joint after total hip arthroplasty of Crowe type III and IV dysplastic hips? J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(2):266-270.
[32] Whiteside LA, Arima J, White SE, et al. Fixation of the modular total hip femoral component in cementless total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(298):184-190.
[33] Cameron HU. Management of femoral deformities during the total hip replacement. Contemp Orthop. 1996;19(9):745-746.
[34] Bernasek TL, Haidukewych GJ, Gustke KA, et al. Total hip arthroplasty requiring subtrochanteric osteotomy for developmental hip dysplasia: 5- to 14-year results. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(6 Suppl 2):145-150.
[35] Onodera S, Majima T, Ito H, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty using the modular S-ROM prosthesis combined with corrective proximal femoral osteotomy. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(5):664-669.
[36] Masonis JL, Patel JV, Miu A, et al. Subtrochanteric shortening and derotational osteotomy in primary total hip arthroplasty for patients with severe hip dysplasia: 5-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(3 Suppl 1):68-73.
[37] Takao M, Ohzono K, Nishii T, et al. Cementless modular total hip arthroplasty with subtrochanteric shortening osteotomy for hips with developmental dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(6):548-555.
[38] Dallari D, Pignatti G, Stagni C, et al. Total hip arthroplasty with shortening osteotomy in congenital major hip dislocation sequelae. Orthopedics. 2011;34(8):e328-333.
[39] Crowe JF, Mani VJ, Ranawat CS. Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61(1):15-23.
[40] State Council of the People's Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01. |
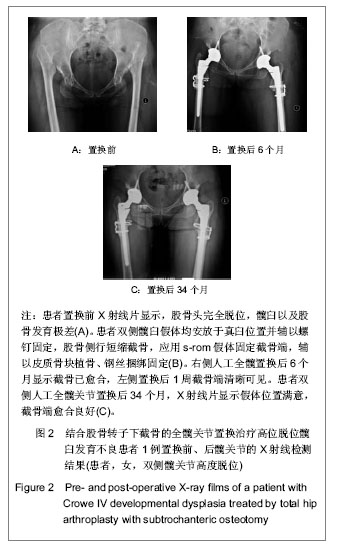
.jpg)
.jpg)