Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (2): 310-315.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.02.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
A Meta-analysis of carotid intima-media thickness and subclinical hypothyroidism
Zhang Zhao-yun, Abulikemu Tuerdi
- Department of Endocrinology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2014-11-18Online:2015-01-08Published:2015-01-08 -
Contact:Abulikemu Tuerdi, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Endocrinology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Zhao-yun, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Endocrinology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Zhao-yun, Abulikemu Tuerdi. A Meta-analysis of carotid intima-media thickness and subclinical hypothyroidism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(2): 310-315.
share this article
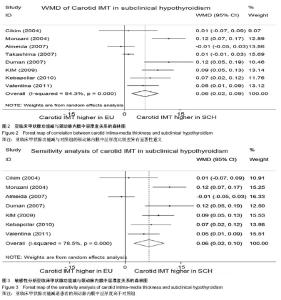
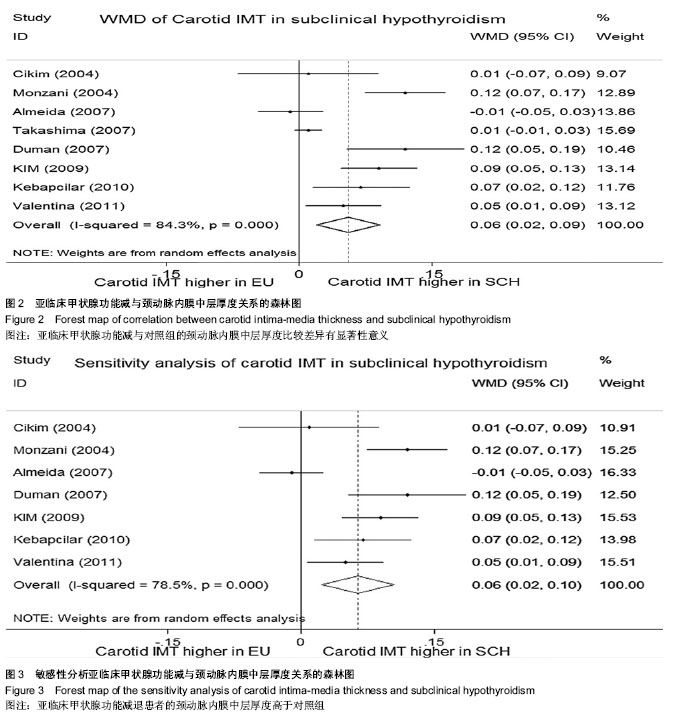
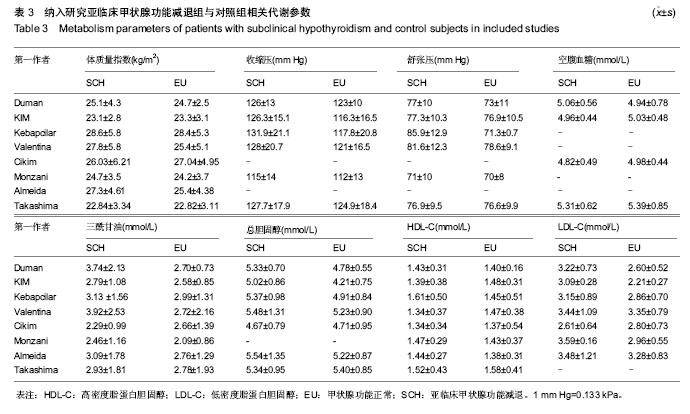
2.1 文献检索结果 最初检索135篇相关文献,按排除标准排除不合格文献后,最终纳入8篇[8-15] ,总样本量3 602例。其中7篇为病例对照研究,1篇为横断面研究。见图1。 2.2 研究及患者相关特点 筛选符合纳入标准的文献后(见表1),将亚临床甲状腺功能减退组及对照组研究的关键特征列在表2及表3中,在研究中,需均衡影响颈动脉内膜中层厚度的混杂因素:年龄、性别、体质量指数、血压、血糖、心血管疾病、吸烟、服用药物等。 2.3 亚临床甲状腺功能减退与颈动脉内膜中层厚度的关系 在纳入的8篇文献中,有7篇证明了相比甲状腺功能正常人群,亚临床甲状腺功能减退患者的颈动脉内膜中层厚度有增长的趋势。但是这些研究结论中只有4篇有统计学意义(见图2),且这些研究之间存在明显异质性(P=0.000,"
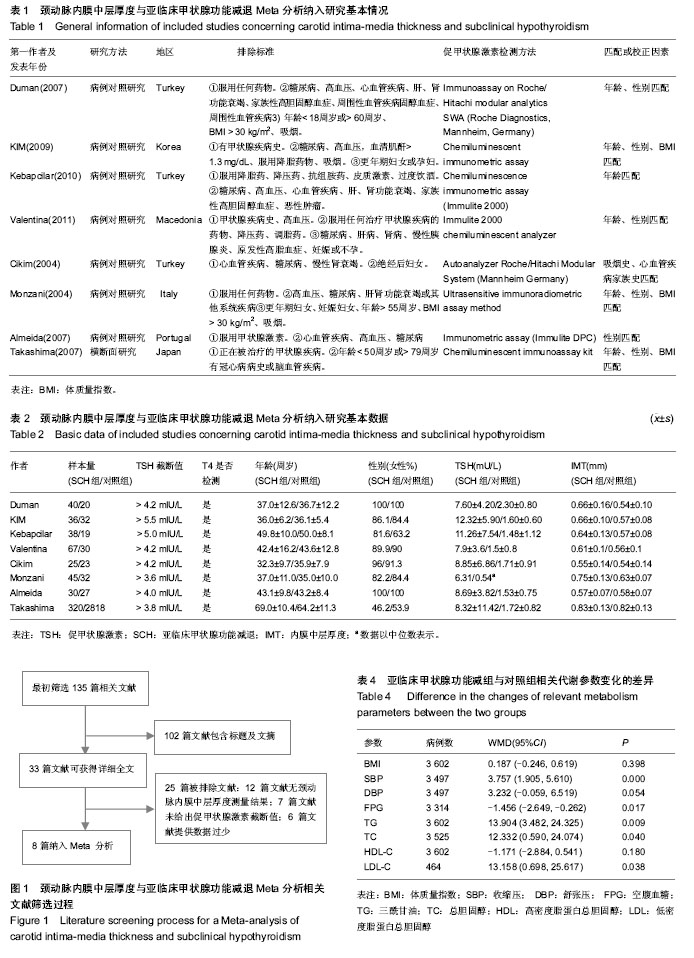
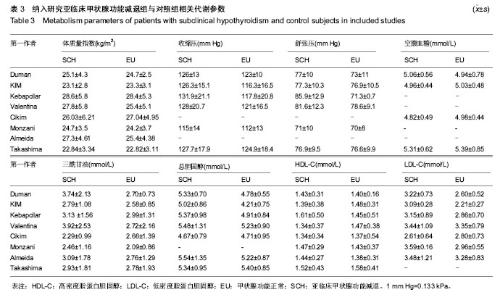
Ⅰ2=84.3%),故采用随机效应模型对各文献进行合并。亚临床甲状腺功能减与对照组的颈动脉内膜中层厚度比较差异有显著性意义(WMD=0.056,95%CI(0.020,0.092),P=0.002),见图2。 2.4 敏感性分析和亚组分析 因横断面研究参与者无特定的均衡因素[15],导致可能包含其他可能影响颈动脉内膜中层厚度的因素(如糖尿病、高血压等),排除横断面研究进一步进行敏感性分析,此项补充分析进一步证明了亚临床甲状腺功能减与对照组的颈动脉内膜中层厚度比较差异有显著性意义(WMD=0.064,95%CI(0.024,0.105),P=0.002),见图3。 将8篇文献中亚临床甲状腺功能减患者分为促甲状腺激素均数<10 mU/L和促甲状腺激素均数≥10 mU/L组,进一步分析亚临床甲状腺功能减组与对照组颈动脉内膜中层厚度情况。促甲状腺激素均数< 10 mU/L组合并后显示亚临床甲状腺功能减与对照组间颈动脉内膜中层厚度差异有显著性意义[WMD=0.048,95%CI(0.024,0.105)];促甲状腺激素均数≥10mU/L组合并后显示亚临床甲状腺功能减与对照组间颈动脉内膜中层厚度差异亦有统计学意义[WMD=0.082, 95%CI(0.049,0.116)];由此可解释,促甲状腺激素水平为亚临床甲状腺功能减与颈动脉内膜中层厚度关联的一项异质性因素。"
| [1] Helfand M. Screening for subclinical thyroid dysfunction in nonpregnant adults: a summary of the evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.Ann Intern Med.2004; 140: 128-41. [2] Canaris GJ, Manowitz NR, Mayor G,et al. The Colorado thyroid disease prevalence study. Arch Intern Med.2000;160: 526-34. [3] Gharib H, Tuttle RM, Baskin HJ, et al. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction: a joint statement on management from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists,the American Thyroid Association, and the Endocrine Society.