Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (40): 7144-7149.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.40.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wnt signaling pathways in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
Pan Jing-hua1, Huang Hao1, Zha Zhen-gang2
- 1 First Clinical College of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2 First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2013-10-01Published:2013-10-31 -
Contact:Zha Zhen-gang, M.D., Professor, Doctoral supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Pan Jing-hua★, Studying for master’s degree, First Clinical College of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China 394805331@qq.com -
Supported by:the Scientific and Technology Plan of Guangdong Province, No. 2011B050300013*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pan Jing-hua, Huang Hao, Zha Zhen-gang. Wnt signaling pathways in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(40): 7144-7149.
share this article
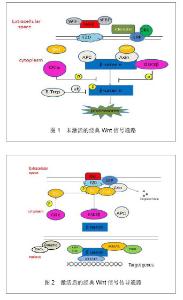
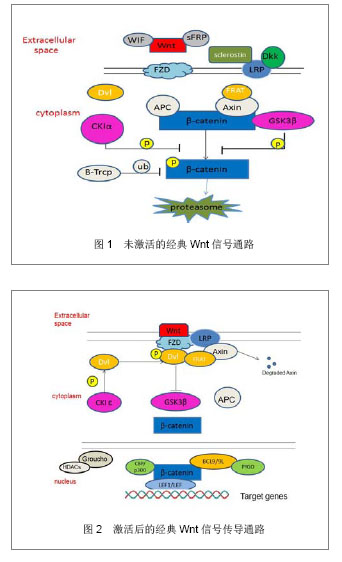
2.1 Wnt蛋白 Wnt最早是由Nusse在1982年通过果蝇wingless(Wg)基因和小鼠的Int-1基因组合而来。Wnt蛋白家族富含L-半胱氨酸、为相对分子质量 39 000-46 000的分泌信号的糖蛋白,其中,Wnt蛋白家族是一个由一段信号肽及23或24个位置保守的半胱氨酸残基组成,在多种组织广泛表达,且在进化上高度保守。至今为止在人类中发现19种Wnt基因能够翻译转录成Wnt蛋白[3]。细胞膜外的Wnt蛋白有2种类型,一类能与LRP/FZD相互结合并发挥协同作用而激活Wnt/β-catenin经典途径,如Wnt1、Wnt2、Wnt3、Wnt3a、Wnt8和Wnt8b等;另一类是能与Frizzled结合激活异源三聚体G-蛋白,提高细胞内钙水平的作用,如Wnt4、Wnt5a、Wnt5b、Wnt6、Wnt7a和Wnt11等[4]。 2.2 Wnt信号传导通路 经典Wnt信号传导通路:经典Wnt信号传导通路描述当Wnt蛋白于细胞表面Frizzled(FZD)受体家族结合后的一系列反应,其中β-catenin是经典Wnt信号传导通路中的关键因子,β-catenin在细胞质中含量最多,可存在于细胞膜及细胞核中。当Wnt信号通路未被激活时,在细胞质中的β-catenin与APC、AXIN、GSK-3β这些因子结合在一起,形成结合体。因GSK-3β和CKIα能促进β-catenin的磷酸化,经磷酸化后的β-catenin随后通过启动β-TrCP介导的泛素/蛋白酶体途径降解[5]。见图1。 Wnt通路中,在细胞膜表面上的FZD受体和LRP5/6受体同样充当着相当重要的角色[6],在当Wnt蛋白与FZD受体和LRP5/6受体结合时,Dvl (disheveled)通过CKIε变得过磷酸化,从而获得更大的亲和力与FRAT和FZD结合,导致LRP5/ 6-Axin-FRAT结合体中的Axin得到降解,因此,结合体内部结构改变后,β-catenin从LRP5/6-Axin-FRAT结合体中游离出来。Wnt在激活Dvl的同时,也相反地抑制GSK3β的活性。在这情况下,β-catenin分子从降解中逃离出来并大量积聚,进入细胞核内,与在TCF/LEF1结合,从而导致抑制TCF/LEF1与转录抑制因子Groucho/HDACs的结合,最后吸收组蛋白乙酰基转移酶CBP/p300从而激活目的基因的表达。见图2。"
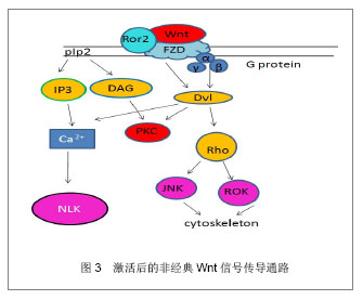
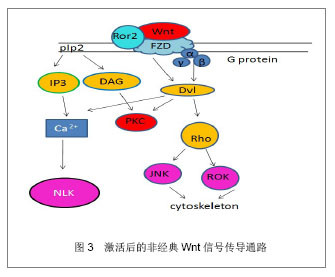
