Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (6): 955-961.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.06.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
Reduced-intensity conditioning regimen in HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Yang Ting1, Jiang Ming1
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Hematologic Disease Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Xinjiang Research Institute of Hematology, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2015-01-15Online:2015-02-05Published:2015-02-05 -
Contact:Jiang Ming, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Doctoral supervisor, Hematologic Disease Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Xinjiang Research Institute of Hematology, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yang Ting, Studying for master’s degree, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the High-Tech Projects of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 201317104
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Ting, Jiang Ming. Reduced-intensity conditioning regimen in HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(6): 955-961.
share this article
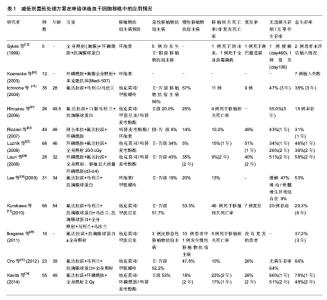
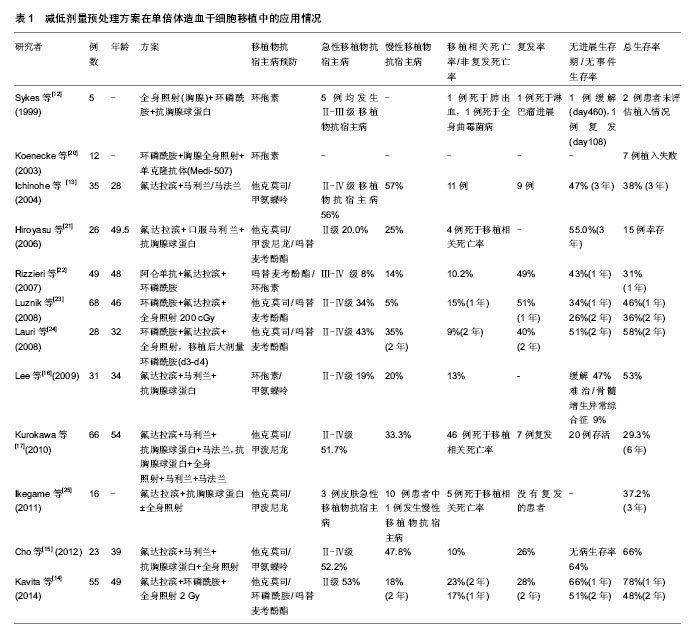
2.1 减低剂量预处理方案的发展演变 2.1.1 减低剂量预处理方案的产生 1997年Giralt等[1]对15例(13例急性髓细胞白血病、2例骨髓增生异常综合征)恶性血液病患者采用氟达拉滨120 mg/m2+阿糖胞苷8 g/m2+伊达比星36 mg/m2或氟达拉滨120 mg/m2+马法兰140 mg/m2或2-氯脱氧腺苷(2-CDA)60 mg/m2+阿糖胞苷5 g/m2的非清髓预处理方案(Nonmyeloablative conditioning regimen,NMC)行异基因造血干细胞移植,结果显示患者一般耐受性良好,植入较好(13例中性粒细胞绝对计数植入,10例血小板植入),开启了非清髓预处理方案时代,即不清除患者的免疫系统,通过移植前后的免疫抑制来克服宿主抗移植物反应,从而使移植物植入,在移植后早期形成混合嵌合状态,必要时在供者淋巴细胞输注的帮助下,依赖移植物抗宿主反应杀灭肿瘤细胞,同时逐渐清除宿主的造血成分,达到完全供体型嵌合。但由于复发和感染的原因(5例死于疾病复发,2例死于感染的后续治疗,1例死于多器官衰竭,1例死于曲霉病),只有1例患者在+170 d持续获得缓解。 1998年Slavin等[2]使用氟达拉滨180 mg/m2+口服马利兰4 mg/kg×2 d+抗胸腺球蛋白10 mg/kg×4 d的预处理方案在26例人类抗白细胞抗原(Human anti-leukocyte antigen,HLA)完全相合的恶性血液病同胞中移植,结果患者获得良好的植入,较好的长期无病生存率。由于该预处理方案中的药物剂量较1997年Giralt等[1]的药物剂量偏大,可能对部分患者也达到清髓的作用,但相对于传统的清髓预处理方案而言减低还是明显的,因此目前看Slavin的预处理方案应该是世界上首个比较成功进行异基因造血干细胞移植的减低剂量预处理方案。 2.1.2 减低剂量预处理方案的应用及发展 继1998年以后,非清髓预处理方案和减低剂量预处理方案如雨后春笋般出现,如Childs等[3]的FCy方案(氟达拉滨 125 mg/m2+环磷酰胺120 mg/kg)、Kottaridis等[4]的FMC方案(阿仑单抗100 mg/m2 +氟达拉滨 150 mg/m2 +马法兰140 mg/m2)、McSweeney等[5]的FT方案(全身照射 200 cGy或全身照射200 cGy+氟达拉滨90 mg/m2)、Giralt等[6]的FM方案(氟达拉滨120-125 mg/m2 +马法兰140-180 mg/m2),这些方案均取得一定的疗效。 2003年Mohty等[7]在101例HLA完全相合同胞高危患者中采用减低剂量预处理方案行异基因造血干细胞移植,其中46例患者使用FB2oralA4or3(氟达拉滨180 mg/m2+口服马利兰4 mg/kg×2 d+抗胸腺球蛋白2.5 mg/kg×4 d/ 3 d),55例患者使用FB2oralA1(氟达拉滨180 mg/m2+口服马利兰4 mg/kg×2 d+抗胸腺球蛋白2.5 mg/kg×1 d),结果发现相对标准的异基因造血干细胞移植而言以抗胸腺球蛋白为基础的减低剂量预处理造血干细胞移植相关感染死亡率较低,但急性移植物抗宿主病和慢性移植物抗宿主病及晚期侵袭性真菌感染仍较高。 