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2005;90:581-585. discussion 586-587. [4] Hak AE, Pols HA, Visser TJ, et al. Subclinical hypothy-roidism is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction in elderly women: the Rotterdam Study. Ann Intern Med.2000;132:270-278. [5] O’Leary DH, Polak JF. Intima-media thickness: a tool for atherosclerosis imaging and event prediction. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90:18L-21L. [6] Baldassarre D, Amato M, Bondioli A,et al. Carotid artery intima-media thickness measured by ultrasonography in normal clinical practice correlates well with atherosclerosis risk factors. Stroke.2000;31:2426-30. [7] Lorenz MW, Markus HS, Bots ML, et al. Prediction of clinicalcardiovascular events with carotid intima-media thickness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2007;115:459-467. [8] Monzani F, Caraccio N, Kozàkowà M, et al. Effect of levothyroxine replacement on lipid profile and intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89: 2099-3106. [9] Duman D, Demirtunc R, Sahin S, et al. The effects of simvastatin and levothyroxine on intima-media thickness of the carotid artery in female normolipemic patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: a prospective,randomized-controlled study. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2007;8:1007-1011. [10] Kim SK, Kim SH, Park KS,et al. Regression of the increased common carotid artery-intima media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism after thyroid hormone replacement. Endocr J.2009;56:753-758. [11] Kebapcilar L, Comlekci A, Tuncel P, et al. Effect of levothyroxine replacement therapy on paraoxonase-1 and carotid intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism. Med Sci Monit.2010;16:CR41-7. [12] Valentina VN, Marijan B, Chedo D,et al. Subclinical hypothyroidism and risk to carotid atherosclerosis. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol.2011;55:475-80. [13] Cikim AS, Oflaz H, Ozbey N, et al. Evaluation of endothelial function in subclinical hypothyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism.Thyroid 2004;14:605-609. [14] Almeida CA, Teixeira Pde F, Soares DV, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness as a marker of cardiovascular risk in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism.Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol.2007;51:472-477. [15] Takashima N, Niwa Y, Mannami T, et al. Characterization of subclinical thyroid dysfunction from cardiovascular and metabolic viewpoints: the Suita study. Circ J.2007;71: 191-195. [16] Huston P, Naylor CD. Health services research: reporting on studies using secondary data sources. CMAJ.1996;155:1697- 709. [17] Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA.2000;283:2008e12. [18] Surks MI, Ortiz E, Daniels GH, et al. Subclinical thyroid disease: scientificreview and guidelines for diagnosis and management. JAMA.2004;291:228-38. [19] Haugen B. When isn’t the TSH normal and why? Clinical implications and causes. Paper presented at the 12th annual meeting of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE). 