非经典Wnt信号传导通路:与经典Wnt信号通路相比,非经典Wnt信号传导通路并不依赖β-catenin在胞内的聚集而发挥作用,在某些时候甚至可以抑制细胞核β-catenin的活性[7]。同时非经典Wnt信号传导通路也更加复杂,非经典Wnt信号传导通路包含着多种分子的参与,该通路Wnt蛋白主要包括Wnt5a,Wnt11,Wnt7a等,内部的联系也是多样化[8]。目前发现非经典Wnt信号通路可以通过Wnt/PCP,Wnt/JNK,Wnt/calcium和Wnt/Rho信号发挥作用。这些信号的开始是由于对FZD和共同受体的激活,如Ror2受体和Ryk受体;也通过潜在的多样机制如Ca2+依赖机制和Dvl依赖机制来进行信号转换[9]。而小鸟嘌呤核苷三磷酸酶RhoA和它的效应器ROK通过Dvl激活,然后在Wnt信号通路参与调节肌动蛋白细胞骨架(cytoskeleton)。JNK是另一个Dvl的下游效应器,它能被RhoA激活从而调控PCP信号。 非经典Wnt信号通路同样通过异源三聚体的G蛋白进行,异源三聚体的G蛋白能激活Dvl,引起下游的钙离子聚集和PKC的激活。Nemo样激酶抗体NLK(Nemo-like kinase)和活化T细胞的核因子(NFAT)在非经典Wnt信号通路中是钙离子依赖的效应器,同样,NLK能使TCF/LEF1磷酸化同时也抑制经典的Wnt信号通路的表达。见图3。 2.3 Wnt信号通路的调控 胞膜受体的调控:几组干扰受体、配体结合和细胞内信号传导的负调节蛋白严格地控制着Wnt信号通路。分泌FZD相关的多肽类sFRPs基因和Wnt信号抑制因子1(WIF-1)竞争性地与FZD受体结合,同时,分泌型糖蛋白DDks (Dickkopfs)和硬化蛋白(Sclerostin)会与LRPs结合从而阻止Wnt信号通路。Sclerostin蛋白是骨细胞中高度表达的SOST基因的蛋白产物,它与LRP5/6结合在一起,阻止FZD-LRP复合体的形成,从而阻止Wnt蛋白激活β-catenin途径。DDKs与Sclerostin相似,通过与LRP5/6结合阻止β-catenin途径。sFRPs 和 WIF-1可以衰减Wnt信号通路传导,有研究表明,sFRPs 和 WIF-1可以通过此机制影响肿瘤的发生[10]。sFRPs同样可以调节骨骼发育和其他组织的形成[11-12]。 胞质中的调控:除了在细胞膜受体的竞争性调节外,在细胞质内许多的蛋白质同样也干扰着Wnt信号传导通路的进行。如与β-catenin结合着的APC、Axin1、Axin2蛋白,需要参与β-catenin的降解过程。GSK-3β和CKIα使β-catenin磷酸化,直接导致了β-catenin的降解。在非经典Wnt信号通路中,Nkd(一种在大多数动物中的胞内蛋白)中的Nkd1和Nkd2蛋白可以和Dvl结合,使Dvl通过刺激JNK的激活,促进Wnt/PCP通路的进行,但同时,也妨碍了Dvl在经典信号通路的作用[13]。与Nkd相类似,NLK通过对抗TCF/LEF1,在激活非经典Wnt信号通路同时,也抑制着经典Wnt信号通路。 细胞外的调控:除了在包膜受体方面和细胞质内的调控外,Wnt信号传导通路还受细胞外的因素影响,如乙酰肝素蛋白聚糖。硫酸乙酰肝素的多聚糖链与成纤维细胞生长因子、Wnt、骨形态发生蛋白这些关键因素结合,从而去调控间充质干细胞的增殖和分化[14]。通过乙酰肝素硫酸盐与Wnt配体结合,从而调整Wnt与FZD受体的通路和调控多种发育的过程。 2.4 Wnt参与间充质干细胞自我增殖 Wnt信号传导通路参与间充质干细胞自我增殖:Wnt信号传导通路在间充质干细胞的增殖和分化调控中具有非常重要的作用。间充质干细胞能够表达许多的Wnt配体,包括Wnt2、Wnt4、Wnt5a、Wnt11和Wnt16;也能表达几种Wnt受体,包括FZD2、FZD3、FZD4、FZD5、FZD6;还有多种的共同受体和Wnt抑制因子[15]。当Wnt蛋白在间充质干细胞中一旦被分泌后,Wnt蛋白就能附上细胞表面或者是细胞外的基质中参与其信号传导通路的机制。 Boland等[16]研究提出:Wnt信号传导通路能够保持干细胞的自我繁殖和未分化状态,外源性应用Wnt3a对间充质干细胞进行培养后,能够使间充质干细胞向多种成熟细胞分化,对人类能生成的脂肪干细胞能够增加其自我繁殖和减少凋亡。此外,对于参与经典Wnt信号通路的关键因素LRP5,能够使间充质干细胞的增殖增加。Baksh等[17]也通过研究表明:而Wnt5a能通过激活非经典Wnt信号传导通路,从而抑制β-catenin/TCF信号,从而降低间充质干细胞的增殖率。另外,Qiu等[18]研究报道提出Wnt经典信号通路可通过一个自分泌或旁分泌方式抑制人间充质干细胞的增殖。因此,这都表明经典Wnt信号传导通路与非经典信号传导通路可能在不同的条件下能够对间充质干细胞产生不同甚至相反的生物效应,使间充质干细胞能够增殖、分化,而Wnt通路中具体如何使间充质干细胞增殖,其内部因子如何调控间充质干细胞的增殖,这些问题机制比较复杂复杂,仍然需要进一步的研究去阐明这些问题。 2.5 wnt信号传导通路与骨生成 研究已经证明了经典Wnt信号传导通路与非经典Wnt信号传导通路能联合调控人间充质干细胞的多向性分化,其中Wnt信号传导通路在参与在间充质干细胞想成骨分化的过程中,其中Wnt11,FZD6,sFRP2,sFRP3和Ror2等因子的表达升高,而Wnt9a和FZD7的表达下降。 Yamada 等[19]的研究发现,通过骨诱导,sFRP3和sFRP4具有调节间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化的潜力,其中sFRP4主要参与经典Wnt信号传导通路调节成骨分化,而sFRP3则通过非经典途径抑制Wnt5a抑制成骨分化。 Wnt3a与间充质干细胞成骨分化:Boland等[20]已经提出了经典Wnt信号中能促进间充质干细胞向骨生成的表达,在Wnt3a的参与间充质干细胞能向成骨分化的过程中,同时可以发现间充质干细胞骨基质矿化和碱性磷酸酶活性增加,还有部分增加骨表达的标记物也增加。deBoer等[21]同样研究指出:通过外源性利用Wnt3a参与间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化时,利用GSK3β的一种抑制剂——锂,去抑制经典Wnt信号传导通路GSK3β参与调控,能够抑制利用地塞米松诱导的间充质干细胞向骨生成。Tang 等[22]研究认为Wnt3a同样与骨形态发生蛋白9存在非常密切的联系,Wnt3a与骨形态发生蛋白9能够增强彼此的能力,引导碱性磷酸酶在间充质干细胞中的生成,从而提高成骨分化。另外,Nemoto等[23]研究证实了sFRP3能减弱Wnt3a抑制碱性磷酸酶和骨形态发生蛋白的mRNA表达,而显性失活的TCF1能提高碱性磷酸酶和骨形态发生蛋白的mRNA的表达,也提高了碱性磷酸酶的活性。