Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (37): 6555-6560.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.37.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Short-time middle-load treadmill exercise affects the bone mineral density of hyperlipidemia male rats
Wang Xiao-hong, Xu Chao, Zhang Zhuo, Guo Lian-ying, Zhou Bo
- Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110034, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2013-03-05Revised:2013-04-18Online:2013-09-10Published:2013-09-10 -
Contact:Zhou Bo, M.D., Professor, Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110034, Liaoning Province, China zhoubo@symc.edu.cn -
About author:Wang Xiao-hong, Chief technician, Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110034, Liaoning Province, China wxh0515@hotmail.com -
Supported by:Science Research Program of Higher Education, Liaoning Education Bureau, No. 2009A693*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xiao-hong, Xu Chao, Zhang Zhuo, Guo Lian-ying, Zhou Bo. Short-time middle-load treadmill exercise affects the bone mineral density of hyperlipidemia male rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(37): 6555-6560.
share this article
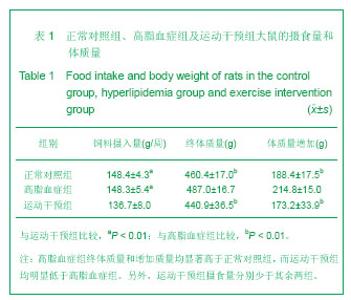
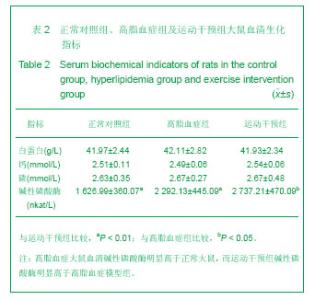
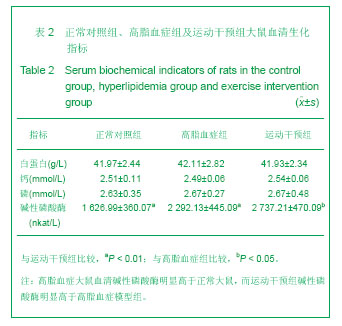
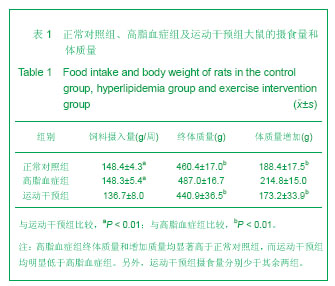
2.1 实验样本数量分析 实验期间,各组大鼠均没有死亡发生,但高脂血症组的1只大鼠股骨标本损坏缺失,因此高脂血症组参与数据分析的动物样本数为8只。 2.2 高脂血症模型的建立 模型大鼠的胆固醇、三酰甘油分别为(2.76±0.49) mmol/L和(1.24±0.34) mmol/L,均分别高于正常对照组(1.55±0.30) mmol/L及(0.89± 0.13) mmol/L (P < 0.01),表明高脂血症动物模型建立成功[3]。 2.3 各组大鼠摄食量和体质量 高脂血症组终体质量和增加质量均显著高于正常对照组,而运动干预组均明显低于高脂血症组。另外,运动干预组摄食量分别少于其余两组。见表1。"
| [1] Zethraeus N, Borgstrom F, Strom O, et al. Cost-effectiveness of the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis- a review of the literature and a reference model. Osteoporos Int. 2007; 18(1): 9-23. [2] Batsis JA, Nieto-Martinez RE, Lopez-Jimenez F. Metabolic syndrome: from global epidemiology to individualized medicine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82: (5):509-524. [3] Shen C, Deng J, Zhou R, et al. Relation between bone mineral density, bone loss and the risk of cardiovascular disease in a Chinese cohort. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110(8):1138-1142. [4] Brandi ML, Guglielmi G, Masala S, et al. When the government actively faces the burden of osteoporosis: the Italian experience. Arch Osteoporos. 2012.7 (1-2): 21-24. [5] 厉婷,崔燎. 脂质代谢紊乱和骨质疏松[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2008,14(6): 428- 432. [6] Gasser RW. Cholestasis and metabolic bone disease – a clinical review. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2008;158/19-20:553-557. [7] Grffith JF, Yeung DK, Antoni GE, et al. Vertebral bone mineral density, marrow perfusion, and fat content in healthy men and men with osteoporosis: dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging and MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 2005;236(3): 945-951. [8] Masse PG, Tranchant CC , Dosy J , et al . Coexistence of osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease risk factors in apparently healthy, untreated postmenopausal women. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2005;75(2) :97-106. [9] Crepaldi G, Maggi. Epidemiologic link between osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease. J Endocrinol Invest.2009; 32 (4Suppl): 2-5. [10] Tarakida A, Iino K, Abe K, et al. Hypercholesterolemia accelerates bone loss in postmenopausal women. Climacteric. 2011;14(1):105-111. [11] Graham LS, Tintut Y, Prhami F, et al. Bone density and hyperlipidemia: the T-lymphocyte connection. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(11): 2460-2469. [12] Huang MS, Lu J, Ivanov Y, et al. Hyperlipidemia impairs osteoanabolic effects of PTH. J Bone Miner Res.2008; 23(10):1672-1679. [13] Russel M, Mendes N, Miller KK, et al. Visceral fat is a negative predictor of bone density measures in obese adolescent girls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(3): 1247-1255. [14] Lac G, Cavalie H, Ebal E, Michaux O. Effects of a high fat diet on bone of growing rats. Correlations between visceral fat, adiponectin and bone mass density. Lipids Health Dis.2008; 28(4):7-16. [15] Nunez NP, Carpenter CL, Perkins SN, et al. Extreme obesity reduces bone mineral density: complementary evidence from mice and women. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15(8): 1980-1987. [16] 马国栋.骨密度与血脂及运动的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(41):8349-8352. [17] Riggs BL, Wahner HW, Seeman E, et al. Changes in bone mineral density of the proximal femur and spine with aging. Differences between the postmenopausal and senile osteoporosis syndromes. J Clin Invest. 1982;70(4):716-723. [18] Cao JJ, Sun L, Gao H. Diet-induced obesity alters bone remodeling leading to decreased femoral trabecular bone mass in mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192(3):292-297. [19] Halade GV, Rahman MD. Williams PJ, et al. High Fat Diet-Induced Animal Model of Age-associated Obesity and Osteoporosis. J Nutr Biochem. 