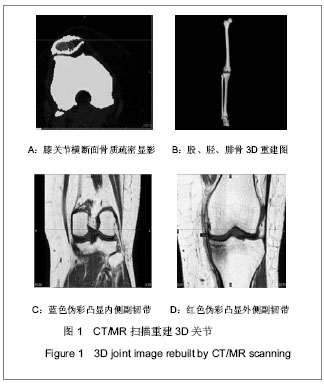
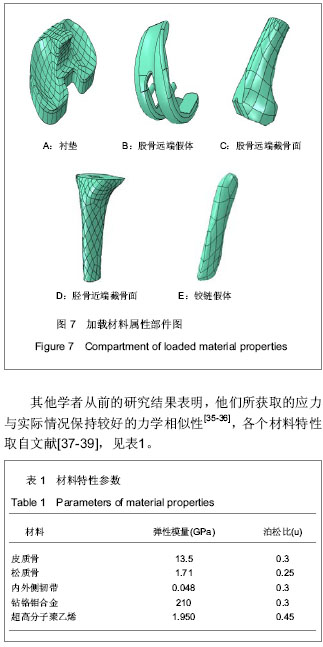
| [1] Goto K, Tajima N, Chosa E,et al. Mechanical analysis of the lumbar vertebrae in a three-dimensional finite element method model in which intradiscal pressure in the nucleus pulposus was used to establish the model. J Orthop Sci. 2002; 7(2):243-246.[2] Seki N, Itoi E, Shibuya Y,et al. Mechanical environment of the supraspinatus tendon: three-dimensional finite element model analysis.J Orthop Sci. 2008;13(4):348-353.[3] Wagner A, Krach W, Schicho K,et al. A 3-dimensional finite-element analysis investigating the biomechanical behavior of the mandible and plate osteosynthesis in cases of fractures of the condylar process.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;94(6):678-686.[4] Wakabayashi I, Itoi E, Sano H,et al. Mechanical environment of the supraspinatus tendon: a two-dimensional finite element model analysis.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(6):612-617.[5] Nabhani F, Sotudeh R, Hart AN, et al. 2D stress analysis of the human patella using the finite element approach. In: Middleton J, Jones ML, Pande GN, editors.Computer methods in biomechanics and biomedical engineering. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Gordon and Breach Science Publishers SA.1996:197.[6] Chien WL, Lo CC, Wang CS, et al. Evaluation and analysis of the onlay patellar component in total knee arthroplasty. Adv Materials Res. 2010;97-101:3773.[7] Shashishekar C, Ramesh CS. Finite element analysis of prosthetic knee joint using ANSYS. Biomed Health. 2007; 12: 65.[8] Yosibash Z, Padan R, Joskowicz L,et al. A CT-based high-order finite element analysis of the human proximal femur compared to in-vitro experiments.J Biomech Eng. 2007; 129(3):297-309.[9] Yosibash Z, Trabelsi N, Milgrom C.Reliable simulations of the human proximal femur by high-order finite element analysis validated by experimental observations.J Biomech. 2007;40 (16):3688-3699.[10] Orwoll ES, Marshall LM, Nielson CM,et al. Finite element analysis of the proximal femur and hip fracture risk in older men.J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(3):475-483. [11] Bougherara H, Zdero R, Miric M,et al.The biomechanics of the T2 femoral nailing system: a comparison of synthetic femurs withfinite element analysis.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2009; 223(3):303-314.[12] Simpson DJ, Brown CJ, Yettram AL,et al. Finite element analysis of intramedullary devices: the effect of the gap between the implant and the bone.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(3):333-345.[13] Lin CL, Wang JC, Chang SH,et al.Evaluation of stress induced by implant type, number of splinted teeth, and variations in periodontal support in tooth-implant-supported fixed partial dentures: a non-linear finite element analysis.J Periodontol. 2010;81(1):121-130.[14] Kitamura E, Stegaroiu R, Nomura S,et al.Biomechanical aspects of marginal bone resorption around osseointegrated implants: considerations based on a three-dimensional finite element analysis.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004;15(4):401-412.[15] Chang CL, Chen CS, Hsu ML.Biomechanical effect of platform switching in implant dentistry: a three-dimensional finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010; 25(2):295-304.[16] Schrotenboer J, Tsao YP, Kinariwala V,et al. Effect of microthreads and platform switching on crestal bone stress levels: a finite element analysis.J Periodontol. 2008;79(11): 2166-2172.[17] Schrotenboer J, Tsao YP, Kinariwala V,et al.Effect of platform switching on implant crest bone stress: a finite element analysis. Implant Dent. 2009;18(3):260-269. [18] Huang CC, Lan TH, Lee HE,et al.The biomechanical analysis of relative position between implant and alveolar bone: finite element method.J Periodontol. 2011;82(3):489-496.[19] Wang TM, Leu LJ, Wang J,et al. Effects of prosthesis materials and prosthesis splinting on peri-implant bone stress around implants in poor-quality bone: a numeric analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002;17(2):231-237.[20] Sütpideler M, Eckert SE, Zobitz M,et al. Finite element analysis of effect of prosthesis height, angle of force application, and implant offset on supporting bone.