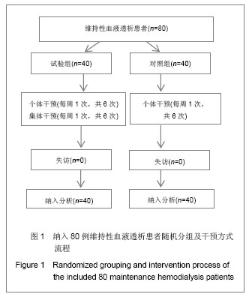
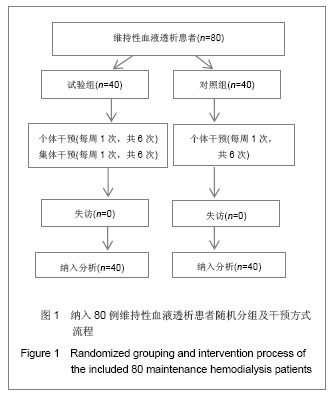
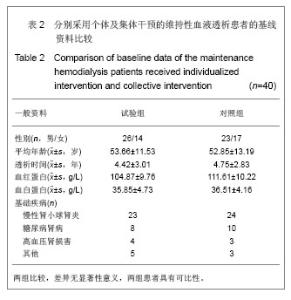
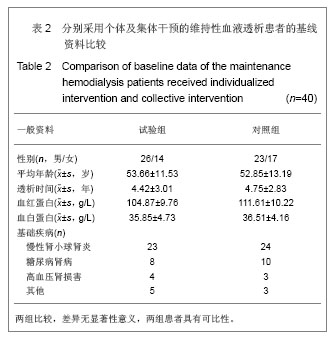
| [1]左力,王梅.我国面临快速增长的终末期肾病治疗负担[J].中国血液净化,2010,9(1): 41-49.
[2]肖月,隋宾艳,赵琨.我国终末期肾病现状及透析技术的应用、费用及支付情况分析[J].中国卫生政策研究,2011,4(5):29-33.
[3]马祖等,郑智化,张涤华,等.血液透析患者生存质量的多中心研究[J].中国血液净化,2004,3(7):380-384.
[4]王苏杭,董春锋.北京基层医院维持性血液透析患者生活质量及其影响因素分析[J].医学综述,2013,19(11):2084-2086.
[5]陈玲,杨连招.授权教育对维持性血液透析患者饮食自我管理的影响[J].全科护理,2013, 11,5(A):1159-1160.
[6]中国医院协会血液净化中心管理分会血液透析登记组.我国面临快速增长的终末期肾病治疗负担[J].中国血液净化,2010, 9(1):47-49.
[7]Qureshi AR, Alvestrand A, Divino-Filho JC, et al. Inflammation, malnutrition, and cardiac disease as predictors of mortality in hemodialysis patients.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13 Suppl 1: S28-36.
[8]王祥花,崔莉,崔岩,等.血液透析患者社会回归及生活质量调查[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(44):8317-8320.
[9]Hecking M, Karaboyas A, Saran R, et al. Predialysis serum sodium level, dialysate sodium, and mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients: the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;59(2): 238-248.
[10]邢伟,吴艳青,宋延锋,等.维持性血液透析患者的健康教育干预与生活质量[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(5): 901-904.
[11]付凤齐,王志稳,万巧琴.社会支持和应对方式对维持性血液透析患者生存质量的影响[J].中华护理杂志,2006,41(2):130-132.
[12]姜敏敏,李鲁.SF-36量表在血透患者中的性能测试[J].中国行为医学科学,2003,12 (1):31.
[13]Brazier JE, Harper R, Jones NMB ,et al. Validating the SF-36 Health Survey Questionnaire: New Outcome Measure for Primary Care. British medical juorna.1992; 305(6846): 160-164.
[14]Maor Y, King M, Olmer L, et al. A comparison of three measures, the time trade-off technique, global healthy related quality of life and the SF-36 in dialysis patients. Joumey of Clinical Epidemiology.2001;54(6):565-570.
[15]Joshi VD, Mooppil N, Lim JF. Validation of the kidney disease quality of life-short form: a cross-sectional study of a dialysis-targeted health measure in Singapore. BMC Nephrol. 2010;11:36.
[16]罗世香, 苏兰若, 王爱平.护理干预对维持性血液透析病人自我管理行为的影响[J].护理研究,2007,21(6B):1526-1528.
[17]黄小妹,张英,张黎民,等.武汉地区维持性血液透析病人生活质量及影响因素[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2005,21(2):88-89.
[18]蔡惠群,陈恒燕,陈亮明等.临床护理路径在维持性血液透析患者护理中的应用[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(11):358-359.
[19]Shahgholian N, Tajdari S, Nasiri M. Reviewing and comparing self-concept in patients undergoing hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.Iranian J Nursing Midwifery Resh. 2012; 17(2): 85-90.
[20]陈玲,梁颖,侯诗箐,等. 维持性血液透析患者自我管理行为的护理干预[J]. 中国临床保健杂志,2013,16(3):321-323.
[21]李敏,刘璐,汪茂宝,等. 细节护理干预在尿毒症血液透析患者中的应用价值[J]. 国际护理学杂志,2013,33(6):1279-1281.
[22]王金兰. 人性化护理干预在尿毒症并发左心衰患者血液透析中的应用[J]. 中外医疗,2013,32(15):158-159.
[23]刘雁凌,刘丹,叶艳,等.人性化护理干预在尿毒症并发左心衰患者血液透析中的应用[J].中国医药导刊,2012,14(5):890-893.
[24]李俊,霍桢,俞翔,等.认知行为团体治疗对维持性血液透析患者心理干预的疗效[J].陕西医学杂志,2013,31(5):553-555.
[25]钱荣. 认知行为干预对终末期肾衰患者自我管理行为的影响[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2013,29(2):296-297.
[26]Aghakhani N, Samadzadeh S, Mafi TM, et al. The impact of education on nutrition on the quality of life in patients on hemodialysis: a comparative study from teaching hospitals.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplantation. 2012; 23(1): 26-30.
[27]王苏容,朱湘竹,范亚平.终末期肾病维持性血液透析108例心理状况及生活质量分析[J].南通医学院学报,2009,29(6):466-467.
[28]Zamarron C, Garcia Paz V, Morete E, et al. Association of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and obstructive sleep apnea conse- quences. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2008;3(4):671-682.
[29]程远娟.实施家属健康教育对维持性血液透析患者生存质量影响的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2012.
[30]Hruby Z, Stanek-Piotrowska M, Turek J,et al. The clinicopathological determinants of native arteriovenous fistula failure in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2013;22(4):495-500.
[31]Song MK, Gilet CA, Lin FC, et al. Characterizing daily life experience of patients on maintenance dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(11):3671-3677.
[32]Tezel A, Karabulutlu E, Sahin O. Depression and perceived social support from family in Turkish patients with chronic renal failure treated by hemodialysis. J Res Med Sci. 2011; 16(5):666-673.
[33]Jung YS, You G, Shin HS, et al. Relationship between Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index and total lymphocyte count and mortality of hemodialysis patients. Hemodial Int. 2013 Aug 14.
[34]Xu Y, Chen Y, Li D, et al. Hypertension, fluid overload and micro inflammation are associated with left ventricular hypertrophy in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail. 2013 Aug 1.
[35]Su CT, Yabes J, Pike F, et al. Changes in Anthropometry and Mortality in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients in the HEMO Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013 Jul 13. |