随后Le Bourgeois等[8]将FB2oralA4方案修改FB1oralA2方案,即氟达拉滨120 mg/m2+口服马利兰× 1 d+抗胸腺球蛋白2.5 mg/kg×2 d,结果发现FB1oralA2有较高的复发率,同时回顾性分析使用抗胸腺球蛋白× 2 d较高剂量的抗胸腺球蛋白×4 d得到充分的植入和较低的移植相关毒性,期间使用静脉注射马利兰得到良好的结果。故欧洲一些研究中心(如Mohty等)制定新的FB2方案,即“FB2ivA2,氟达拉滨120-150 mg/m2+静脉注射马利兰×2 d +抗胸腺球蛋白×2 d”。该方案不仅获得良好的植入,而且能降低非复发死亡率。 一些研究表明,减低剂量预处理方案较传统的清髓性预处理方案而言复发较高。针对减低剂量预处理方案复发的问题,一些研究者设想是否加大马利兰的剂量可以使复发率降低呢?2014年欧洲多中心研究(Kharfan-Dabaja等[9])在437例CR1的急性髓细胞白血病患者中分别使用FB4iv即氟达拉滨+静脉注射马利兰× 4 d与FB2iv行异基因造血干细胞移植治疗急性髓细胞白血病(其中FB2组中多数使用抗胸腺球蛋白,FB4组中少数使用抗胸腺球蛋白),比较其结果发现:对≥50岁急性髓细胞白血病患者来说,在FB2iv组中非复发死亡率较低、耐受较好、无白血病生存率和总生存率均较好;在<50岁患者而言,两组移植物抗宿主病基本相似。但FB4iv对于< 50岁急性髓细胞白血病患者而言有显著低的复发的累计发生率,但没有转化成更好的2年总生存率和无白血病生存率。加大马利兰的剂量并没有带来更多的益处,是否与使用抗胸腺球蛋白有关还有待进一步研究。因此,通过对欧洲移植多中心(EBMT)使用减低剂量预处理方案的研究发现,尤其是“FB2ivA2”,对恶性血液病患者来说还是一个不错的选择,但进一步研究发现对于难治、复发、不适合清髓移植使用减低剂量预处理方案移植效果尚不太理想的患者可选择使用减低毒性预处理方案(reduced-toxicity conditioning regimen,RTC)。 减低毒性预处理方案中的药物剂量低于传统的清髓方案中的药物剂量,但是高于减低剂量预处理方案中的药物剂量。2014年Oudin等[10]报道165例急性髓细胞白血病或骨髓增生异常综合征患者分别使用减低剂量预处理方案(氟达拉滨30 mg/m2×3-5 d+马利兰260 mg/m2+抗胸腺球蛋白2.5 mg/kg×2 d)和减低毒性预处理方案(氟达拉滨30 mg/m2×3-5 d+马利兰390-520 mg/m2+抗胸腺球蛋白2.5 mg/kg×2 d)行异基因造血干细胞移植,结果发现减低毒性预处理方案组复发率较低,且有很好的耐受且能长期控制疾病,更高剂量的马利兰并没有较高的毒性,这样的方案可以有效的根据疾病状态和毒性风险来调整马利兰剂量。绝大多数研究中剂量强度对移植影响仍然是一个核心问题,需要一个随机前瞻性研究提供一个最终的答案。这种性质的随机对照多中心临床研究,现在正在法国进行(AAA研究-IPC2°11-003,EUDRACT号:2013-001935-36),旨在基于氟达拉滨在一个共同的调节平台上联合3种不同剂量的白消安(260,390和520 mg/m2)和兔抗胸腺球蛋白(5 mg/kg),这将有助于确定高剂量的白消安是否会导致复发风险降低,不增加移植相关毒性。 综上所述,目前学者们广义上认为减低剂量预处理方案包含传统意义上真正的非清髓预处理方案和减低毒性预处理方案。 2.2 减低剂量预处理方案在亲缘HLA单倍体相合的应用 减低剂量预处理方案越来越多应用于临床HLA相合的同胞异基因造血干细胞移植,而随着中国计划生育政策普及,找到HLA配型完全相合同胞供者也只有25%的机会[11]。目前大部分研究都聚焦在HLA匹配的无关成年供者、脐血或HLA部分匹配的相关供者身上。尽管世界各地的无关供者登记显著改善为寻找供体提供机会,但患者的本身疾病状态不允许长期等待寻找一个合适的无关供者。事实上几乎所有的患者至少有一个HLA配型部分相合的家人、父母、兄弟姐妹或者孩子,亲缘间HLA单倍体相合可以及时作为供体为诊治疾病争取时间,同时减少寻找无关供者及脐血移植的经费,因此越来越多的异基因造血干细胞移植选择了亲缘HLA单倍体相合的供者。最初结果显示HLA不匹配的清髓异体移植有较高的移植物抗宿主病发生及感染并发症发生,但随着对移植物抗白血病效应作用的深入认识,HLA单倍体相合的减低剂量预处理方案逐渐应用于临床,该方案在有效降低移植相关死亡率和移植物抗宿主病同时提供足够的免疫抑制,植入的供体免疫活性细胞和移植后供体的淋巴细胞输注共同诱导和发挥移植物抗白血病效应,最终达到完全治愈疾病的目的。1999年Sykes等[12]行非清髓预处理的单倍体造血干细胞移植治疗非霍奇金淋巴瘤患者5例,使患者获得良好的植入及嵌合。2004年Ichinohe等[13]在35例亲缘HLA单倍体相合患者中行减低剂量预处理方案为基础的异基因造血干细胞移植,患者获得较好的植入、总生存率及无事件生存率。 在过去的十几年,以减低剂量预处理方案为基础的异基因造血干细胞移植取得良好的效果,特别对于年老者、合并器官障碍及并发症的恶性血液病患者在找不到全相合供者时获益颇多。 2.2.1 具体方案及移植后植入及感染的情况 目前亲缘HLA单倍体相合的减低剂量预处理方案众多,多数方案使用低剂量全身照射或氟达拉滨、马利兰、马法兰、环磷酰胺(Cy),绝大多数加免疫抑制剂,这些方案获得良好的植入及造血恢复[12,14-17]。 Sykes等[12]首先在5例HLA单倍体相合的难治性非霍奇金淋巴瘤患者身上使用环磷酰胺(总共200 mg/kg)+全身照射700 cGy+抗胸腺球蛋白30 mg/kg(或抗胸腺球蛋白15 mg/kg)组成的预处理方案行异基因造血干细胞移植,4例患者中性粒细胞绝对计数植入时间发生在10 d和17 d,3例患者血小板恢复时间为9-72 d;研究结果表明宿主免疫抵抗与特异性靶向的环磷酰胺+抗胸腺球蛋白+胸腺全身照射组合可以有效地克服宿主抵抗HLA不匹配的骨髓植入,该组合比常规清髓性治疗方案的毒性更低。最终5例患者中只有2例存活,较差的存活是否跟药物的剂量或移植物抗宿主病预防或移植物来源有关,尚需有待进一步探索。 