2003, San Diego, Calif. [20] Lee S. When is the TSH normal? New criteria for diagnosis and management. Paper presented at the 12th annual meeting of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE).2003, San Diego, Calif. [21] Ochs N, Auer R, Bauer DC, et al. Meta-analysis: subclinical thyroid dysfunction and the risk for coronary heart disease and mortality. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:832-45. [22] Christ-Crain M, Meier C, Guglielmetti M, et al. Elevated C-reactive protein and homocysteine values: cardiovascular risk factors in hypothyroidism? A crosssectional and a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Atherosclerosis. 2003; 166:379-86. [23] Zhang W, Tian LM, Han Y, et al. Presence of thyrotropin receptor in hepatocytes:not a case of illegitimate transcription. J Cell Mol Med.2009;13:4636e42. [24] Cai Y, Ren Y, Shi J. Blood pressure levels in patients with subclinical thyroid dysfunction: a meta-analysis of cross-sectional data. Hypertens Res. 2011;34:1098-105. [25] Gumieniak O, Perlstein TS, Hopkins PN, et al. Thyroid function and blood pressure homeostasis in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:3455-61. [26] Marcisz C, Jonderko G, Kucharz EJ. Influence of short-time application of a low sodium diet on blood pressure in patients with hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism during therapy. Am J Hypertens.2001;14:995-1002. [27] Maratou E, Hadjidakis DJ, Kollias A, et al. Studies of insulin resistance in patients with clinical and subclinical hypothyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009;160:785-790. |
| [1] | Li Songtao, Li Xinyi, Song Yunfeng, Ning Jiayin, Ren Qiang, Yang Renxu, Peng Bo. Maxing Xiongting Mixture regulates factors relevant to lung reshaping and vascular remodeling of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 274-280. |
| [2] | Chen Xinling, Wang Shenglan. Cell autophagy, pathway, regulation and its multiple correlations with pulmonary hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 311-316. |
| [3] | Ye Quanying, Chen Qisheng, Li Yanwen, Wang Ting, Chen Xiaoyan, Yue Yun. Effect of cassia seed aqueous extract on blood pressure level in N-nitro-L-arginine-methyl ester induced hypertensive rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1705-1711. |
