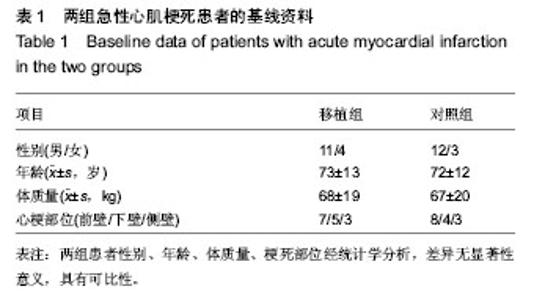
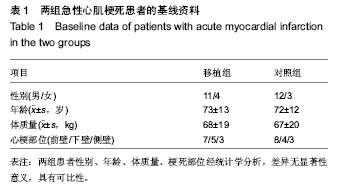
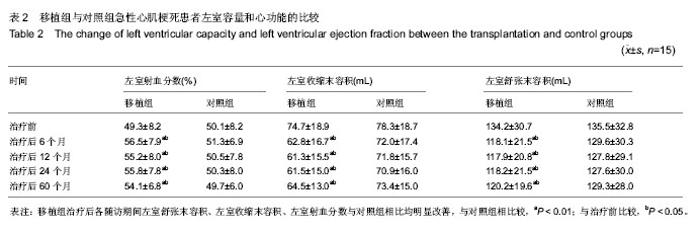
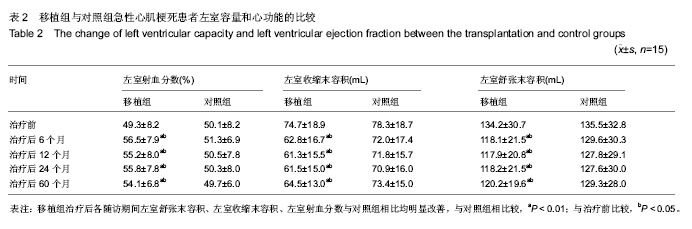
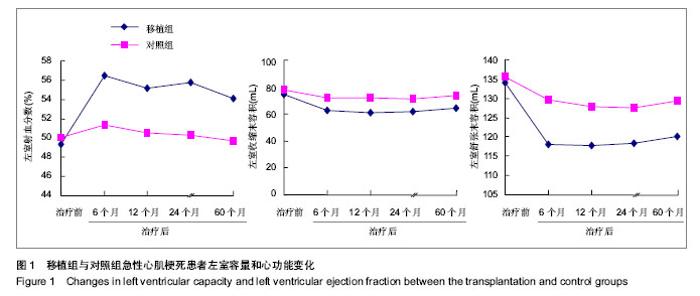
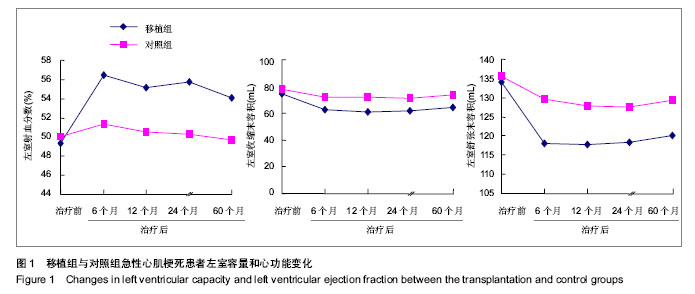
| [1] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S,et al.Transplanted adult bone marrow cells repair myocardial infarcts in mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;938:221-229.[2] Boyle AJ, Schulman SP, Hare JM,et al. Is stem cell therapy ready for patients? Stem Cell Therapy for Cardiac Repair. Ready for the Next Step.Circulation. 2006;114(4):339-352.[3] Hsieh PC, Segers VF, Davis ME,et al. Evidence from a genetic fate-mapping study that stem cells refresh adult mammalian cardiomyocytes after injury. Nat Med. 2007;13(8): 970-974.[4] Bergmann O, Bhardwaj RD, Bernard S,et al. Evidence for cardiomyocyte renewal in humans.Science. 2009;324(5923): 98-102.[5] Kajstura J, Urbanek K, Perl S,et al. Cardiomyogenesis in the adult human heart. Circ Res. 2010;107(2):305-315.[6] Fuchs S, Baffour R, Zhou YF,et al. Transendocardial delivery of autologous bone marrow enhances collateral perfusion and regional function in pigs with chronic experimental myocardial ischemia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37(6):1726-1732.[7] Bearzi C, Rota M, Hosoda T,et al. Human cardiac stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(35):14068-14073.[8] Laugwitz KL, Moretti A, Lam J,et al. Postnatal isl1+ cardioblasts enter fully differentiated cardiomyocyte lineages. Nature. 2005;433(7026):647-653. [9] Wu SM, Fujiwara Y, Cibulsky SM,et al. Developmental origin of a bipotential myocardial and smooth muscle cell precursor in the mammalian heart. Cell. 2006;127(6):1137-1150. [10] Smith RR, Barile L, Cho HC,et al. Regenerative potential of cardiosphere-derived cells expanded from percutaneous endomyocardial biopsy specimens.Circulation. 2007;115(7): 896-908.[11] Segers VF, Lee RT.Stem-cell therapy for cardiac disease.Nature. 2008;451(7181):937-942.[12] Schächinger V, Erbs S, Elsässer A,et al. Improved clinical outcome after intracoronary administration of bone-marrow-derived progenitor cells in acute myocardial infarction: final 1-year results of the REPAIR-AMI trial. Eur Heart J. 2006;27(23):2775-2783.[13] Mazhari R, Hare JM. Mechanisms of action of mesenchymal stem cells in cardiac repair: potential influences on the cardiac stem cell niche.Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007; 4 Suppl 1:S21-26.[14] Hare JM, Traverse JH, Henry TD,et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study of intravenous adult human mesenchymal stem cells (prochymal) after acute myocardial infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009; 54(24):2277-2286.[15] Menasché P. Cell transplantation for the treatment of heart failure. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;14(2):157-166.[16] Tomita S, Li RK, Weisel RD,et al. Autologous transplantation of bone marrow cells improves damaged heart function.Circulation. 1999;100(19 Suppl):II247-256.[17] Okamoto K, Miyoshi S, Toyoda M,et al. 'Working' cardiomyocytes exhibiting plateau action potentials from human placenta-derived extraembryonic mesodermal cells. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313(12):2550-2562.[18] Rafii S, Meeus S, Dias S,et al. Contribution of marrow-derived progenitors to vascular and cardiac regeneration.