因此可以看出,在Wnt信号通路当中,Wnt3a是通过与受体结合之后,激活一系列的因子反应,在与骨形态发生蛋白的协同作用下,促进间充质干细胞向成骨分化的表达。 Wnt多水平、多方向调控间充质干细胞成骨分化:Sclerostin是一个非常关键的调节器,Sclerostin和Wnt竞争地与LRP相结合,通过该机制作为骨形态发生蛋白的抑制物,从而能下调骨形态发生蛋白的活性而抑制成骨,Rybchyn等[24]研究表明,锶可以通过抑制Sclerostin与LRP的结合,从而促进间充质干细胞的成骨生成。因其机制,目前Sclerostin被认为可能是下个骨质疏松治疗的靶点之一。经典Wnt信号传导通路在间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的过程中的作用应该是多样化的,这基于不同级别的Wnt蛋白活性,还有在其它因素的影响之下,也会是间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化产生不同的效果。Qiu等[18]研究指出,高剂量的外源性Wnt3a或通过过量表达的LRP5和稳定变异的β-catenin都可以增强间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化;Hartmann等[25]提出:Wnt信号通路中的LRP5功能获得性突变,或sFRP、DKK失活,则会引起高骨密度症,LRP5的功能丧失也会导致骨质疏松-假性神经胶质瘤综合征。也有研究指出,Wnt信号传导通路可以通过上调其RUNX2,Dlx5 或 osterix(成骨相关转录因子抗体)[26],从而促进间充质干细胞和骨先质细胞向成骨细胞分化。 非经典Wnt信号传导通路与骨生成:非经典Wnt途径,可通过Frizzled和Rorl/2 辅助受体复合体对Wnt的识别进行转换,可分别激活RhoA,JNK和Ca通道,从而促进间充质干细胞的多向分化。Amsdorf等[27]提出,非经典途径中尤其是通过激活小GTP酶RhoA和他们的直接效应蛋白ROCK对于决定骨髓间充质干细胞分化方向上有相当重要的作用,同时,有活力的肌动蛋白细胞骨架同样在诱导分化的基因表达中是必不可少的。参与非经典Wnt途径的Wnt11已经被证明可以对人类胚胎骨胳发育具有重要作用[28],且Wnt5a是参与非经典Wnt信号通路中的一个重要因子,已被证明在骨髓间充质细胞中是通过抑制PPARγ来诱导成骨的。有Takada等[29]研究报道认为,非经典Wnt通路通过招募抑制性组氨酸甲基,使染色体失活而抑制PPARγ的功能,从而促进成骨细胞生成。在Wnt5a参与非经典信号传导通路的基础上,配子Ror2也被研究证明可以通过被骨髓瘤细胞激活后产生损伤骨生成的分化[30]。除此之外,Nemoto等[31]还表明了Wnt5a信号也被证明是一种实质的成分,通过骨形态发生蛋白2介导间充质干细胞的成骨发生[31]。 "
| [1]Pittenger MF,Mackay AM,Beck SC,et al.Multilineage pontential adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science.1999;(284):143. [2]万晓晨,刘翠平,陈海啸,等. TGF-β/BMPs、Wnt和MAPK信号通路在间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化中的作用[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2008,30 (6):697-700. [3]Nusse R. Wnt signaling in disease and in development. Cell Res. 2005;(15):28-32. [4]Huelsken J, Behrens J. The Wnt signaling pathway. Journal of Cell Science. 2002;(115): 3977-3978. [5]Ling L, Nurcombe V. Wnt signaling controls the fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene.2009;(433):1-7. [6]Logan CY, Nusse A. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.2004;(20):781-810. [7]Ishitani T, Kishida S, Hyodo-Miura J, et al.The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Mol Cell Biol.2003; (23):131-139. [8]Liu F, Kohlmeier S, Wang CY.Wnt signaling and skeletal development. Cell. Signal. 