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004;19(6):819-825.[21] Geng JP, Tan KB, Liu GR.Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: a review of the literature.J Prosthet Dent. 2001;85(6):585-598.[22] Nagasawa S, Hayano K, Niino T,et al.Nonlinear stress analysis of titanium implants by finite element method.Dent Mater J. 2008;27(4):633-639.[23] Qian L, Todo M, Matsushita Y,et al. Effects of implant diameter, insertion depth, and loading angle on stress/strain fields in implant/jawbone systems: finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(5):877-886.[24] Lin CL, Chang SH, Chang WJ,et al. Factorial analysis of variables influencing mechanical characteristics of a single tooth implant placed in the maxilla using finite element analysis and the statistics-based Taguchi method.Eur J Oral Sci. 2007;115(5):408-416.[25] Alikhasi M, Siadat H, Geramy A,et al.Stress distribution around maxillary anterior implants as a factor of labial bone thickness and occlusal load angles: a 3D-finite-element analysis.J Oral Implantol. 2011. [Epub ahead of print][26] Ormianer Z, Palti A, Demiralp B,et al. Implant-supported first molar restorations: correlation of finite element analysis with clinical outcomes.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27(1): e1-12.[27] Gupte CM, Bull AM, Thomas RD,et al.The meniscofemoral ligaments: secondary restraints to the posterior drawer. Analysis of anteroposterior and rotary laxity in the intact and posterior-cruciate-deficient knee.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85(5):765-773.[28] Lee KK, Teo EC, Fuss FK,et al. Finite-element analysis for lumbar interbody fusion under axial loading.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2004;51(3):393-400.[29] Polikeit A, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP,et al.Factors influencing stresses in the lumbar spine after the insertion of intervertebral cages: finite element analysis.Eur Spine J. 2003;12(4):413-420.[30] Li XF, Dai LY.Three-dimensional finite element model of the cervical spinal cord: preliminary results of injury mechanism analysis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(11):1140-1147.[31] García JM, Doblaré M, Seral B,et al.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of several internal and external pelvis fixations. J Biomech Eng. 2000;122(5):516-522.[32] 李孝林.基于CT图像应用Mimics软件快速构建人体胸腰段骨骼有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(39): 7619-7622.[33] 唐先智,刘飞,李绪武,等.面向逆向工程的网络化共享应用系统的设计及应用[J].重庆大学学报,2009,32(5):339-356.[34] Feikes JD, O'Connor JJ, Zavatsky AB.A constraint-based approach to modelling the mobility of the human knee joint.J Biomech. 2003;36(1):125-129.[35] Peña E, Calvo B, Martínez MA,et al.A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the combined behavior of ligaments and menisci in the healthy human knee joint.J Biomech. 2006; 39(9):1686-1701.[36] Bendjaballah MZ, Shirazi-Adl A, Zukor DJ.Biomechanical response of the passive human knee joint under anterior-posterior forces.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1998; 13(8):625-633.[37] LeRoux MA, Setton LA. Experimental and biphasic FEM determinations of the material properties and hydraulic permeability of the meniscus in tension.J Biomech Eng. 2002; 124(3):315-321.[38] Li G, Lopez O, Rubash H.Variability of a three-dimensional finite element model constructed using magnetic resonance images of a knee for joint contact stress analysis.J Biomech Eng. 2001;123(4):341-346.[39] Mesfar W, Shirazi-Adl A. Biomechanics of the knee joint in flexion under various quadriceps forces.Knee. 2005;12(6): 424-434. [40] Brekelmans WA, Poort HW, Slooff TJ.A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts.Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317.[41] Matsuda S, White SE, Williams VG 2nd,et al. Contact stress analysis in meniscal bearing total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(6):699-706.[42] Shiramizu K, Vizesi F, Bruce W,et al.Tibiofemoral contact areas and pressures in six high flexion knees.Int Orthop. 2009; 33(2):403-406. [43] 王海鹏,容可,钟砚琳,等.膝关节周围韧带三维有限元模型的建立[J].上海交通大学学报,2008,28(4):367-370. |