2010;21(12):1162-1169. [20] Philip GR, Forrest HN, George CF. AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American institute of nutrition Ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr.1993;123(11):1939-1951. [21] Bedford TG, Tipton CM, Wilson NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol. 1979; 47(6): 1278-1283. [22] 姚璐,张缨,张连峰.跑台运动在动物实验研究中的应用[J].中国比较医学杂志,2010,20(6):75-81. [23] 尤婷婷,吴铁,邹丽宜.高脂血症致大鼠骨质疏松作用初探[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2007,12(3):299-303. [24] Macri EV, Gonzales Chaves MM, Rodriguez PN, et al. High-fat diets affect energy and bone metabolism in growing rats. Eur J Nutr. 2012;51(4): 399-406. [25] Pirih F, Lu J, Ye F, et al. Adverse effects of hyperlipidemia on bone regeneration and strength. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27(2): 309-308. [26] 谢顺成,马学军,郭成吉,等.强度不同的间歇跑台训练对生长期大鼠骨代谢及相关激素的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2012, 28(3):271-274. [27] 房冬梅.大强度间歇跑台运动对大鼠长骨生长的影响[J].山东体育学院学报, 2009,25(6):32-34. [28] Hagihara Y, Fukuda S, Goto S, et al. How many days per week should rats undergo running exercise to increase BMD? J Bone Miner Metab. 2005;23(4):289-294. [29] 张崇林,郑陆.不同负荷运动对雌性大鼠骨骼的作用及其位点效应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,25(28):5173-5176. [30] Hamrick MW, Skedros JG, Pennington C, et al. Increased osteogenic response to exercise in metaphyseal versus diaphyseal cortical bone. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2006;6(3):258-263. [31] Ma H, Turpeinen T, Silvennoion M, et al. Effects of diet-induced obesity and voluntary wheel running on the microstructure of the murine distal femur. Nutr Metab. 2011; 8(1):1-11. [32] 秦岭,陈启明,梁国穗. 体育运动与骨髂、骨密度和结构与生物力学适应性[J].中国运动医学杂志,2004,23(5):532-536. [33] Daly RM. The effect of exercise on bone mass and structural geometry during growth. Med Sport Sci. 2007;51(1): 33-49. [34] 梁鸿,郑陆,阎守扶,等.运动对骨形态结构、骨密度和骨生物力学特征的影响[J].首都体育学院学报,2009,21(2):202-204. [35] 卜淑敏,陈永杰,郝利科,等.中等强度跑台运动预防去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松[J].中国比较医学杂志,2010,20(4):14-18. [36] Shen CL, Cao JJ, Dagda RY, et al. Green tea polyphenols benefits body composition and improves bone quality in long-term high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Nutr Res. 2012 ; 32(6):448-457. [37] Laskowski ER. The role of exercise in the treatment of obesity. PMR. 2012,4(11):840-844. [38] 乔林,许良智,杨定焯,等.体质量对去卵巢大鼠骨密度影响的初步探讨[J].四川大学学报医学版,2009,40(1):145-148. [39] 徐健,杨定焯,马锦富,等.骨力学负荷对峰值骨量的影响及骨量标准化方法探索[J].现代预防医学,2010,37(7):1306-1309. [40] Gerbaix M,Metz L,Mac-Way F, et al. Impact of an obesogenic diet program on bone densitometry, micro architecture and metabolism in male rat. Lipdis health and dis. 2012,11: 91-100. [41] Cao JJ, Gregoire BR, Gao H, et al. High-fat diet decreases cancellous bone mass but has no effect on cortical bone mass in the tibia in mice. Bone.2009;44(6):1097-1104. [42] Ionova-Martin SS, Do SH, Barth HD, et al. Reduced size-independent mechanical properties of cortical bone in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Bone. 2010;46(1):217-225. [43] 张慧,苏全生,李建新,等.运动对骨组织代谢的影响[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(16): 147-149. [44] Hitnton PS, Rector RS, Thomas TR, et al. Weight-bearing, acerobic exercise increases markers of bone formation during short-time weight loss in overweight and obese men and women. Metabolism. 2006;55(12): 1616-1618. [45] Bensimhon DR, KrausWE, Donahue MP. Obesity and physical activity: A review. Am Heart J. 2006;151(3):598-603. [46] Chao OT, Terrillion CE, Moran TH, et al. High-fat diet offsets the long-lasting effects of running-wheel access on food intake and body weight in OLETF rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2011;300(6):R 1459-1467. |
| [1] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [2] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [5] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [6] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [7] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [8] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [9] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [10] | Kong Lingbao, Lü Xin. Effect of implant selection and approach on support in the operation of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 942-947. |
| [11] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [12] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [13] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [14] | Lü Jiaxing, Bai Leipeng, Yang Zhaoxin, Miao Yuesong, Jin Yu, Li Zhehong, Sun Guangpu, Xu Ying, Zhang Qingzhu. Evaluation of internal fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [15] | Xiang Feifan, Ye Junwu, Zhang Xihai, Ge Jianhua, Tang Lian, Yang Yunkang. Comparison of three different internal fixation methods in treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 403-408. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||