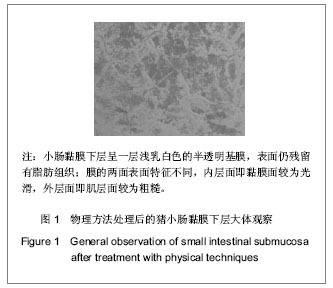
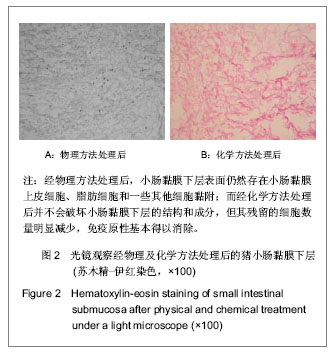
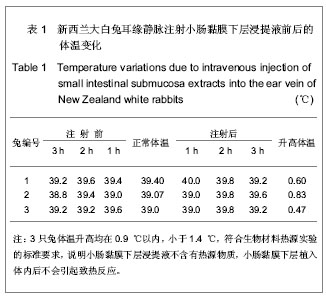
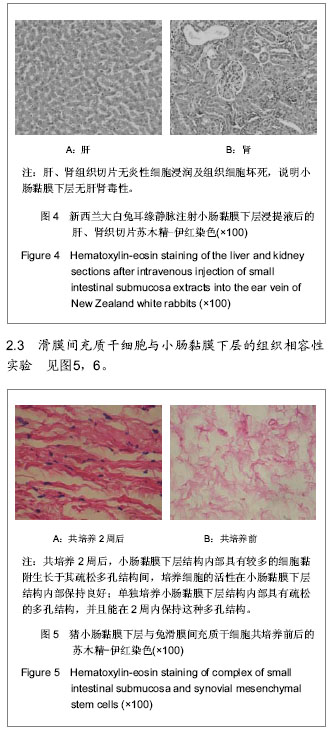
| [1] 吴海山,徐青镭.膝半月板外科与组织工程学重建[M].上海: 第二军医大学出版社, 1999.
[2] Allman AJ,McPherson TB,Badylak SF,et al.Xenogeneic extracellular matrix grafts elicit a TH2-restricted immune response. Transplantation.2001; 71(11): 1631-1640.
[3] Sarikaya A,Record R,Wu CC,et al.Antimicrobial activity associated with extracellular matrices. Tissue Eng.2002;8(1): 63-71.
[4] Grimes M, Pembroke JT, McGloughlin T. The effect of choice of sterilisation method on the biocompatibility and biodegradability of SIS (small intestinal submucosa). Biomed Mater Eng.2005;15(1-2): 65-71.
[5] Roeder R,Wolfe J,Lianakis N,et al.Compliance, elastic modulus, and burst pressure of small-intestine submucosa (SIS) small-diameter vascular grafts. Boimed Mater Res. 1999;47: 65-70.
[6] Cook JL,Fox DB,Malaviya P,et al.Evaluation of small intestinal submucosa grafts for meniscal regeneration in a clinically relevant posterior meniscectomy model in dogs.J Knee Surg. 2006;19(3):159-167.
[7] 祝云利,荆鑫,缪志和,等.纤维软骨细胞-胶原复合物修复半月板损伤的实验研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2002,27(1): 20-21.
[8] 徐青镭,万年宇,吴海山,等.兔骨髓干细胞向软骨细胞分化用于半月板组织工程重建[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(6): 912-913.
[9] Kobayashi M,Chang YS,Oka M.A two year in vivo study of polyvinyl alcohol-hydrogel (PVA-H) artificial meniscus. Biomaterials.2005;26: 3243-3248.
[10] Bejjani GK,Zabramski J,Durasis Study Group.Safety and efficacy of the porcine small intestinal submucosa dural substitute: results of a prospective multicenter study and literature review. J Neurosurg.2007; 106(6): 1028-1033.
[11] Lawrence BJ,Maase EL,Lin HK,et al.Multilayer composite scaffolds with mechanical properties similar to small intestinal submucosa. J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;88(3): 634-643.
