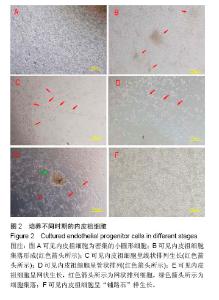
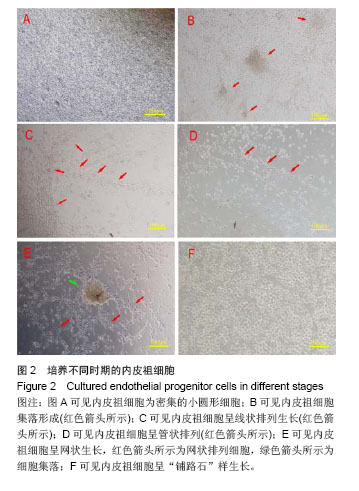
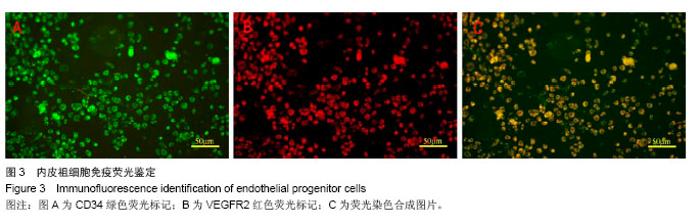
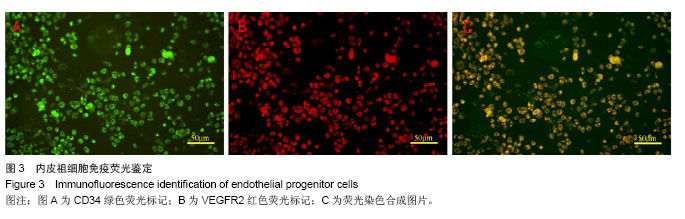
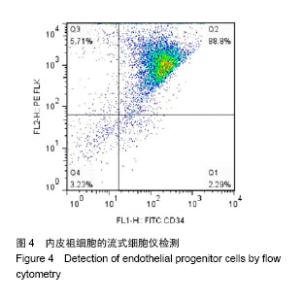
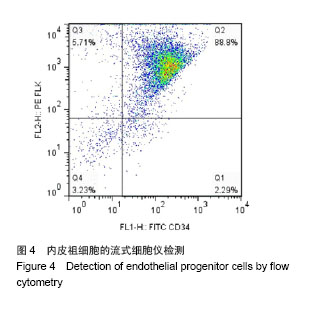
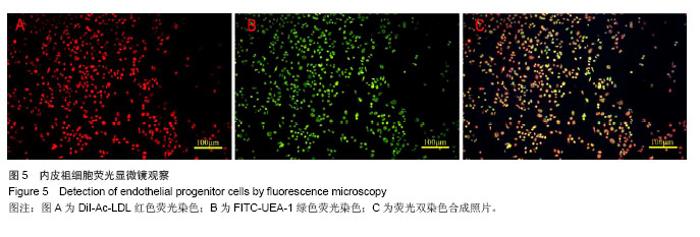
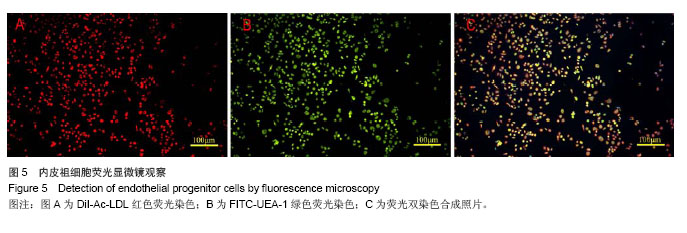
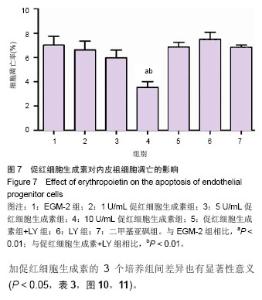
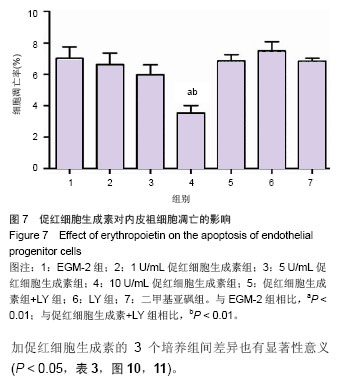
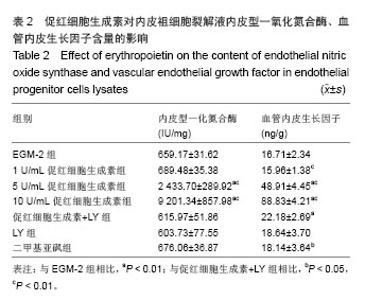
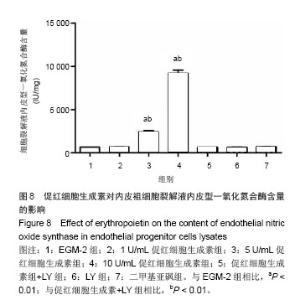
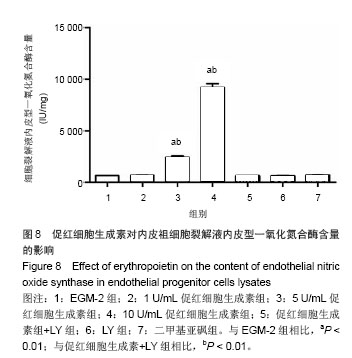
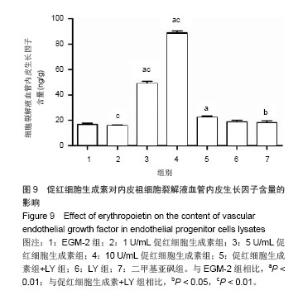
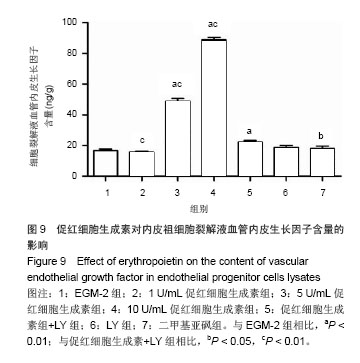
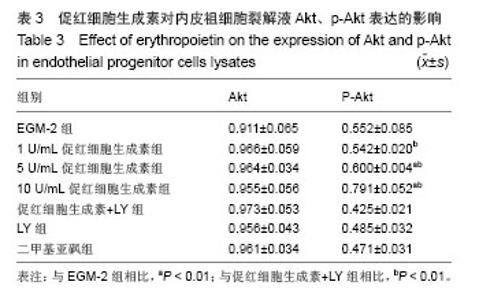
| [1]Heeschen C, Aicher A, Lehmann R,et al.Erythropoietin is a potent physiologic stimulus for endothelial progenitor cell mobilization.Blood. 2003;102(4):1340-1346.
[2]Bahlmann FH, De Groot K, Spandau JM,et al. Erythropoietin regulates endothelial progenitor cells.Blood. 2004;103(3): 921-926.
[3]Dignat-George F, Sampol J.Circulating endothelial cells in vascular disorders: new insights into an old concept.Eur J Haematol. 2000;65(4):215-220.
[4]Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A,et al.Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis.Science. 1997; 275(5302):964-967.
[5]Stellos K, Bigalke B, Langer H,et al.Expression of stromal-cell-derived factor-1 on circulating platelets is increased in patients with acute coronary syndrome and correlates with the number of CD34+ progenitor cells.Eur Heart J. 2009;30(5):584-593.