| [4] |
Wen Shuangwei, Wu Qingmei.
Aerobic exercise combined with levothyroxine and vitamin D3 relieves osteoporosis in subclinical hypothyroidism rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4118-4124. |
| [5] | Yuan Guoqiang, Qin Yongsheng, Peng Peng. High-intensity interval training for treating pathological cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3708-3715. |
| [6] | Zhang Chaohui, Zhao Feng, Feng Yunpeng, Wang Wenbin, Kuang Baoping, Huang He. Research progress and medical application of modeling and simulation of cardiovascular system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1115-1121. |
| [7] | Zhou Xiao-xiong, Wei Wei-chao, Sun Ce, Ye Tao-chun, Wang Song, Qing Li-jin, Wu Hui, Xian Shao-xiang. Transplantation of lentiviral-transfected endothelial progenitor cells for pulmonary hypertension and the interventional effect of astragalosides [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(9): 1425-1431. |
| [8] | Cen Yan-hui1, 2, Lin Yong3, Lin Jiang1, Jia Wei1, Zhao Jing1. Hydrolysis of Nanzhu fluid promotes proliferation and migration of human microvascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(16): 2564-2569. |
| [9] | Wang Yong, Zhang Ya-guang. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation alleviates myocardial injury due to systolic hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(50): 7518-7523. |
| [10] | Wu Jin. Application of felodipine sustained-release tablets in the hypertension treatment in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(47): 7127-7132. |
| [11] | Cui Xue-mei, Jing Xiao-xiao. Interventional effect of umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation in rats with gestational hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(45): 6795-6800. |
| [12] |
Chen Yao.
Properties of sustained-release and controlled-release polymeric materials and application in the treatment of hypertension
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(43): 6530-6536.
|
| [13] | Li Wen-hua, Zhang Qun-hui, Rong Hao, Cai Peng, Yuan Dong-ya. Application and progress in endothelial progenitor cells in hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(15): 2273-2280. |
| [14] | Wang Pei-cheng, Cao Li, Yang De-sheng, Xu Bo-yong, Guo Wen-tao, Aili•Rehei. Correlation between hypertension and deep venous thrombosis after bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(9): 1335-1339. |
| [15] | Ma Jian, Zhang Yong, Cao Zheng. Endothelial cell differentiation function varies during telmisartan intervention for hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(7): 1117-1121. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||