2008;(20):999-1009. [9]Lu W, Yamamoto V, Ortega B, et al.Mammalian Ryk is a Wnt coreceptor required for stimulation of neurite outgrowth. Cell. 2004;(119):97-108. [10]Aguilera O, Fraga MF, Ballestar E, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of the Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 (DKK-1) gene in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene.2006;(25):4116-4121. [11]Cho SW, Her SJ, Sun HJ, et al.Differential effects of secreted frizzled-related proteins on osteoblastic differentiation of mouse mesenchymal cells and apoptosis of osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367(2):399-405. [12]Ehrlund A, Mejhert N, Lorente-Cebrián S, ,et al. Characterization of the Wnt Inhibitors Secreted Frizzled-Related Proteins (SFRPs) in Human Adipose Tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Mar;98(3):E503-508. [13]Van Raay TJ,Coffey RJ,Solnica-Krezel L. Zebrafish Naked1 and Naked2 antagonize both canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling.Dev Biol.2007;(309):68. [14]Schmidt A, Ladage D, Schinköthe T, et al.Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Controls Migration in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells.2006;24(7):1750-1758. [15]Song L, Webb NE, Song Y, et al.Identification and Functional Analysis of Candidate Genes Regulating Mesenchymal Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Multipotency. Stem Cells. 2006; 24(7): 1707-1718. [16]Boland GM, Perkins G, Hall DJ, et al.Wnt 3a promotes proliferation and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2004; (93):1210-1230. [17]Baksh D, Tuan RS. Canonical and non-canonical Wnts differentially affect the development potential of primary isolate of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol.2007;(212):817-826. [18]Qiu W, Andersen TE, Bollerslev J, et al.Patients with high bone mass phenotype exhibit enhanced osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Miner Res.2007;(22): 1720-1731. [19]Yamada A, Iwata T. Diverse functions of secreted frizzled-related proteins in the osteoblastogenesis of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Biomaterials.2013; 34(13):3270-3278. [20]Boland GM, Perkins G, Hall DJ, et al.Wnt 3a promotes proliferation and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2004; (93):1210-1230. [21]de Boer J, Siddappa R, Gaspar C, et al. Wnt signaling inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Bone.2004;(34):818-826. [22]Tang N, Song WX, Luo J, et al. BMP-9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitors requires functional canonical Wnt/β-catenin signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13(8B): 2448-2464. [23]Nemoto E,Koshikawa Y. Wnt signaling inhibits cementoblast differentiation and promotes proliferation. Bone.2009;44(5): 805-812. [24]Rybchyn MS, Slater M, Conigrave