[6]Jia L, Takahashi M, Yoshioka T,et al.Therapeutic potential of endothelial progenitor cells for cardiovascular diseases.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2006;4(1):59-65.
[7]Reynolds JA, Robertson AC, Bruce IN,et al.Improving cardiovascular outcomes in rheumatic diseases: therapeutic potential of circulating endothelial progenitor cells.Pharmacol Ther. 2014;142(2):231-243.
[8]Hu CH, Wu GF, Wang XQ,et al.Transplanted human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells improve left ventricular function through angiogenesis in myocardial infarction.Chin Med J (Engl). 2006;119(18):1499-1506.
[9]Zangi L, Lui KO, von Gise A,et al.Modified mRNA directs the fate of heart progenitor cells and induces vascular regeneration after myocardial infarction.Nat Biotechnol. 2013; 31(10):898-907.
[10]Iwaguro H, Yamaguchi J, Kalka C,et al.Endothelial progenitor cell vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer for vascular regeneration.Circulation. 2002;105(6):732-738.
[11]Devanesan AJ, Laughlan KA, Girn HR,et al. Endothelial progenitor cells as a therapeutic option in peripheral arterial disease.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2009;38(4):475-481.
[12]George J, Goldstein E, Abashidze A,et al.Erythropoietin promotes endothelial progenitor cell proliferative and adhesive properties in a PI 3-kinase-dependent manner. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;68(2):299-306.
[13]Sautina L, Sautin Y, Beem E,et al.Induction of nitric oxide by erythropoietin is mediated by the {beta} common receptor and requires interaction with VEGF receptor 2.Blood. 2010;115(4): 896-905. |