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13(1):61-67.[19] Baffour R, Pakala R, Hellinga D,et al. Bone marrow-derived stem cell interactions with adult cardiomyocytes and skeletal myoblasts in vitro. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2006;7(4): 222-230.[20] Robinson SN, Ng J, Niu T,et al. Superior ex vivo cord blood expansion following co-culture with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006; 37(4):359-366.[21] Meyer GP, Wollert KC, Lotz J,et al. Intracoronary bone marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: eighteen months' follow-up data from the randomized, controlled BOOST (BOne marrOw transfer to enhance ST-elevation infarct regeneration) trial.Circulation. 2006;113(10): 1287-1294. [22] Assmus B, Rolf A, Erbs S,et al. Clinical outcome 2 years after intracoronary administration of bone marrow-derived progenitor cells in acute myocardial infarction. Circ Heart Fail. 2010;3(1):89-96. [23] Yousef M, Schannwell CM, Köstering M,et al. The BALANCE Study: clinical benefit and long-term outcome after intracoronary autologous bone marrow cell transplantation in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(24):2262-2269.[24] Meyer GP, Wollert KC, Lotz J,et al. Intracoronary bone marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: 5-year follow-up from the randomized-controlled BOOST trial. Eur Heart J. 2009;30(24):2978-2984. [25] Makkar RR, Smith RR, Cheng K,et al. Intracoronary cardiosphere-derived cells for heart regeneration after myocardial infarction (CADUCEUS): a prospective, randomised phase 1 trial.Lancet. 2012;379(9819):895-904.[26] Huang RC,Yao K,Qian JY,et al.Emergency Intracoronary Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction (TCT-STAMI-2): Long-Term Outcome .Circulation. 2008;118:S_791.[27] Yousef M, Schannwell CM, Köstering M,et al. The BALANCE Study: clinical benefit and long-term outcome after intracoronary autologous bone marrow cell transplantation in patients with acute myocardial infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(24):2262-2269.[28] Wang JS, Shum-Tim D, Galipeau J,et al. Marrow stromal cells for cellular cardiomyoplasty: feasibility and potential clinical advantages. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;120(5): 999-1005.[29] Sedov VM, Nemkov AS, Afanas'ev BV,et al. Effectiveness of using autologous mono-nuclears of the bone marrow in treatment of patients with ischemic heart disease.Vestn Khir Im I I Grek. 2006;165(4):11-14.[30] Mocini D, Colivicchi F, Santini M.Stem cell therapy for cardiac arrhythmias. Ital Heart J. 2005;6(3):267-271.[31] Pannitteri G, Petrucci E, Testa U.Coordinate release of angiogenic growth factors after acute myocardial infarction: evidence of a two-wave production.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2006;7(12):872-879.[32] Vasa M, Fichtlscherer S, Aicher A,et al. Number and migratory activity of circulating endothelial progenitor cells inversely correlate with risk factors for coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 2001;89(1):E1-7.[33] Seeger FH, Tonn T, Krzossok N,et al. Cell isolation procedures matter: a comparison of different isolation protocols of bone marrow mononuclear cells used for cell therapy in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(6):766-772. |