Raj等[14]报道55例亲缘HLA单倍体相合的高危恶性血液病患者行氟达拉滨(总共剂量:150 mg/m2)+环磷酰胺14.5 mg/kg×2 d+全身照射2 Gy,移植后大剂量环磷酰胺(d3,d4)组成的预处理方案行异基因造血干细胞移植,中性粒细胞绝对计数和血小板恢复的中位时间为 17 d和21 d,除2例患者外所有患者均成功植入;巨细胞病毒阳性反应79%,没有CMV疾病发生。研究结果表明该方案使患者获得良好的植入及较好的生存,并发现对高危恶性血液病患者而言,使用不同的移植物来源(外周血干细胞和骨髓)的单倍体造血干细胞移植,其结果可以相媲美。 Cho等[15]曾报道23例亲缘HLA单倍体相合患者使用全身照射800 cGy+氟达拉滨150 mg/m2+马利兰 6.4 mg/kg+抗胸腺球蛋白5 mg/kg组成的减低剂量预处理方案行异基因造血干细胞移植,中性粒细胞绝对计数和血小板恢复的中位时间为11 d和12 d,所有患者均成功植入;巨细胞病毒DNA血症的累积发生率91.3%。研究结果表明亲缘HLA单倍体相合患者使用减低剂量预处理方案且无体外T细胞耗竭是可行的,该方案促进植入且没有增加严重移植物抗宿主病的风险且获得良好的生存。但巨细胞病毒DNA血症的风险增加,因此需要更积极的预防巨细胞病毒。 Lee等[16]曾报道31例(高风险急性白血病/骨髓增生异常综合征25例或骨髓衰竭6例)亲缘HLA单倍体相合患者使用氟达拉滨180 mg/m2+马利兰6.4 mg/kg+抗胸腺球蛋白12 mg/kg组成的减低剂量预处理方案行异基因造血干细胞移植,中性粒细胞绝对计数和血小板恢复的中位时间为16.5 d和23 d,除3例患者外所有患者均成功植入;巨细胞病毒DNA血症的累积发生率91.3%;20例患者中至少1例患者巨细胞病毒抗原检测阳性,2例患者发展为巨细胞病毒结肠炎,其他显著感染是皮肤水痘-带状疱疹病毒感染(n=7),败血症(n=6)和肺炎(n=5,包括1例卡氏肺囊虫)。研究结果表明亲缘HLA不相合/单倍体患者使用减低剂量预处理方案且无体外T细胞耗竭是可行的,该方案使供体细胞高效的植入、没有过度的移植物抗宿主病和移植相关死亡。 Kurokawa等[17]报道66例亲缘HLA单倍体相合患者行抗胸腺球蛋白5 mg/kg+全身照射2 Gy+口服马利兰 8 mg/kg+马法兰140 mg/m2,氟达拉滨180 mg/m2+全身照射2 Gy+马利兰6.4 mg/kg+马法兰140 mg/m2为基础"
| [1] Giralt S, Estey E, Albitar M,et al.Engraftment of allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cells with purine analog-containing chemotherapy: harnessing graft-versus-leukemia without myeloablative therapy.Blood. 1997;89(12):4531-4536. [2] Slavin S, Nagler A, Naparstek E,et al.Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation and cell therapy as an alternative to conventional bone marrow transplantation with lethal cytoreduction for the treatment of malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases.Blood. 1998;91(3): 756-763. [3] Childs R, Clave E, Contentin N,et al.Engraftment kinetics after nonmyeloablative allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation: full donor T-cell chimerism precedes alloimmune responses.Blood. 1999;94(9):3234-3241. [4] Kottaridis PD, Milligan DW, Chopra R, et al.In vivo CAMPATH-1H prevents graft-versus-host disease following nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation.Blood. 2000;96(7): 2419-2425. [5] McSweeney PA, Niederwieser D, Shizuru JA,et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation in older patients with hematologic malignancies: replacing high-dose cytotoxic therapy with graft-versus-tumor effects.Blood. 2001;97(11): 3390-3400. [6] Giralt S, Aleman A, Anagnostopoulos A, et al. Fludarabine/melphalan conditioning for allogeneic transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;30(6):367-373. [7] Mohty M, Jacot W, Faucher C,et al. Infectious complications following allogeneic HLA-identical sibling transplantation with antithymocyte globulin-based reduced intensity preparative regimen.Leukemia. 