AD, et al. An Akt-dependent Increase in Canonical Wnt Signaling and a Decrease in Sclerostin Protein Levels Are Involved in Strontium Ranelate-induced Osteogenic Effects in Human Osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(27):23771-23779. [25]Hartmann C.A Wnt canon orchestrating osteoblastogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16(3):151-158. [26]Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, et al. Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(9):3324-3329. [27]Arnsdorf EJ, Tummala P, Kwon RY, et al. Mechanically induced osteogenic differentiation-the roleofRhoA,ROCKIIand eytoskeletal dynamics. J Cell Se.2009;(122):546-553. [28]Lako M, Strachan T, Bullen P, et al. Iso lation,characterisation and embryonic expression of WNT11, a gene which maps to 11q13.5 and has possible roles in the development of skeleton, kidney and lung. Gene.1998;(219):101-110. [29]Takada I, Mihara M,Suzawa M,et al.A histone lysine methyltransferase activated by non-canonical Wnt signalling suppresses PPAR-γ transactivation. Nature Cell Biology.2007; (9):1273-1285 . [30]Bolzoni M, Donofrio G, Storti P, et al. Myeloma cells inhibit non-canonical wnt co-receptor ror2 expression in human bone marrow osteoprogenitor cells: effect of wnt5a/ror2 pathway activation on the osteogenic differentiation impairment induced by myeloma cells. Leukemia.2013;(27): 451-463. [31]Nemoto E, Ebe Y. Wnt5a signaling is a substantial constituent in bone morphogenetic protein-2-mediated osteoblastogenesis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2012;422(4):627-632. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [5] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [6] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [7] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [8] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [11] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [12] | Yang Sidi, Wang Qian, Xu Nuo, Wang Ronghan, Jin Chuanqi, Lu Ying, Dong Ming. Biodentine enhances the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 516-520. |
| [13] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [14] | Cao Wei, Mao Furong, Hu Xiaohua, Yang Xiaohong. N-6 methyladenosine RNA methylation regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 266-270. |
| [15] | Fan Danyang, Fu Runze, Mi Jiajing, Liu Chunyan. Expression and role of cannabinoid receptors during bone remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 283-288. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||