[12] Roeder RA,Lantz GC,Geddes LA.Mechanical remodeling of small-intestine submucosa small-diameter vascular grafts-a preliminary report. Biomed Instrum Technol.2001;35(2): 110-120.
[13] Hadlock TA,Sundback CA,Huntar DA,et al.A new artificial nerve graft containing rolled Schwann cell monolayers. Microsurgery.2001;21(3): 96-101.
[14] Keskin M,Kelly CP,Moreira-Gonzalez A,et al.Repairing critical-sized rat calvarial defects with a periosteal cell-seeded small intestinal submucosal layer. Plast Reconstr Surg.2008; 122(2): 400-409.
[15] Welch JA,Montgomery RD,Lenz SD,et al.Evaluation of small-intestinal submucosa implants for repair of meniscal defects in dogs. Am J Vet Res. 2002;63(3): 427-431.
[16] Prilbitkin EA,Ambro BT,Bloeden E,et al.Rabbit ear cartilage regeneration with a small intestinal submucosa graft. Laryngoscope.2004;114(9 Pt 2 Suppl 102):1-19.
[17] Murphy KD,Mushkudiani IA,Kao D,et al.Successful incorporation of tissue-engineered porcine small-intestinal submucosa as substitute flexor tendon graft is mediated by elevated TGF-beta1 expression in the rabbit. J Hand Surg Am.2008;33(7): 1168-1178.
[18] Derwin K,Androjna C,Spencer E,et al.Porcine small intestine submucosa as a flexor tendon graft. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;423: 245-252.
[19] Musahl V,Abramowitch SD,Gilbert TW,et al.The use of porcine small intestinal submucosa to enhance the healing of the medial collateral ligament--a functional tissue engineering study in rabbits. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(1): 214-220.
[20] Dejardin LM,Arnoczky SP,Ewers BJ,et al.Tissue-engineered rotator cuff tendon using porcine small intestine submucosa: histologic and mechanical evaluation in dogs. Am J Sports Med.200l;29(2):175-184.
[21] Aiken SW,Badylak SF,Toombs JP,et al.Small intestinal submucosa as an intra-articular ligamentous graft material: A pilot study in dogs. Vet Comp Orthoped Traumatol.1994;7: 124-136.
[22] Nihsen ES,Johnson CE,Hiles MC,et a1.Bioactivity of small intestinal submucosa and oxidized regenerated cellulose/collagen. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2008;21(10): 479-486.
[23] Suckow MA,voytik-Harbin SL,Terril LA,et al.Enhanced bone regeneration using porcine small intestinal submucosa. J Invest Surg. 1999;12: 277-287.
[24] Cook JL,Tomlinson JL,Arnoczky SP,et al.Kinetic study of the replacement of porcine small intestinal submucosa grafts and the regeneration of meniscal-like tissue in large avascular meniscal defects in dogs. Tissue Eng.2001;7(3): 321-334.
[25] Rosen M,Ponsky J,Petras R,et al.Small intestinal submucosa as a bioscaffold for biliary tract regeneration. Surgery.2002; 132(3): 480-486.
[26] Record RD,Hillegonds D,Simmons C,et al.In vivo degradation of 14C-labeled small intestinal submucosa(SIS) when used for urinary bladder repair. Biomaterials.2001;22(19): 2653-2659.
[27] Hodde JP,Record RD,Liang HA,et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor in porcine-derived extracellular matrix. Endothelium. 2001;8(1): 11-24.
[28] Voytik-Harbin SL,Brightman AO,Kraine MR,et al.Identification of extractable growth factors from small intestinal submucosa. J Cell Biochem. 1997;67(4): 478-491.
[29] Mcpherson TB,Stephen F.Characterization of fibronectin derived from porcine small intestinal submucosa. Tissue Eng. 1998;4(1): 75-83.
[30] Hodde J,Hiles M. Bioactive FGF-2 in sterilized extracellular matrix. Wounds. 2001;13(5): 195-201.
[31] Abraham GA,Murray J,Billiar K,et al.Evaluation of the porcine intestinal collagen layer as a biomaterial.J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51(3): 442-452. |