2003;17(11):2168-2177. [8] Le Bourgeois A, Lestang E, Guillaume T,et al.Prognostic impact of immune status and hematopoietic recovery before and after fludarabine, IV busulfan, and antithymocyte globulins (FB2 regimen) reduced-intensity conditioning regimen (RIC) allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT). Eur J Haematol. 2013r;90(3):177-186. [9] Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Labopin M, Bazarbachi A,et al. Comparing i.v. BU dose intensity between two regimens (FB2 vs FB4) for allogeneic HCT for AML in CR1: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49(9):1170-1175. [10] Oudin C, Chevallier P, Furst S,et al.Reduced-toxicity conditioning prior to allogeneic stem cell transplantation improves outcome in patients with myeloid malignancies.Haematologica. 2014;99(11):1762-1768. [11] Confer DL.Unrelated marrow donor registries.Curr Opin Hematol. 1997;4(6):408-412. [12] Sykes M, Preffer F, McAfee S,et al.Mixed lymphohaemopoietic chimerism and graft-versus-lymphoma effects after non-myeloablative therapy and HLA-mismatched bone-marrow transplantation.Lancet. 1999;353(9166): 1755-1759. [13] Ichinohe T, Uchiyama T, Shimazaki C,et al.Feasibility of HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation between noninherited maternal antigen (NIMA)-mismatched family members linked with long-term fetomaternal microchimerism.Blood. 2004;104(12):3821-3828. [14] Raj K, Pagliuca A, Bradstock K,et al. Peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation of hematological diseases from related, haploidentical donors after reduced-intensity conditioning.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(6):890-895. [15] Cho BS, Yoon JH, Shin SH,et al.Comparison of allogeneic stem cell transplantation from familial-mismatched/haploidentical donors and from unrelated donors in adults with high-risk acute myelogenous leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18(10): 1552-1563. [16] Lee KH, Lee JH, Lee JH,et al.Hematopoietic cell transplantation from an HLA-mismatched familial donor is feasible without ex vivo-T cell depletion after reduced- intensity conditioning with busulfan, fludarabine, and antithymocyte globulin.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009;15(1):61-72. [17] Kurokawa T, Ishiyama K, Ozaki J,et al.Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to adults with hematologic malignancies: analysis of 66 cases at a single Japanese center.Int J Hematol. 2010;91(4):661-669. [18] Symons HJ, Fuchs EJ.Hematopoietic SCT from partially HLA-mismatched (HLA-haploidentical) related donors.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008;42(6):365-377. [19] Tanaka J, Kanamori H, Nishiwaki S,et al.Reduced-intensity vs myeloablative conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic SCT for patients aged over 45 years with ALL in remission: a study from the Adult ALL Working Group of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (JSHCT).Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(11):1389-1394. [20] Koenecke C, Shaffer J, Alexander SI,et al.NK cell recovery, chimerism, function, and recognition in recipients of haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation following nonmyeloablative conditioning using a humanized anti-CD2 mAb, Medi-507.Exp Hematol. 2003;31(10):911-923. [21] Ogawa H, Ikegame K, Yoshihara S,et al.Unmanipulated HLA 2-3 antigen-mismatched (haploidentical) stem cell transplantation using nonmyeloablative conditioning.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006;12(10):1073-1084. [22] Rizzieri DA, Koh LP, Long GD,et al.Partially matched, nonmyeloablative allogeneic transplantation: clinical outcomes and immune reconstitution.J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25(6):690-697. [23] Luznik L, O'Donnell PV, Symons HJ,et al.HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies using nonmyeloablative conditioning and high-dose, posttransplantation cyclophosphamide.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(6):641-650. [24] Burroughs LM, O'Donnell PV, Sandmaier BM,et al. Comparison of outcomes of HLA-matched related, unrelated, or HLA-haploidentical related hematopoietic cell transplantation following nonmyeloablative conditioning for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(11):1279-1287. [25] Ikegame K, Yoshihara S, Taniguchi Y,et al.Allogeneic stem cell transplantation as treatment for heavily treated, refractory acute graft-versus-host disease after HLA-mismatched stem cell transplantation.Exp Hematol. 2011;39(8):880-890. |
| [1] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [2] | Cao Linlin, Ding Kaiyang, Song Hao, Wu Guolin, Hu Maogui, Fan Dandan, Zhou Chenyang, Wang Cuicui, Feng Yuanyuan. Efficacy and influencing factors of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of malignant lymphoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1993-1998. |
| [3] | Zhang Suping, Sun Ling, Wan Dingming, Cao Weijie, Li Li, Liu Changfeng, Liu Yufeng, Wang Dao, Guo Rong, Jiang Zhongxing, Xie Xinsheng. Effectiveness of unrelated peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4994-5001. |
| [4] | Wei Yuanfeng, Huang Dongping. Current status of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3093-3100. |
| [5] | Zhang Ling, Sun Yanling, Wang Xiaozhen, Long Bing , Liu Jiajun. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2034-2038. |
| [6] | Xue Hui, Feng Shuqing, Hu Yongchao, Liu Zhibin, Li Xiaoyu, Gao Feng. Stratification therapy for cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 756-760. |
| [7] | Chen Xiaoling, Deng Huilan, Lu Quanyi, Hong Xiuli, Hu Jiasheng. Pure red cell aplasia follows allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a two-case report and literature review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 761-766. |
| [8] | Guo Zhi, Ren Hua, Ji Yong, Chen Liping, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zheng Shanshan, Liu Xiaodong, Chen Huiren. Thrombopoietin improves platelet recovery after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: an assessment of safety and efficacy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5269-5274. |
| [9] | Liu Jiao, Wang Daming, An Taixue, Hu Xuesong, Li Nankai, Wang Hongfu, Ma Wen, Nie-He Zhongrong, Xiao Lijia, Zhou Yiwen, Zheng Lei. Expression profile analysis of miRNAs in serumal exosomes as sensitive biomarkers in patients with graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3418-3425. |
| [10] | Wang Xiaoning, Chen Ying, Zhu Huachao, Zhang Mei, He Pengcheng. Protective effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on acute drug-induced liver injury after conditioning in haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2690-2695. |
| [11] | Wei Yuanfeng, Wei Zhongling, Yang Yuqiong, Qi Jing, Yan Jiawei, Huang Dongping. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia in 10 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2042-2048. |
| [12] | Wan Ding-ming, Sun Lin-lin, Xie Xin-sheng, Guo Rong, Cao Wei-jie, Zhang Su-ping, Li Li, Chen Xiao-na, Liu Yu-ye. Peripheral blood haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: monitoring minimal residual diseases to intervene recurrence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1413-1418. |
| [13] | Wan Ding-ming, Liu Yu-ye, Cao Wei-jie, Xing Hai-zhou, Xie Xin-sheng, Wang Dao, Zhang Su-ping, Li Li, Chen Xiao-na, Sun Lin-lin. Genetic haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome: a 2-year follow-up visit of 21 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(5): 662-668. |
| [14] | Ren Juan, Zhao Juan, Wang Xiao-ning. Co-transplantation of umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells and haploidentical hematopoietic stem cells for treatment of severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5297-5302. |
| [15] | Wang Kun, Han Jun-yong, Chen Jin-yan, Liu Shen-min, Xue Shi-jie, Jin Jing-jun. Measurements of T-cell receptor excision cycles in early stage of immune reconstitution after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4643-4649. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||